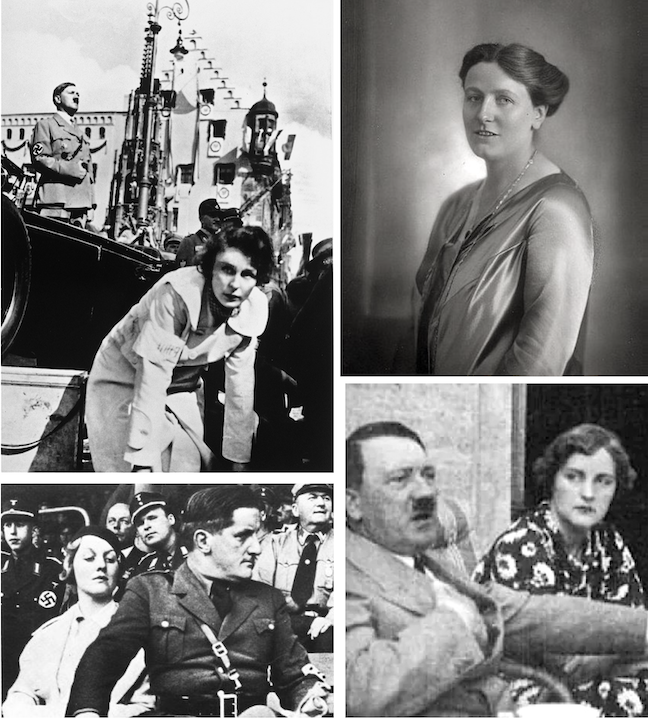
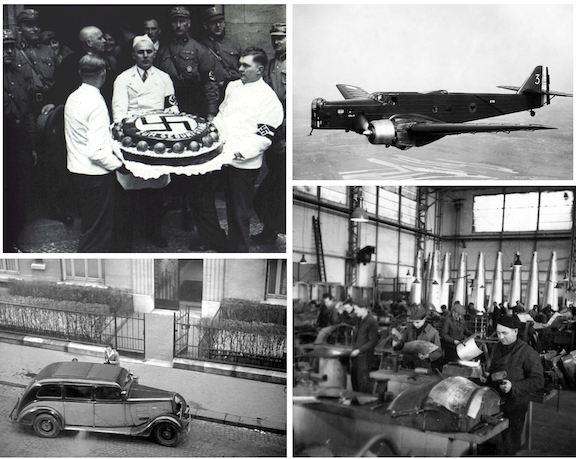
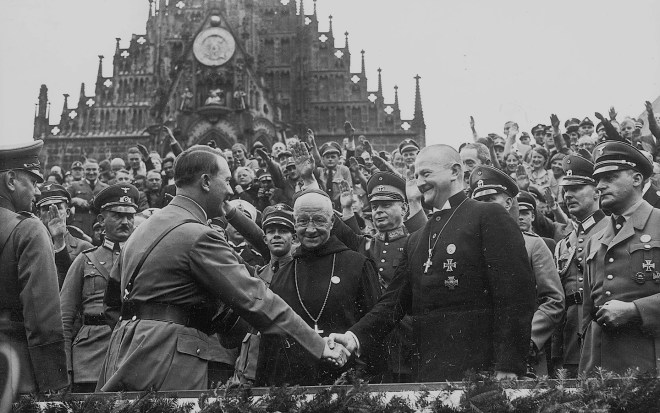
Above: At left, the Nazi Party sought to remake Christian holidays such as Christmas into Nazi-themed, pagan events, even trying to redefine St. Nicholas as Wotan, the ancient Germanic deity; at right, Adolf Hitler rejected Christianity, calling it a Jewish plot to undermine the heroic ideals of the Aryan-dominated Roman Empire. Here he is seen meeting the nuncio to Germany, Cesare Orsenigo, on January 1, 1935. (reddit.com/Wikipedia)
For the March 7 issue we look at the second part of Janet Flanner’s profile of German dictator Adolf Hitler, in which she attempted to identify the social and political influences that led to his peculiar vision of the world.


Flanner described Hitler’s struggles as an artist (rejected twice by the Vienna Academy of Fine Arts), however his real disappointment was nationalistic; serving as a courier (and wounded) in World War I, he blamed internal traitors for Germany’s defeat. To bolster his patriotic ideals, Hitler turned to books, and particularly to poet and dramatist Friedrich Schiller (1759–1805)—the Nazis would later manipulate Schiller’s works to fit the Party’s themes of nationalism, struggle, and obedience. Hitler would further hone his world view through the works of white supremacist Count de Gobineau (1816–1882), nihilist philosopher Friedrich Nietzsche (1844–1900), and philologist Max Müller (1823–1900), whose work inadvertently contributed to the idea of a superior “Aryan” race.

