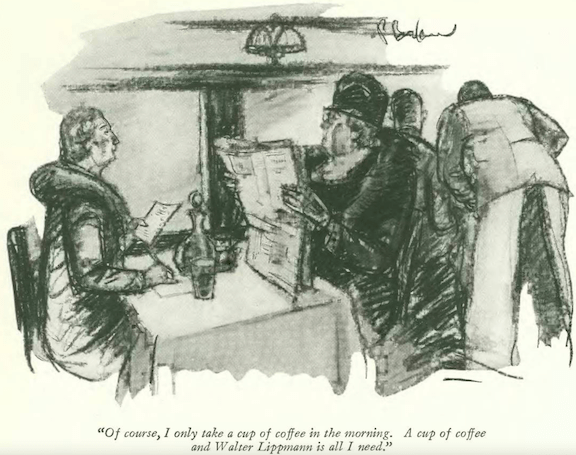
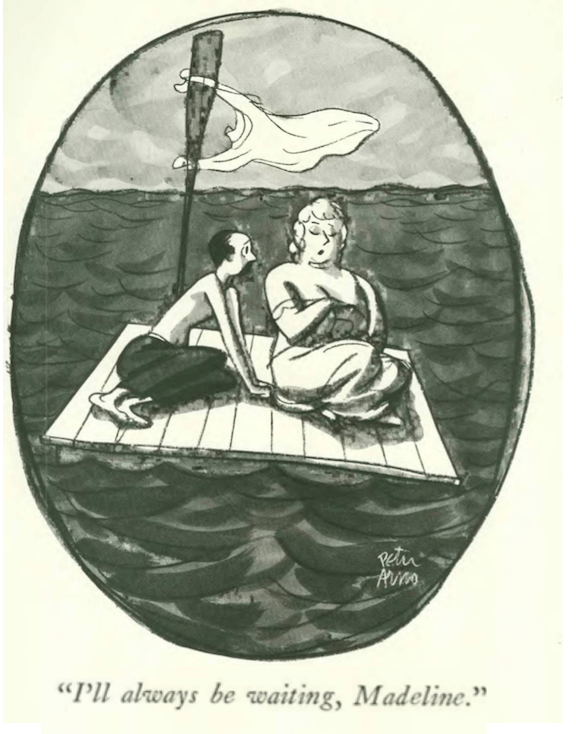
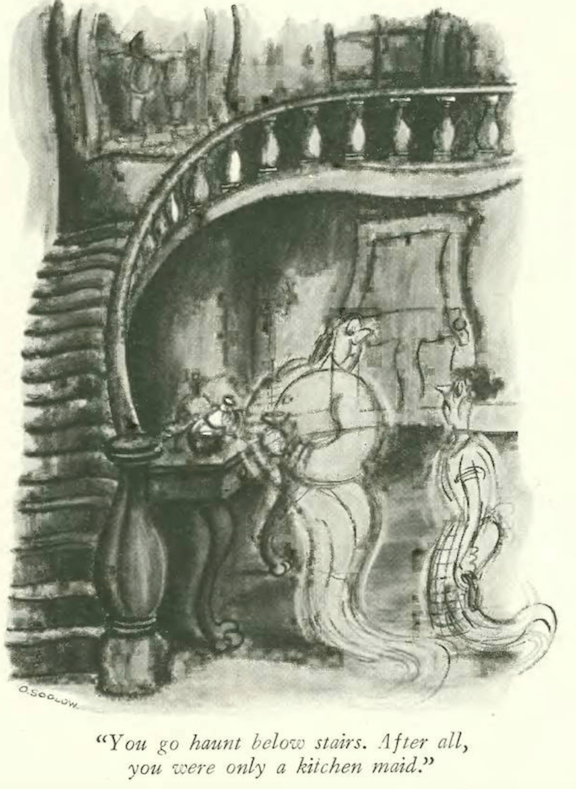“Nobody said not to go” was a phrase often used by Emily “Mickey” Hahn when returning from one of her far-flung and often wild adventures.

