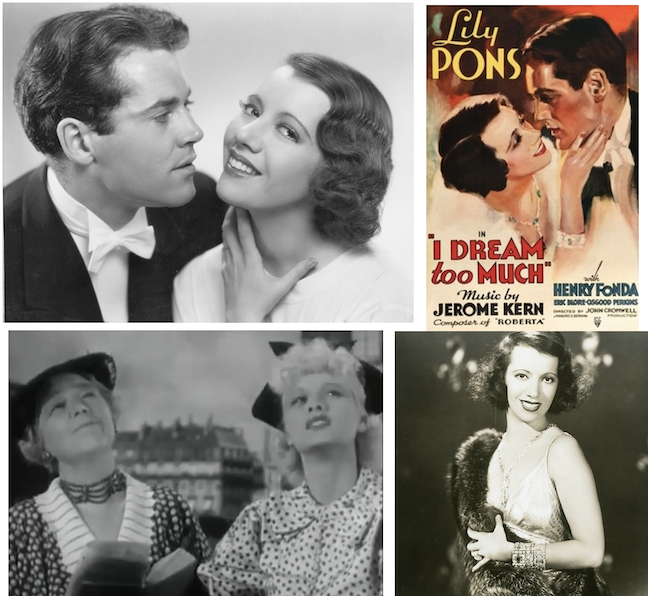
Above: Left image, coloratura soprano Lily Pons with Henry Fonda in I Dream Too Much;at right, Kitty Carlisle and Groucho Marx in A Night at the Opera. (rottentomatoes.com/IMDB)
The title of this post refers to two items below, which you’ll discover as we make our way through the December 7, 1935 issue of The New Yorker.


*
Our first night at the opera comes courtesy of RKO Pictures, which presented French-American coloratura soprano Lily Pons as the star of the musical rom-com I Dream Too Much. Critic John Mosher found the film enjoyable, singling out Pons for praise while chastising the screenwriters for interrupting the lively farce with some “social research.”

Mosher also said farewell to Will Rogers in his final film, In Old Kentucky, which he found to be a “minor affair.” He also reviewed The Land of Promise, a film about Palestine that indicated to Mosher that “life there is highly successful for all present.”


* * *
E.B. White keeps us on the cinema trail with some thoughts on the film, Mutiny on the Bounty, namely a certain historical inaccuracy:

* * *
They Had It First
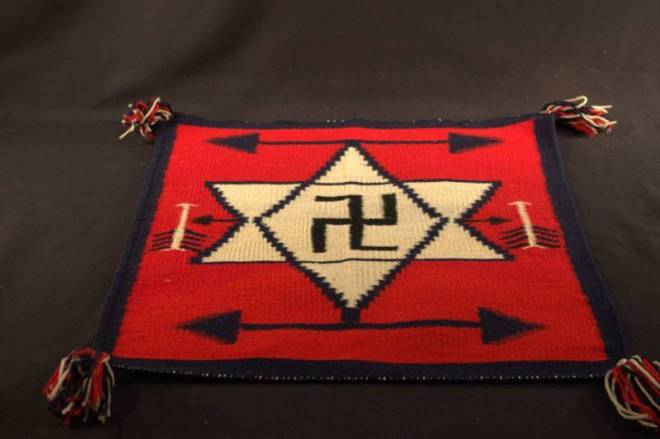
The swastika was among the more popular designs incorporated into southwestern tribal art during the American tourist era (roughly 1890 to the 1930s). For the Navajo, the symbol represented humanity and life, and was used in healing rituals (it was also widely used by tribal peoples across Europe and Asia). Tourism promoters (called “hotel men” here) encouraged the symbol’s use until the 1930s, when it was increasingly associated with Germany’s Nazi Party. E.B. White explained:

* * *
Lois Long’s fashion column continued to be dominated by exhaustive Christmas shopping lists, in this issue stretching from pages 58 to 97…here are the first and last paragraphs of the column…
* * *
A Woolly Read
Perhaps your special someone was hoping for a thousand-page book under the tree; then look no further than The Woollcott Reader, a collection of stories, essays and other literary gems by New Yorker personality and former “Shouts and Murmurs” columnist Alexander Woollcott. In this excerpt, book critic Clifton Fadiman noted that a signed copy could be had for $7.50.