In her conclusion, Flanner noted Hitler’s dislike of jokes at his own expense, and she was surprised that German comedian Weiss Ferdl, known for his “Führer gibes,” wasn’t in a concentration camp with cabaret singer Claire Waldorff (somehow both survived the regime and the war). Flanner also touched on Hitler’s antipathy toward Christianity.


* * *
Thrill Ride
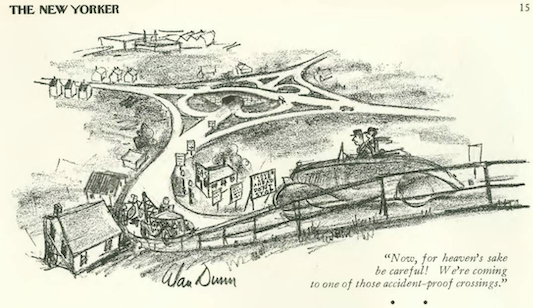
In his “Notes and Comment,” E.B. White described “one of the strangest nightmares of motordom”…

* * *
Ding-dong
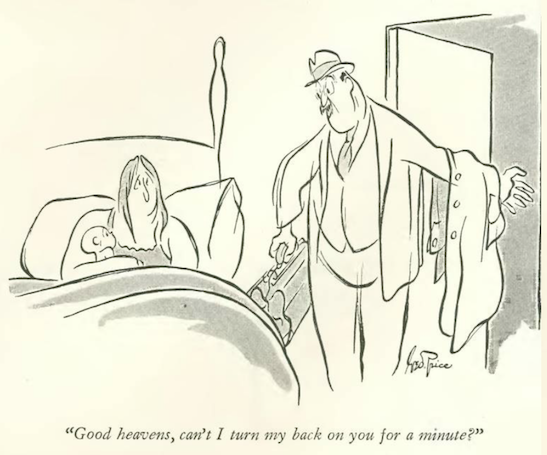
Robert Benchley filed a brief review of The Postman Always Rings Twice, a stage adaptation at the Lyceum Theatre