And nobody ever told Hahn (1905–1997) what she could write about, and so she wrote, with brio and authority, on a variety of subjects ranging from feminism, diamond mining, and animal behavior to Chinese history and cooking. The author of 54 books, Hahn also penned a number of biographies including those of Leonardo da Vinci, Chiang Kai-shek, and D. H. Lawrence among others. In the Feb. 4 issue Hahn wrote about spending the night at a New York flophouse, not out of necessity but rather to write about the experience. Excerpts:

In the following two excerpts, Hahn described her sleepless night, and her exit from the flophouse the following morning…
More on Emily Hahn, who defied convention from the very start of her adult life: before graduating from the University of Wisconsin in 1926 (the first woman to earn a degree in mining engineering there), she drove across the U.S. in a Model T, dressed a man. She wrote about her experiences in letters to her brother-in-law who, unbeknownst to Hahn, shared them with New Yorker editors. This would lead to a longtime relationship with the magazine, to which she would contribute nearly 200 articles (and one poem) between 1929 and 1996. She would also serve as China correspondent from 1935 to 1943.
In 1930 she traveled to the Belgian Congo, where she lived for two years with a pygmy tribe while working for the Red Cross; she later crossed Central Africa alone on foot. In his 2006 memoir, Let Me Finish, Roger Angell described Hahn as the magazine’s “Belle Geste,” a woman “deeply, almost domestically, at home in the world. Driven by curiosity and energy, she went there and did that, and then wrote about it without fuss.”

* * *
Chief Stooge
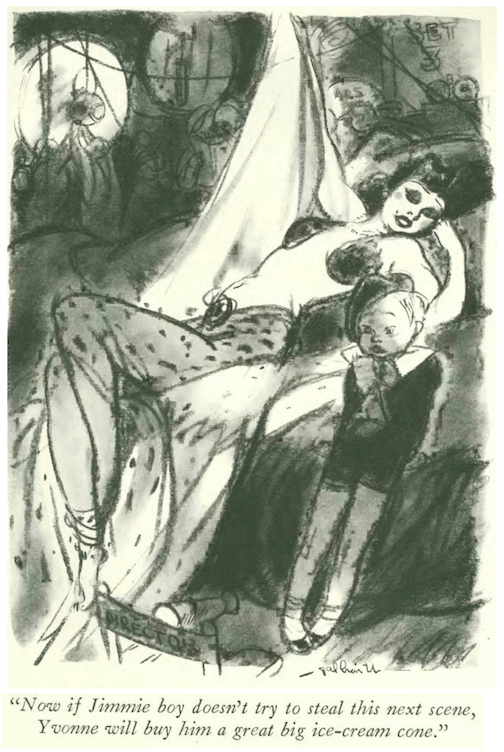
Theatrical promoter Alfred Cleveland Blumenthal (1885–1957) was well-known to New Yorkers in the 1920s and 30s as a speakeasy owner, buddy to Mayor Jimmy Walker and husband to actress Peggy Fears. Although “Blumey” is largely forgotten today, in 1933 he merited a two-part profile by Alva Johnston. Here are excerpts from the opening lines:

* * *
Coward’s Ménage
Playwright Noel Coward existed in the orbit of the Algonquin Round Table, so it was doubtless challenging for Robert Benchley to critically review his friend’s work. Fortunately, Benchley found Design For Living mostly to his liking. Note how Benchley subtly refers to the play’s gay subtext, and to the fact that it mirrored the real-life relationships of the play’s trio.

Benchley did have a few quibbles, but reasoned there was no need to be overly critical when there was such a dearth of quality stage entertainment. Note the great caricatures by Al Frueh (below) that accompanied the review.

Benchley had a different sort of dilemma criticizing Elmer Rice’s earnestly patriotic We, the People, a play about the misfortunes of a working class family in Depression America.
Rice, who won the Pulitzer Prize for Drama in 1929, was an occasional contributor to The New Yorker from 1929 to 1931, including his sci-fi satire on the film industry, Voyage to Purila, which was serialized in eleven installments (with illustrations by Peter Arno) in The New Yorker from Oct. 12 to Dec. 21, 1929.