* * *
From Our Advertisers
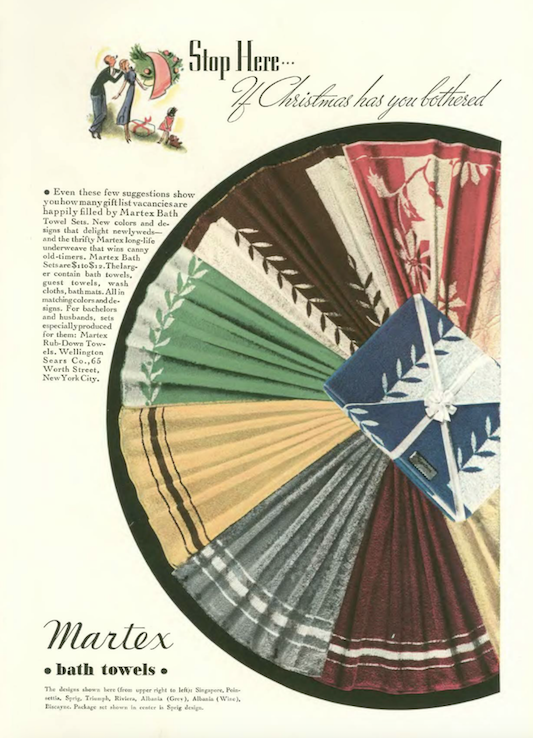
Colorful advertisements brightened the 149 pages of the Dec. 7 issue…we begin with this colorful array from Martex…
…the women’s specialty shop Jane Engel commissioned one of the best-known commercial photographers of the day, Ruzzie Green, to capture this glamorous image…
…Caron Paris offered up this cheerful bouquet…
…the makers of White Rock were enjoying the fruits of post-Prohibition days…
…the publishers of Stage magazine highlighted Beatrice Lillie’s Broadway revue, At Home Abroad…
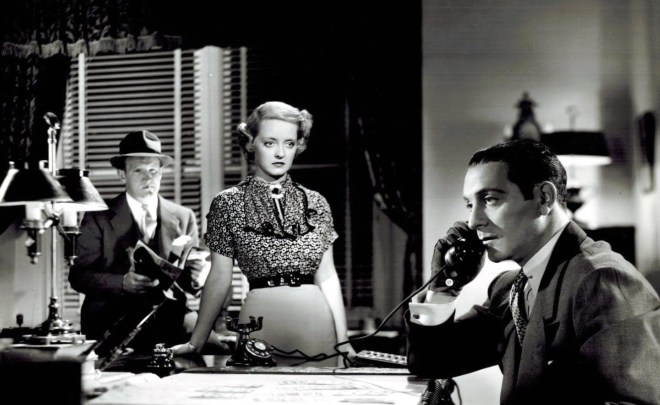
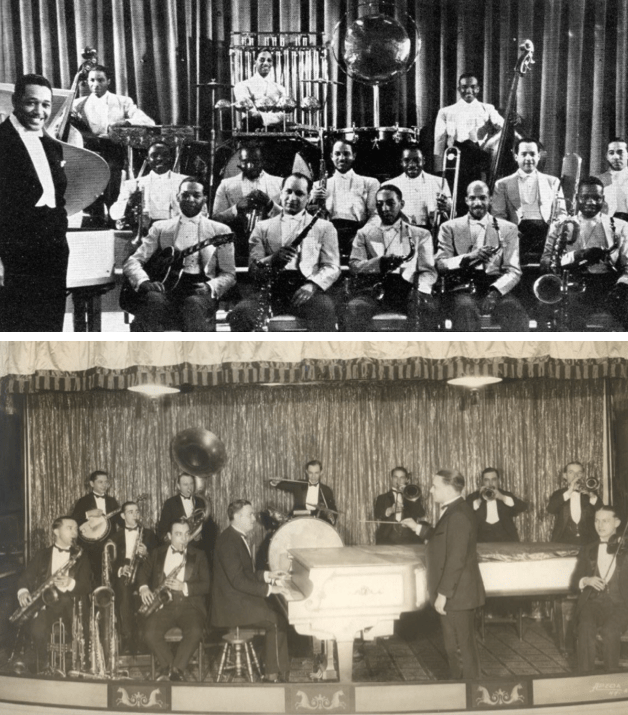
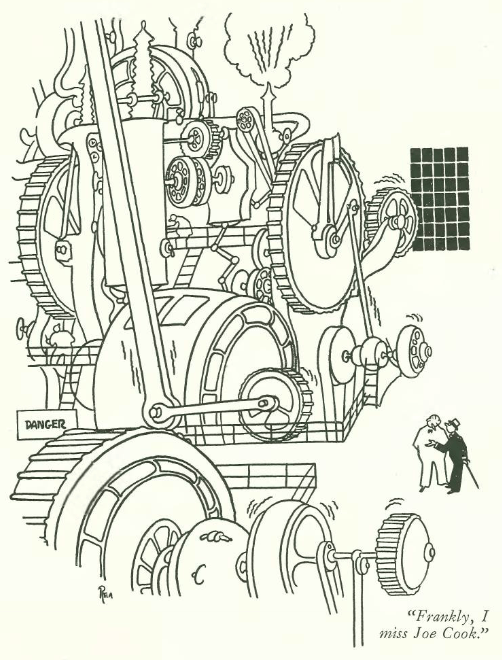
…the Capitol Theatre took out this full-page advertisement to tout the opening of the latest Marx Brothers film…
…here is a close-up of the ad’s “testimonials”…
…and what awaited audiences…

