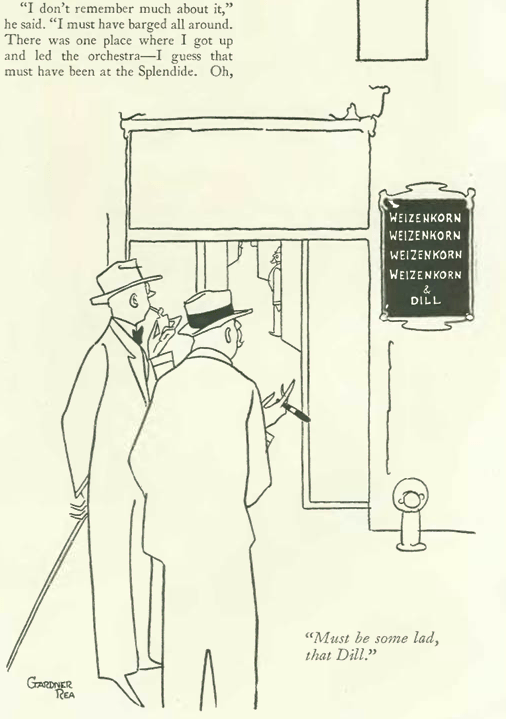
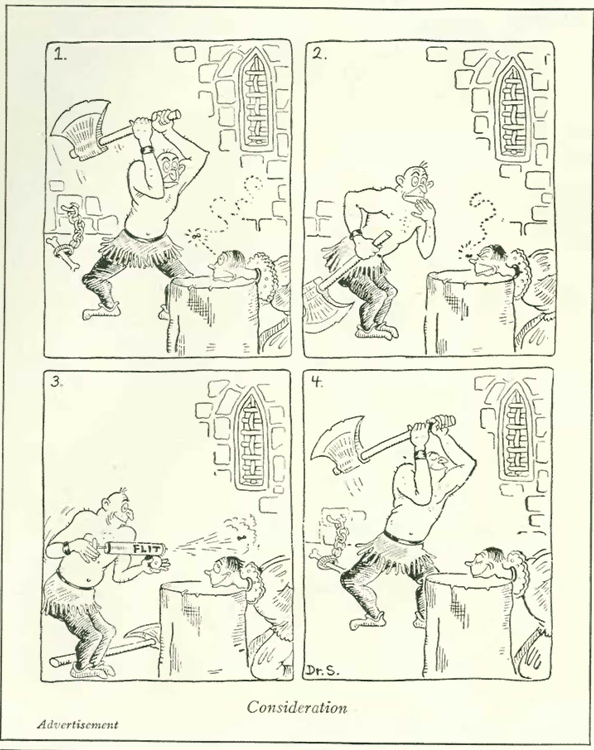
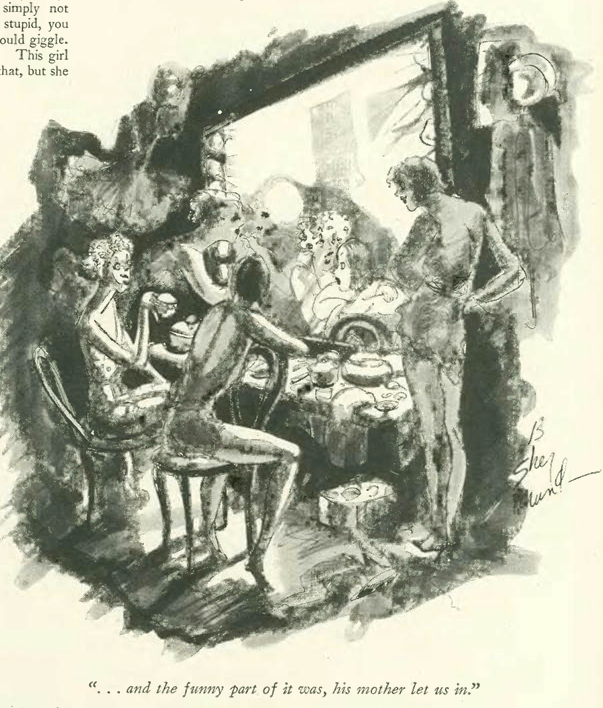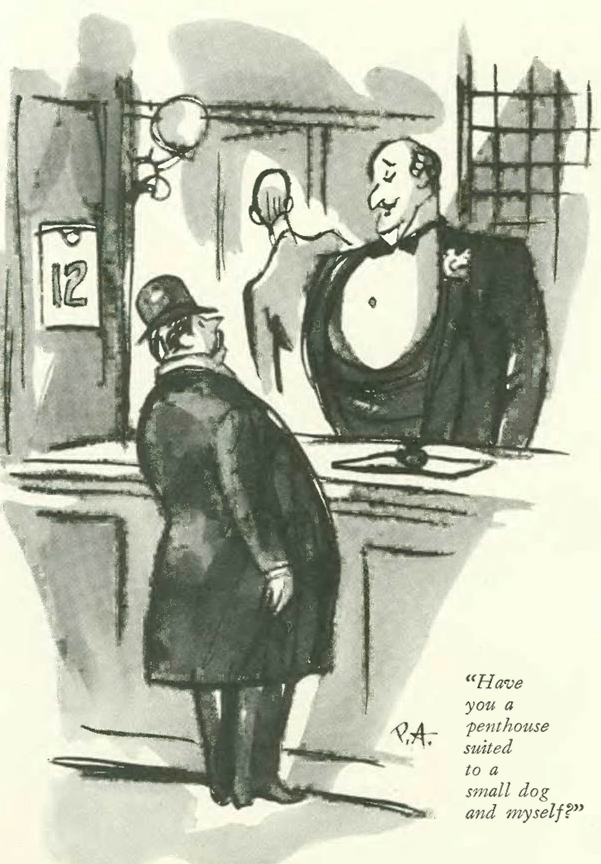If you lived in small town America in the 20th century, it was a big deal when the circus came to town with its entourage of clowns, acrobats and exotic animals from distant lands.