of James M. Cain’s acclaimed novel. Although the play was well received by audiences, many reviewers found the subject matter distasteful. Cain would later describe the 1936 production as “a dreadful experience from beginning to end.”

* * *
At the Movies
Critic John Mosher commented on familiar Hollywood tropes (doctors chasing nurses, execs pursuing secretaries etc.) and offered up the “tepid” example of Wife vs. Secretary, which featured three of Tinseltown’s top stars.

Mosher didn’t find much excitement in the dog-themed picture The Voice of Bugle Ann, and was left flat after seeing Road Gang and the German film Liebelei.


* * *
Language Arts
H.L. Mencken continued his exploration of American English by taking a look at past attempts to simplify spelling—most of them unsuccessful. Excerpts:


Mencken noted the Chicago Tribune’s radical approach to simplified spelling in 1934, and the lasting effects of Noah Webster’s American dictionary.

* * *
First World Problem
Food critic Sheila Hibben looked into the complexities of tea-drinking during the cocktail hour, and vice-versa.

* * *
Finer Things
Rebecca West was a brilliant journalist and gifted prose writer, and when she published something people took notice, including critic Clifton Fadiman, who noted her return with The Thinking Reed. A brief excerpt:

* * *
From Our Advertisers
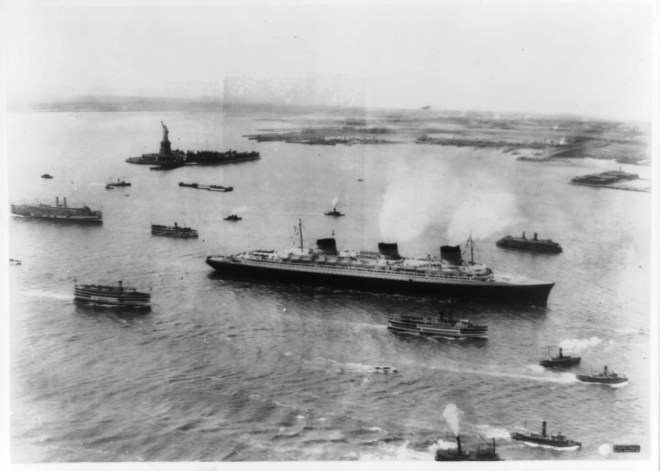
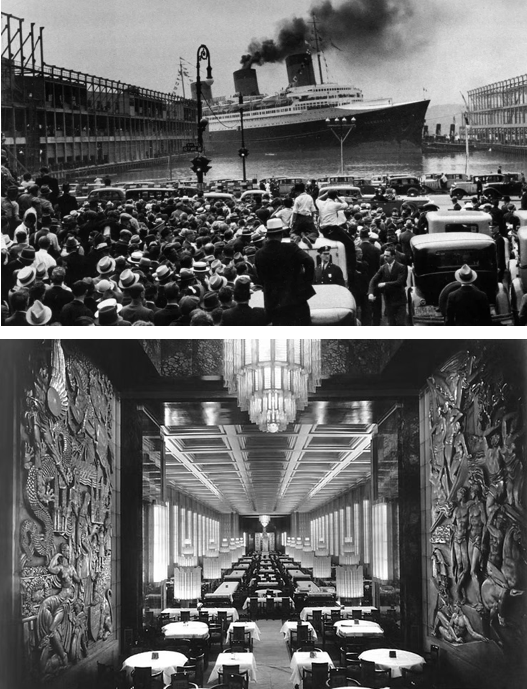
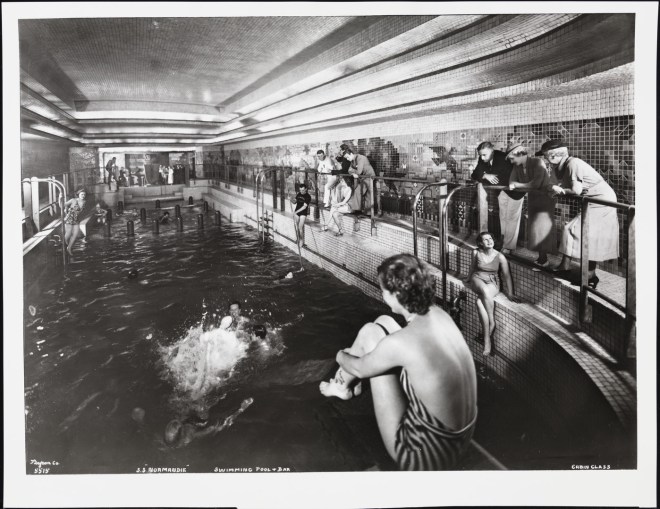
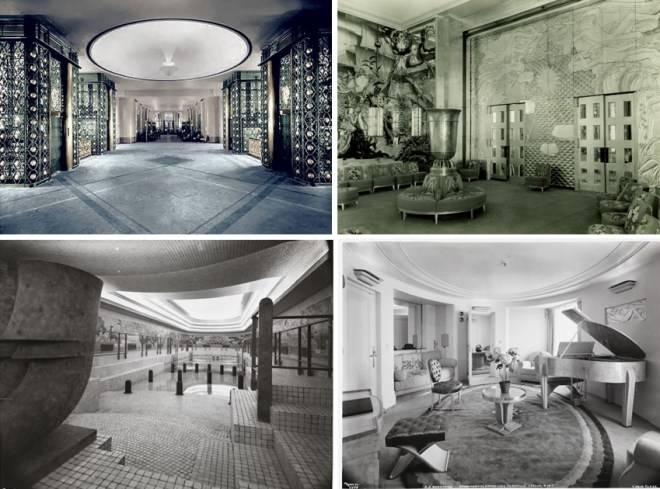
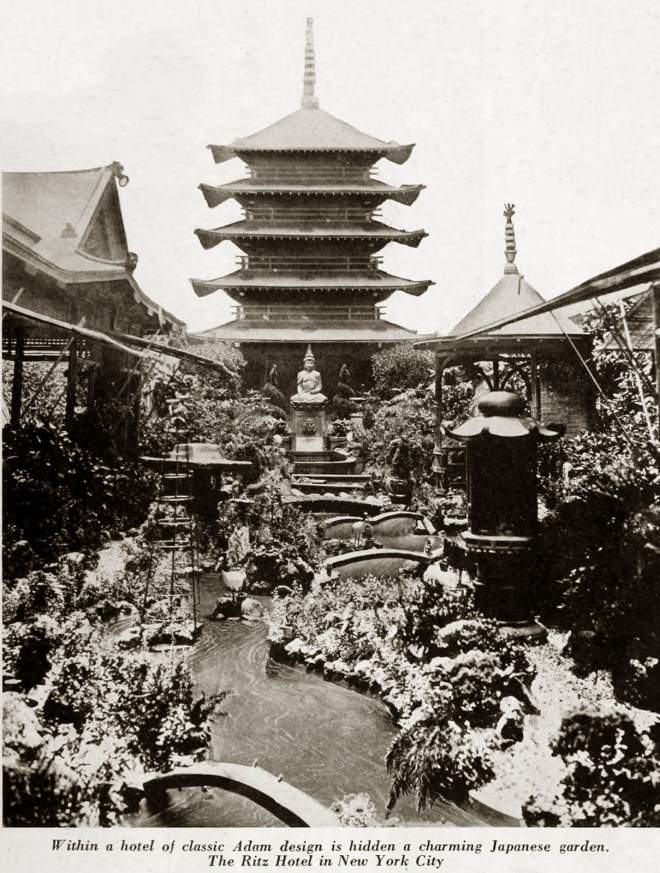
The March 7 issue opened to this sumptuous image of luxury travel aboard the Normandie…
…the salons of Dorothy Gray returned with another tale of a magical transformation, here the plain “Miss Adams” suddenly becomes lovely and exciting thanks to the illusion of cosmetics…
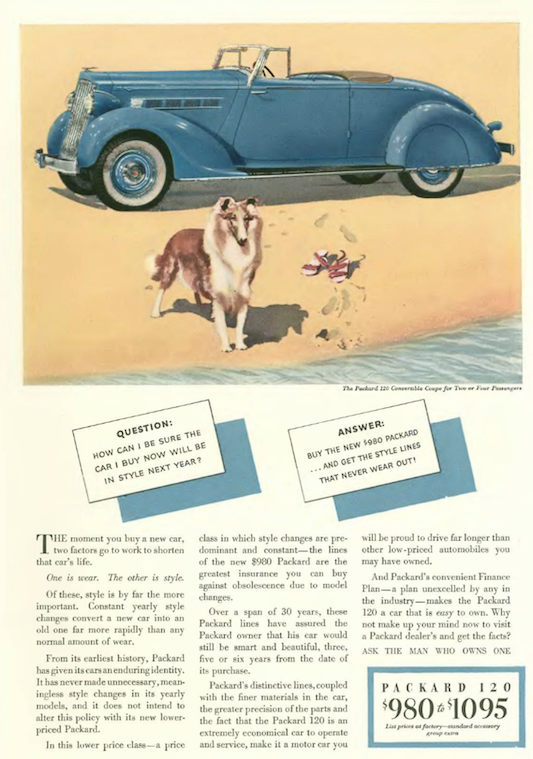
…the makers of Packard automobiles took out this full page ad to gently chastise Time magazine for questioning the carmaker’s adherence to a timeless, “basic design”…