Meanwhile, film critic John Mosher was trying his best to enjoy the latest Hollywood fare, another Broadway play adapted to the silver screen. Whistling in the Dark…

However, Mosher was surprisingly enthused by the rustic charms of Iowa country folk in State Fair…

* * *
Form Follows Function
E.B. White paid close attention to all the little details of daily life, including the advertisements that appeared in The New Yorker. In “The Talk of the Town” he wrote about a Camel ad that inspired a sudden fashion trend:
…here is the Dec. 24, 1932 New Yorker ad to which White referred:
* * *
From Our Advertisers
We keep our cigs lit for our first ad, from Lucky Strike, keeping it simple with their familiar slogan…
…this ad from Powers Reproduction shows us the beach caps that were all the rage in the early ’30s…
…this may look like an old car to modern eyes, but in 1933 these sweeping curves were la dernière mode in the auto world…
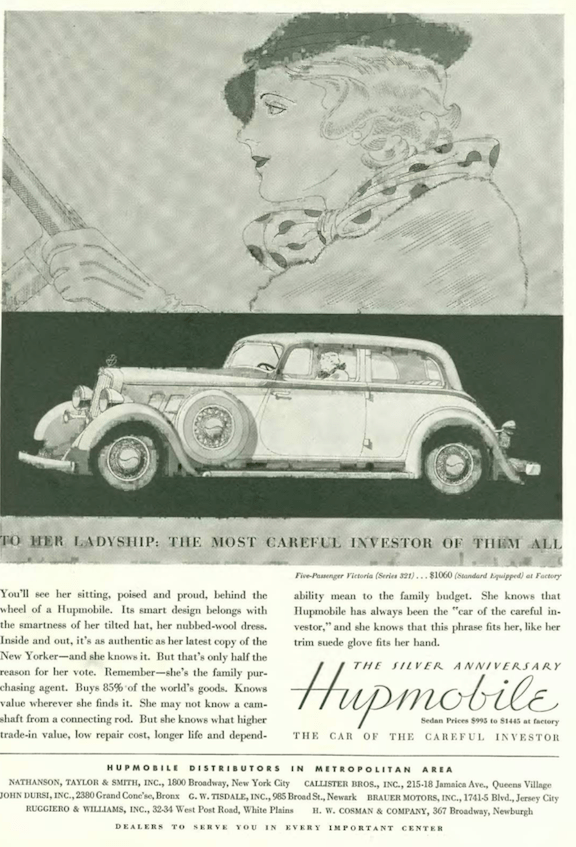
…and then there was Hupmobile, trying its best to stay relevant in the Depression…
…the company folded in 1939, but a few reminders live on…

…Valentine’s Day was just around the corner, so time to buy your sweetheart something special, like this scarf that was all the rage among the Miami snowbirds…
…Greenwich Village restaurateur and personality Don Dickerman took out this two-page ad to trumpet his partnership with puppeteer and illustrator Tony Sarg at the Bohemia restaurant on Broadway…
…the German-American Sarg is also known as the creator, in 1927, of the first giant balloons for Macy’s Thanksgiving Parade…