Even New Yorkers, it seems — who could be quite blasé about such things — got a thrill when the Ringling Brothers and Barnum & Bailey Circus rolled into town for its annual spectacle at Madison Square Garden. The New Yorker marked the occasion with its April 12 cover by Theodore Haupt:
For the April 19 issue, E.B. White welcomed the circus on a cautionary note, airing concerns in his “Notes and Comment” column that this old-timey entertainment might be falling under the “base influences” of broadcast radio, Broadway, and Hollywood:

José Schorr, who wrote a number of humorous columns in The New Yorker from 1926 to 1930 on the subject of “how to the pass the time” in various situations, offered this advice on attending the spectacle at Madison Square Garden…

…for example, Schorr advised circus-goers to pass the time by considering the inner lives of performers such as “The Human Projectile”…
* * *
Funny Farm
Perhaps you’ve never heard of Joe Cook (1890-1950), but in the 1920s and 30s he was a household name and one of America’s most popular comedic performers. “Talk of the Town” looked in on his antics at his Lake Hopatcong farm, “Sleepless Hollow”…

* * *
Fun With Balloon Animals
One thing that distinguishes the 1930s from today is that era’s apparent lack of safety standards, or fear of liability. A case in point was Macy’s Thanksgiving Day Parade, which began a tradition in the late 1920s of releasing its giant balloons into the sky at the conclusion of the parade — a $50 reward was offered by Macy’s for their return. “The Talk of the Town” explained:

Perhaps the craziest anecdote attached to the parade’s annual balloon release belonged to Annette Gipson. While flying a biplane at 5,000 feet with her instructor, she spotted the parade’s 60-foot “Tom Cat” balloon rising high above Queens. Looking to have a bit of fun, the 22-year-old Gipson flew the plane directly into the cat. According to the book Macy’s Thanksgiving Day Parade, “Upon impact, the balloon wrapped itself around the left wing. The plane went into a deep tailspin (nearly throwing Gipson from the cockpit) and sped toward the ground out of control.” Fearing the plane would catch fire when it hit the ground, the instructor killed the ignition, and somehow managed to pull the plane out of the spin and land it safely at Roosevelt Field.

A footnote: Following Gipson’s brush with death, Macy’s announced it would not give prize money to those who tried to down the balloons with their airplanes. The incident also brought an end to the company’s tradition of releasing the balloons.
* * *
Birth of the Soundtrack
Songs from popular theater productions were first made available to the masses in the mid-19th century via printed sheet music and later through early recordings. Part of this lineage is the movie soundtrack, which has its origins in the early days of sound pictures. According to The New Yorker’s “Popular Records” column, these new recordings would bring the talkies into your home, albeit without the picture…

* * *
Cosmo Calvin
Before Helen Gurley Brown came along in the 1960s and sexed it up, Cosmopolitan was known as a somewhat bland literary magazine, and it was certainly bland enough in 1930 to welcome the scribblings of America’s blandest president to its pages. E.B. White mused in his “Notes”…