…although in Time’s defense the Packard didn’t look much different from this Lincoln…
…what did look different was the Chrysler/DeSoto Airflow, which had disappointing sales due to a streamlined design that was a bit too radical for consumers…
…actress and costume designer Kate Lawson (1894-1977) made her image available to promote washable wallpaper…
…in addition to calming nerves and boosting energy, Camels apparently aided one’s digestion, or so this ad claimed…
…Liggett & Myers stuck with the homespun approach, here three generations light up Chesterfields in the warm glow of the parlor…
…did you spot the cigarettes in the ad?…
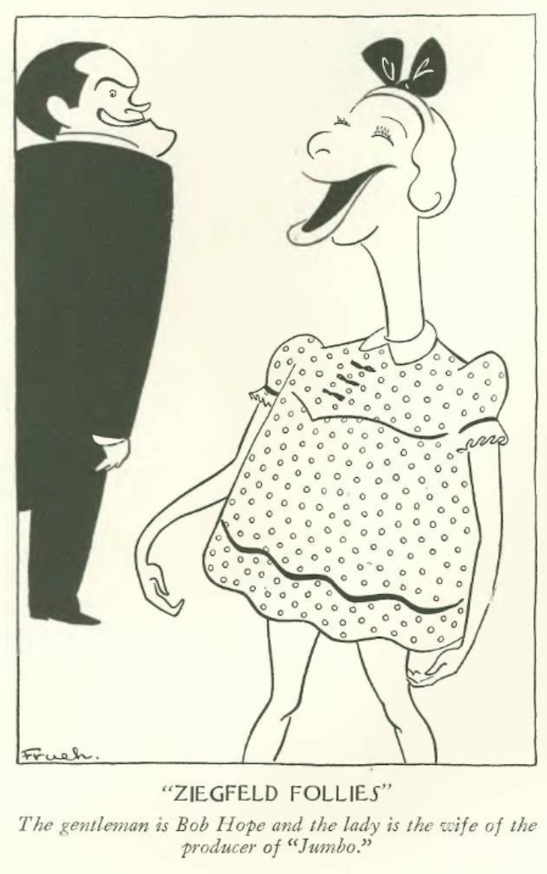
…on to the cartoons, we have Al Frueh’s take on the Ziegfeld Follies…
…James Thurber contributed this to the calendar section…
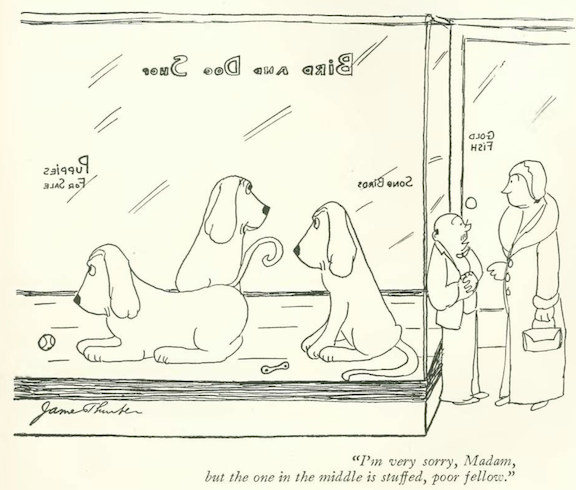
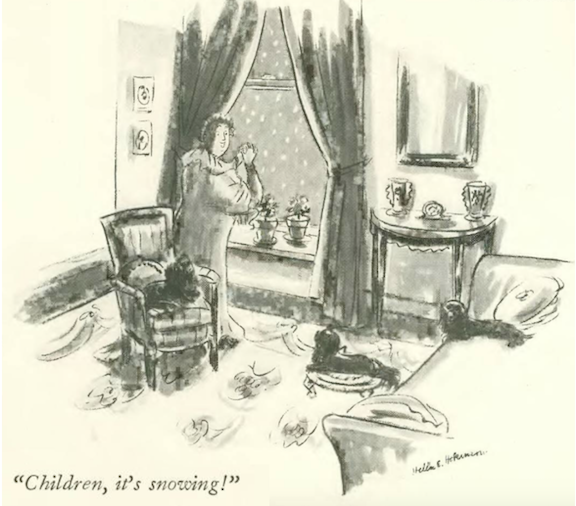
…and Thurber again with his beloved dogs…
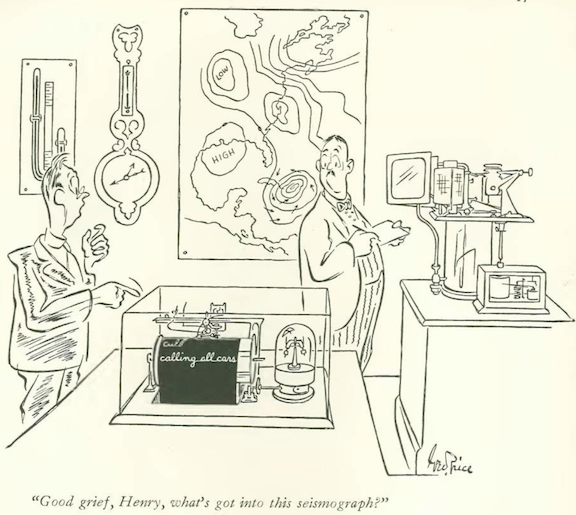
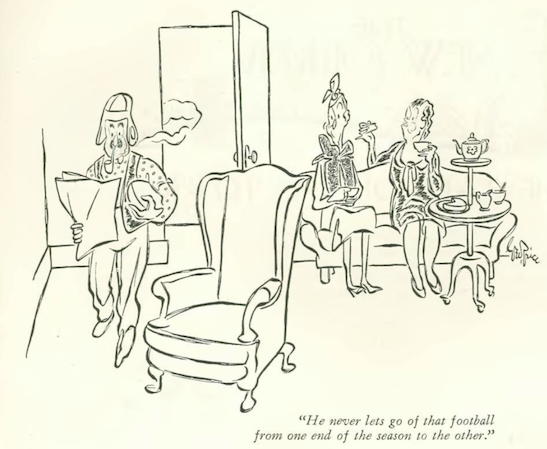
…George Price found a glitch at the weather bureau…
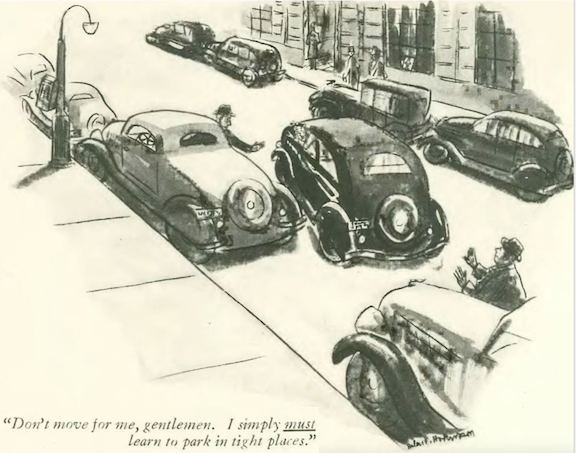
…Californians circled their wagons in the hostile Midwest, per Carl Rose…
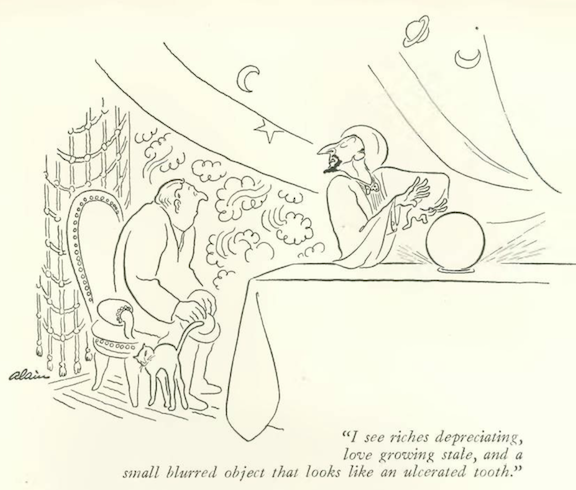
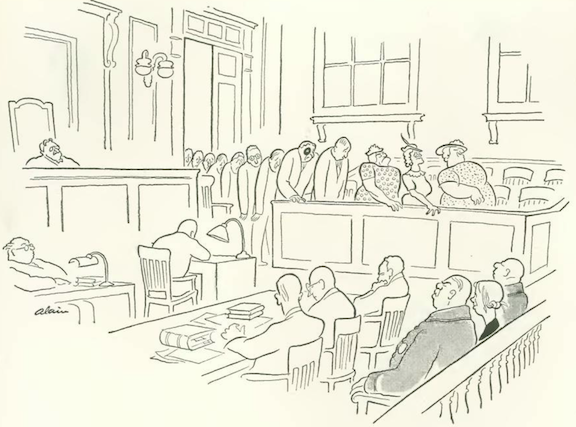
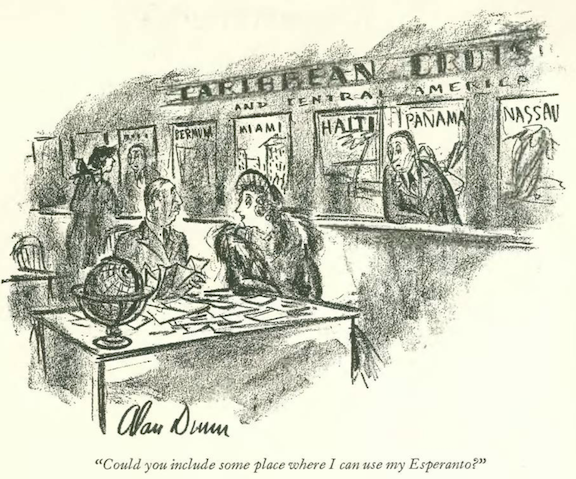