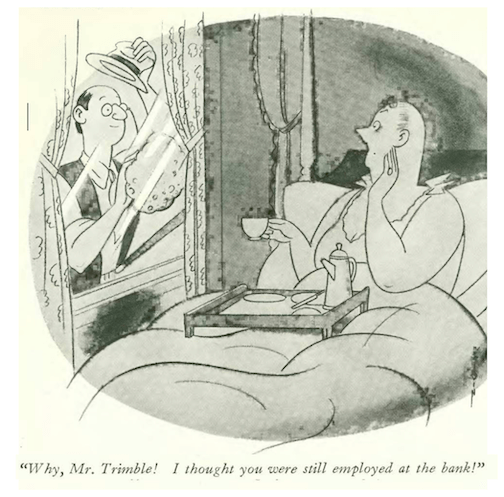
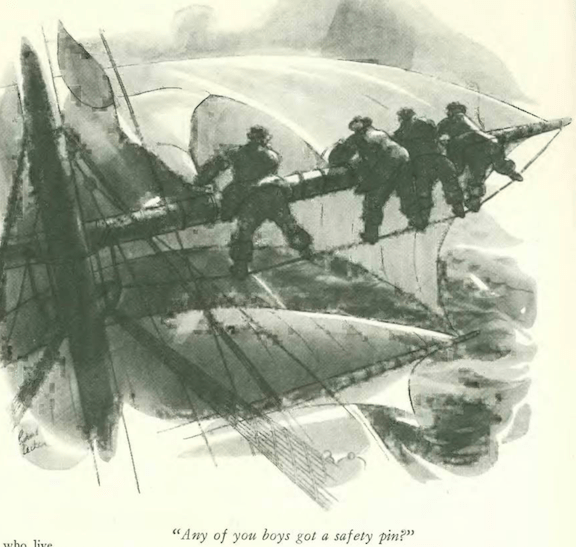
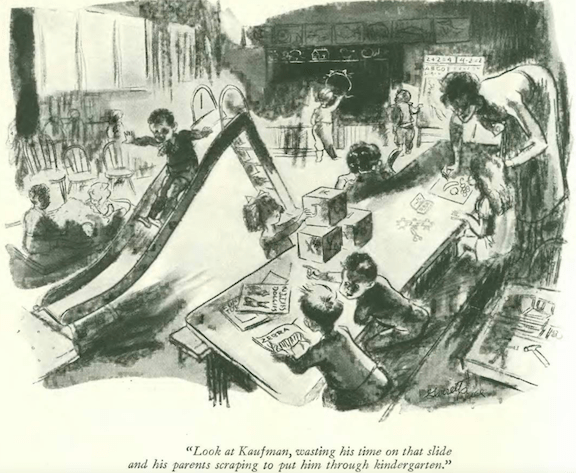
…on to our cartoons, and what a big day for The New Yorker…the Feb. 4, 1933 issue featured the first captioned cartoon by Charles Addams…
…for the record, Addams’s very first contribution to the magazine was this spot illustration (below) featured on page 65 of the Feb. 6, 1932 issue…
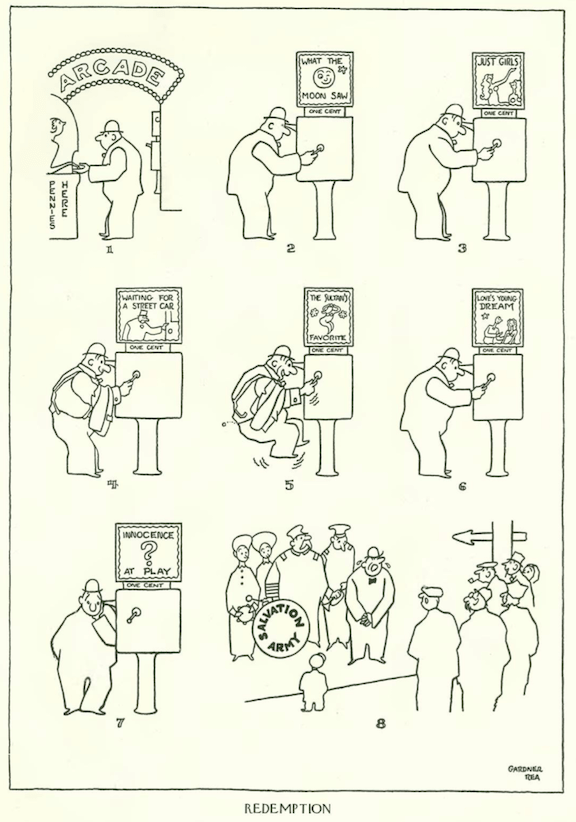
…one of the original contributing artists to The New Yorker, Gardner Rea, continued his skewering of America’s plutocrats…