* * *
How Dry I Am
After a decade of living under Prohibition, John Ogden Whedon (1905-1991) put pen to paper and shared his sentiments in a poem for The New Yorker…
…Whedon would go on to a successful career as a screenwriter, especially finding acclaim for his television writing on The Donna Reed Show, Leave It to Beaver, The Andy Griffith Show, and The Dick Van Dyke Show, among others. He was also the grandfather of screenwriter and director Joseph “Joss” Whedon and screenwriters Jed Whedon and Zack Whedon.
Another poem in the April 19 issue was contributed by John Held Jr., who was perhaps better known to New Yorker readers for his “woodcut” cartoons…
…example of Held’s work from the April 12 issue, featured in an Old Gold advertisement…
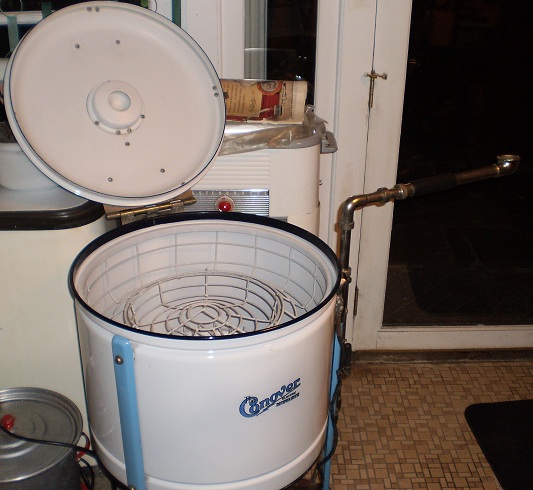
…and that provides a segue into our ads for the April 19 issue, beginning with this spot for an early electric dishwasher…

…I couldn’t find a review in The New Yorker for Emily Hahn’s new book, Seductio Ad Absurdum, but her publisher did take out an ad to get the attention of readers. Many years later The New Yorker would call the journalist and author “a forgotten American literary treasure”…