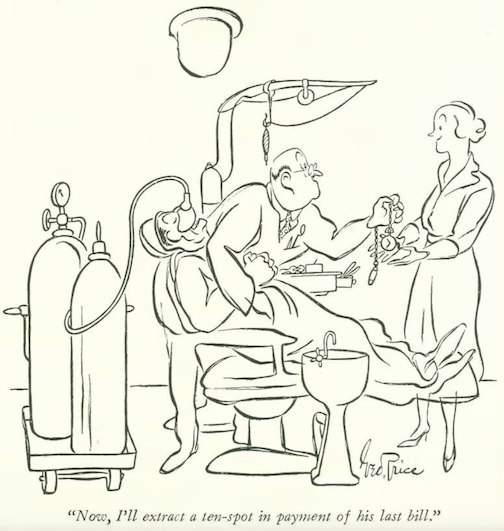
…Alain saw a trip to the dentist in this man’s future…
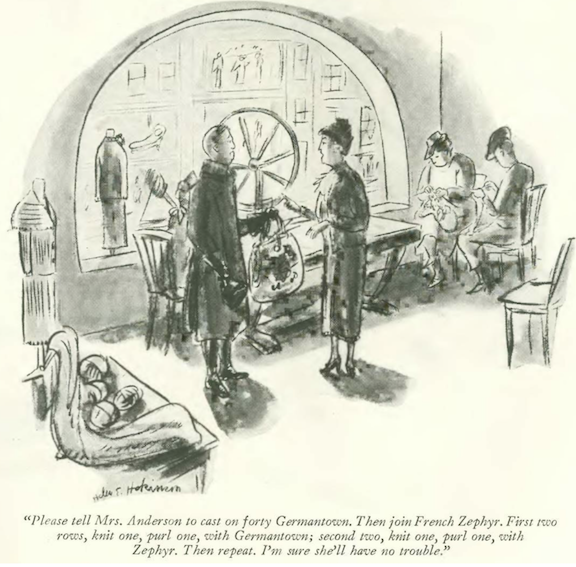
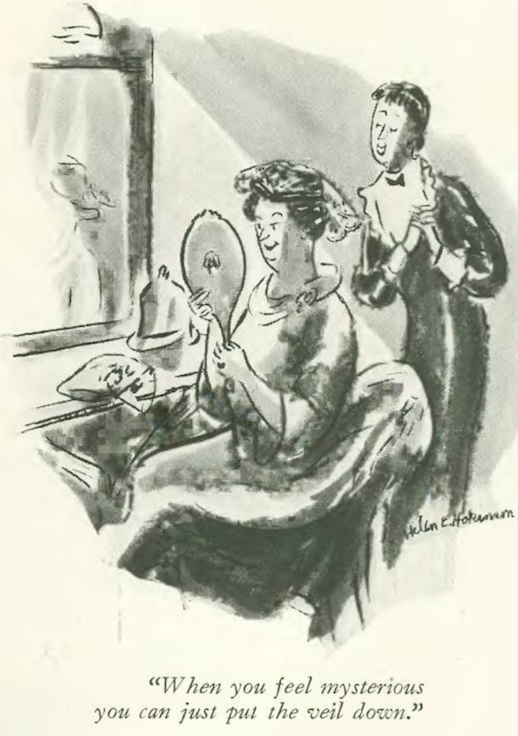
…Helen Hokinson lost us in the peculiarities of needlepoint…
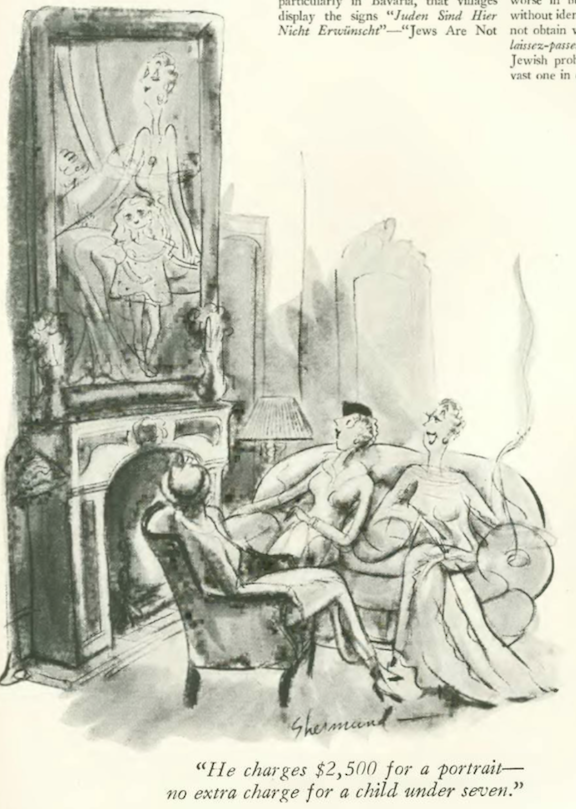
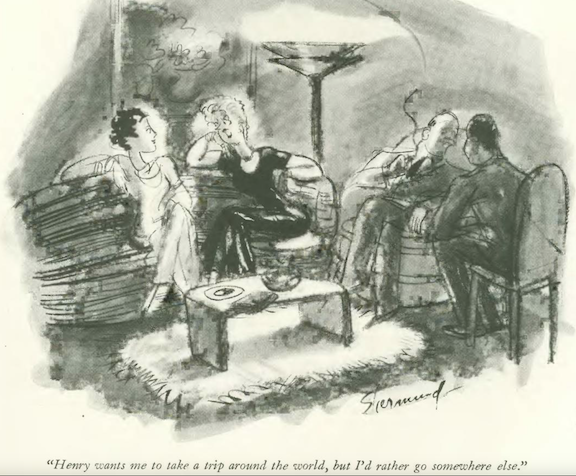
…Barbara Shermund found a bargain in portraiture…
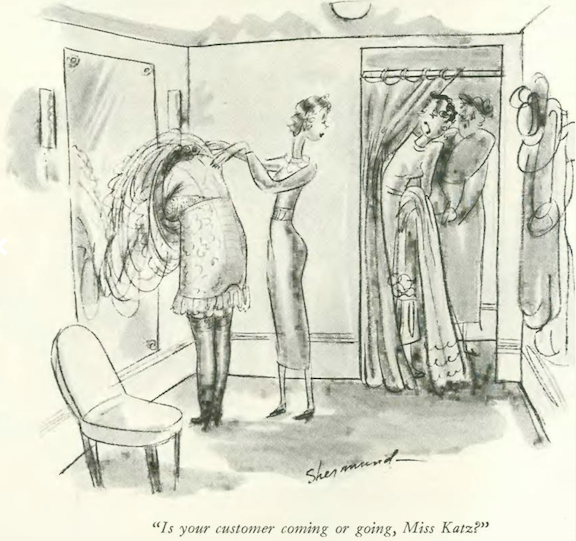
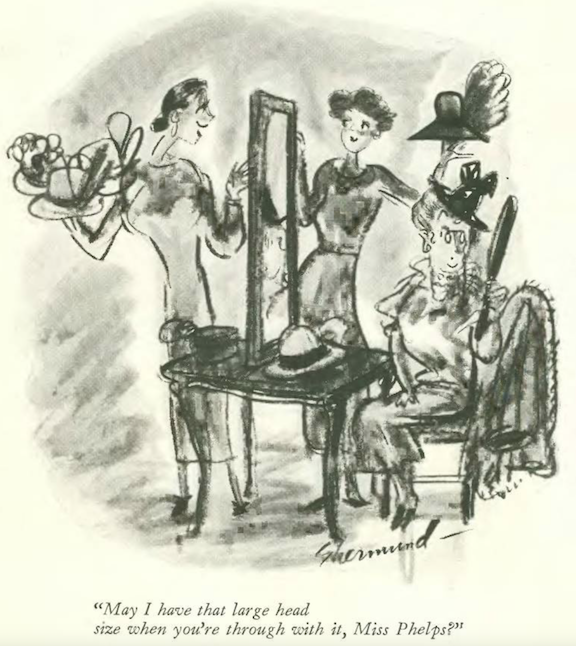
…and Shermund again, in the dress department…
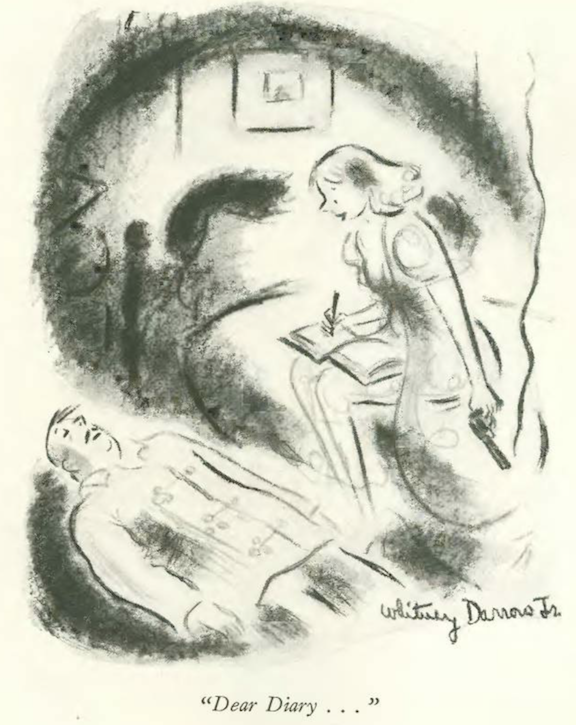
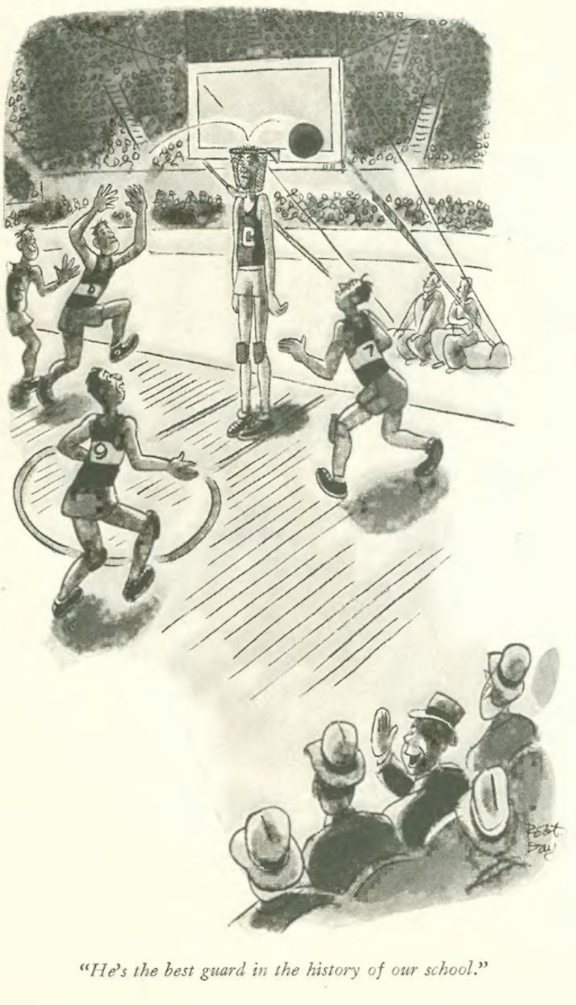
…and we close with Whitney Darrow Jr, and something to write about…
Next Time: Nostalgic Notes…