…William Steig took us before the bench to make an honest plea…
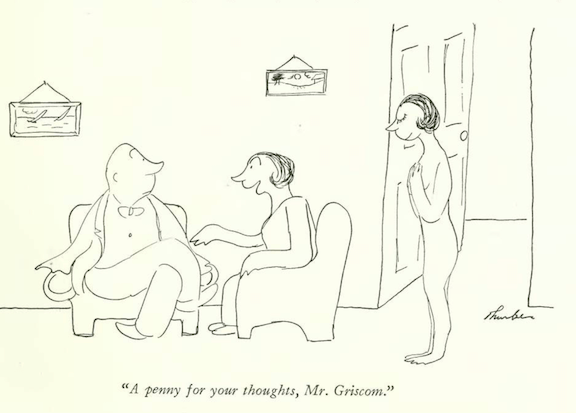
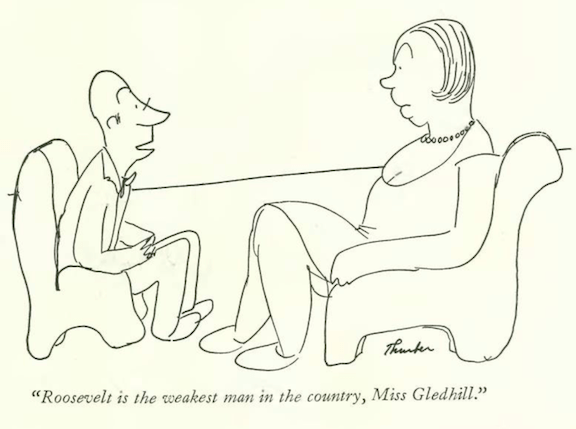
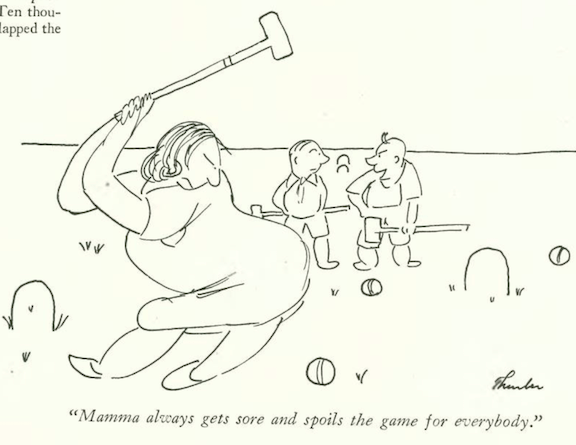
…James Thurber gave us another skirmish between the sexes…
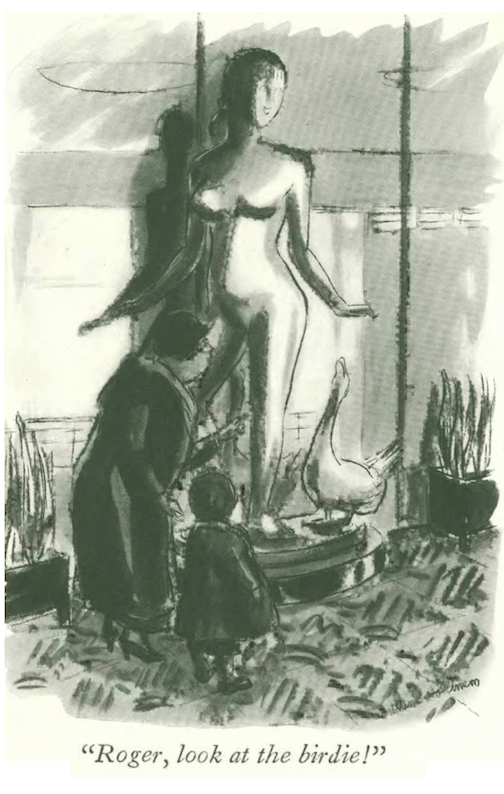
…and recalling my Jan. 12 post (about the Jan. 7, 1933 issue), in which the puritans got their knickers in a bunch over Robert Laurent’s Goose Girl sculpture in the Radio City Music Hall lobby…
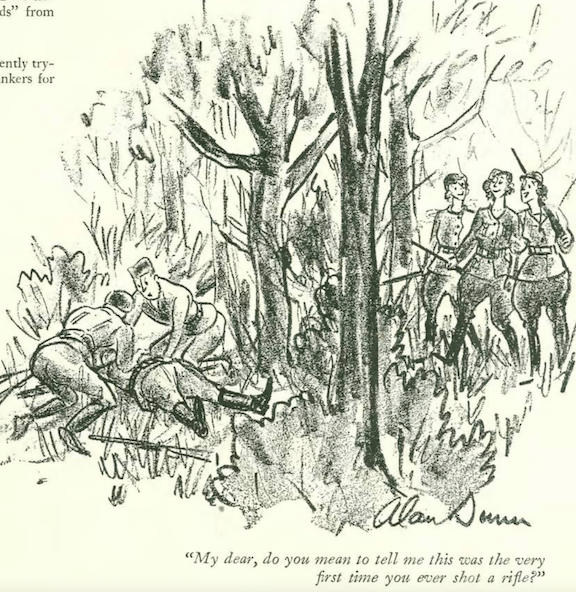
…we end with Helen Hokinson, inspired by Laurent’s work…
Next Time: Role Reversal…