…and here we have another sumptuous ad from illustrator Carl “Eric” Erickson, a far cry from the “Joe Camel” ads that would come along decades later…
…on to our cartoons, Reginald Marsh offered a blue collar perspective on city fashions…
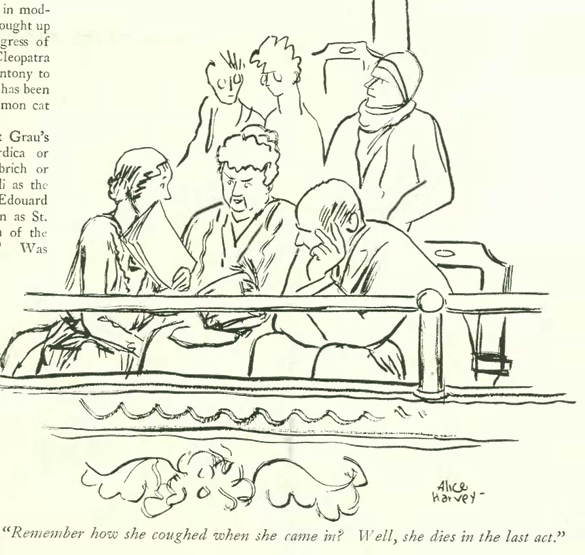
…Alice Harvey captured a moment of reflection by an overworked housewife…
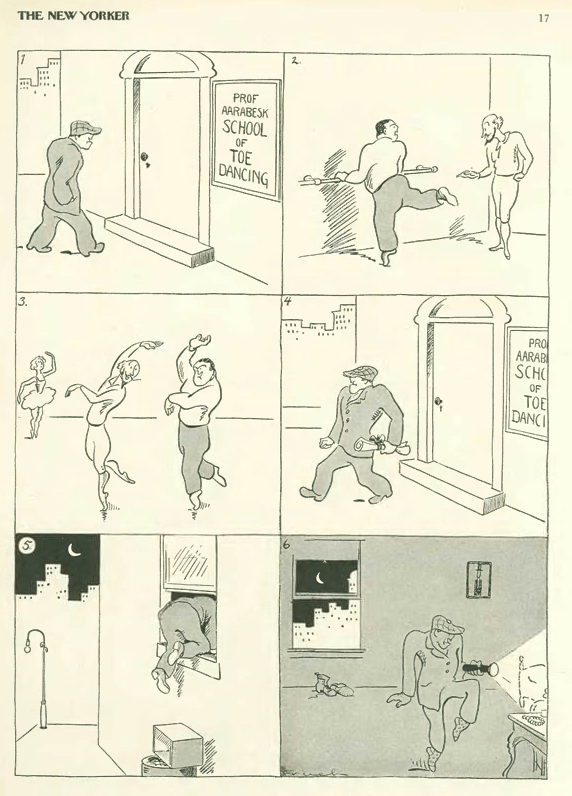
…and Isadore Klein looked in on a couple of working stiffs in need of a dictionary…
…now over to the posh set, with Barbara Shermund…
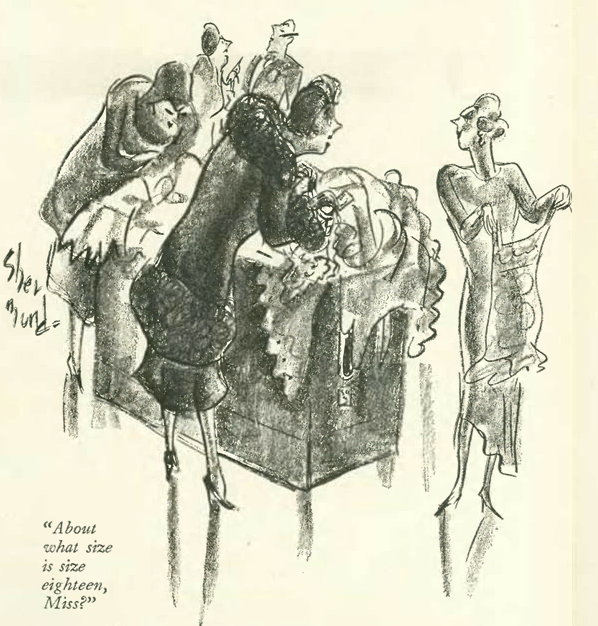
…Leonard Dove found humor on the chorus line…
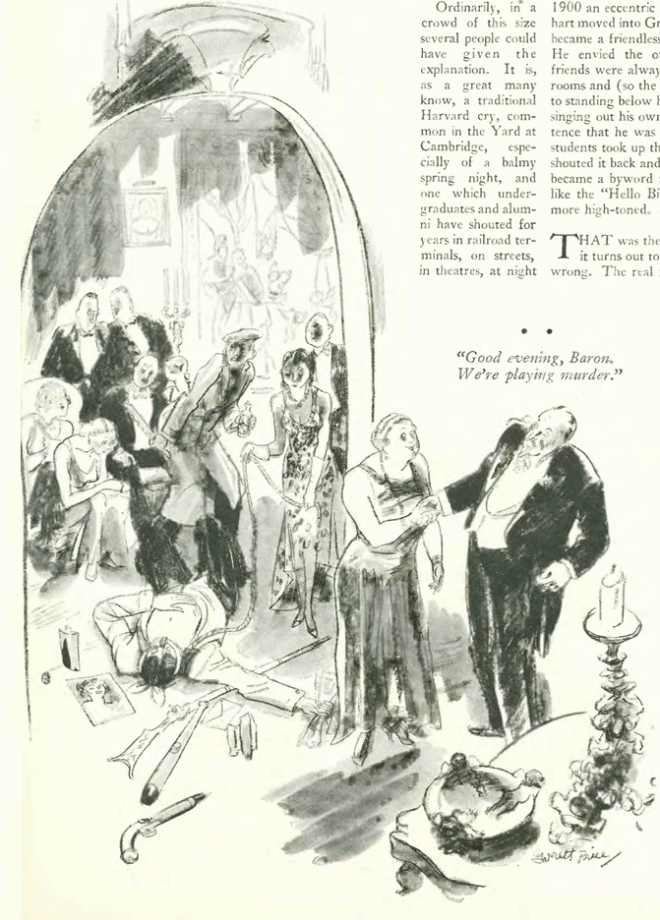
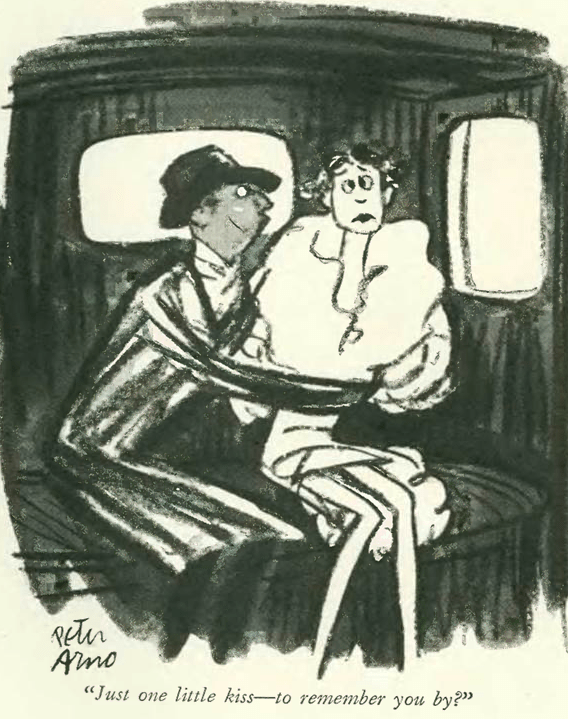
…and we end with this terrific cartoon by Peter Arno, and the perils of apartment life…
Next Time: Paramount on Parade…