…the Lord & Thomas advertising firm imitated the New Yorker style in this full-page promotion…
…now who wouldn’t want a Philco “Radiobar” for the holidays?…
…found this one on 1stdibs.com…pretty cool…
…or you could get a little something for every one of your smoking friends (likely everyone)…
…and you could keep those holiday memories alive with a swell Kodak movie camera…
…Schrafft’s must have been something like an upscale Cracker Barrel…
…house ads from The New Yorker included this Otto Soglow-illustrated full pager…
…the magazine also touted books and poems by its contributors…
…and the Seventh New Yorker Album…
…more James Thurber here in this spot drawing for the “Books” section…
…and in this cartoon filled with holiday hijinks…
…Ilonka Karasz gave us a hockey goalie to open the calendar listings…
…George Price drew up this Depression-themed drawing at the bottom of the “Goings On” section…
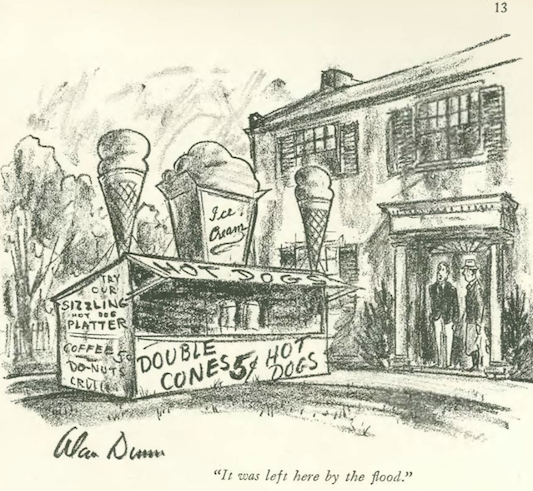
…a great spot drawing by Aaron Sopher (1905–1972), who is perhaps best known for his depictions of everyday life in Baltimore…it was oddly placed amidst the “Christmas Gifts” section…
…according to Michael Maslin’s Ink Spill, Sopher contributed just two cartoons to the magazine, in the issues of June 15, 1929, and December 6, 1930 (pictured below)… 
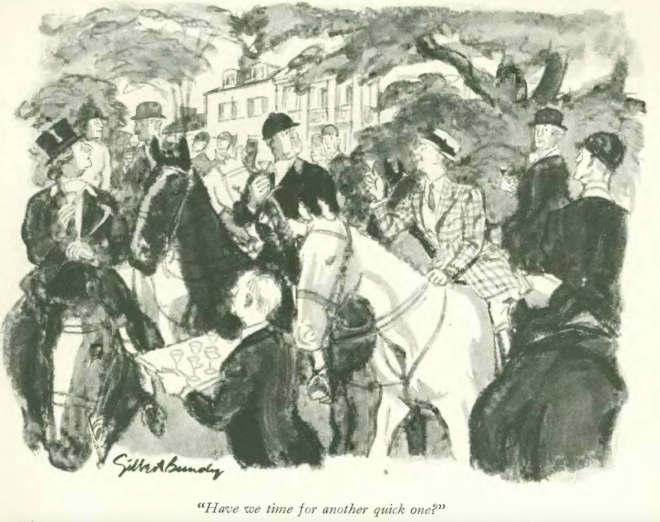
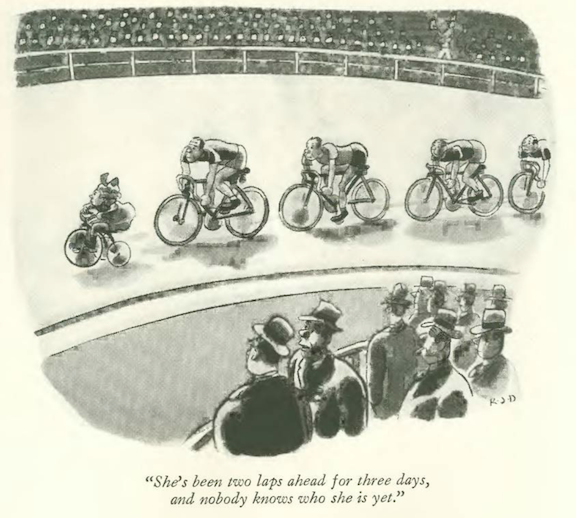
…back to the Dec. 7 issue, and at the Velodrome with Robert Day…
…who also visited an ill-suited Santa…
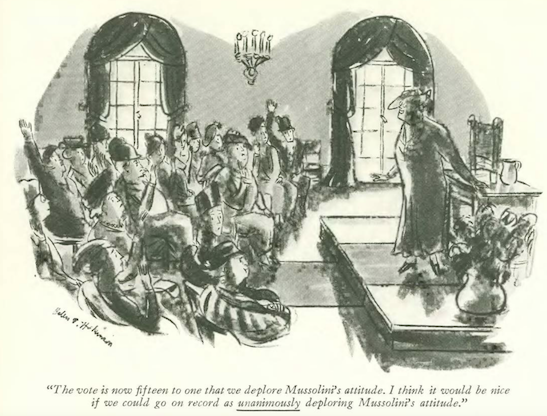
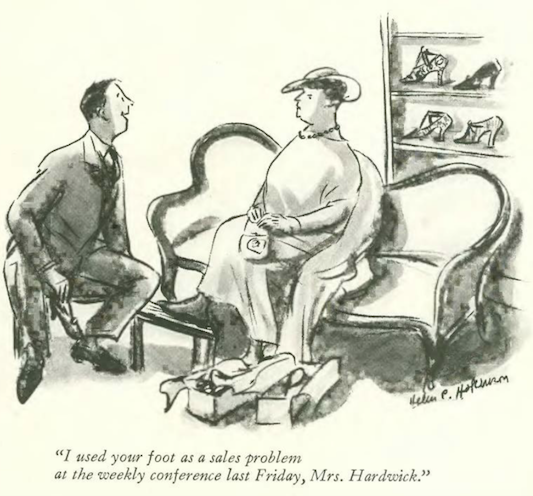
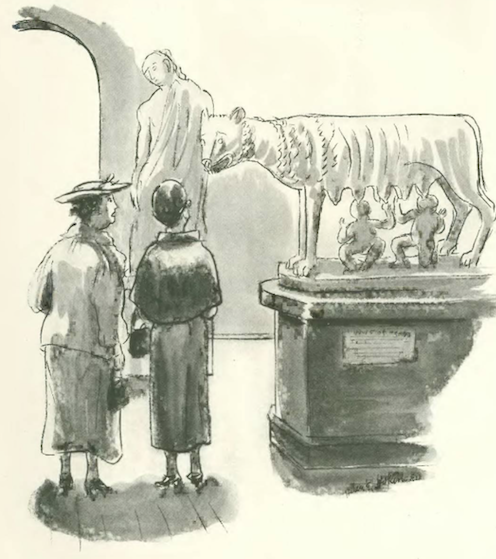
…Helen Hokinson pondered gift ideas…
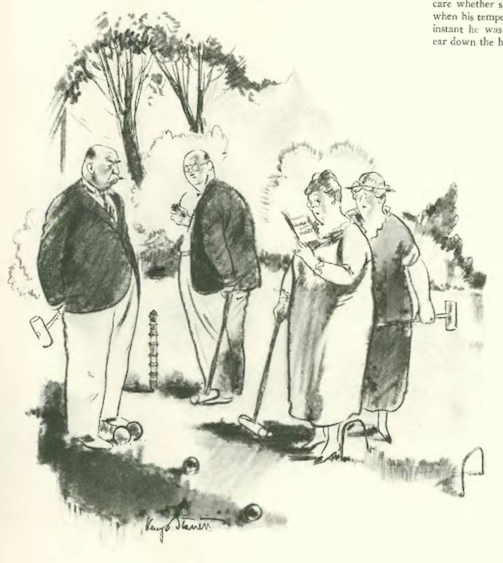
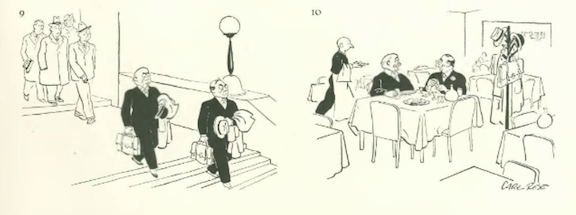
…Carl Rose illustrated an unspeakable act at a progressive school…
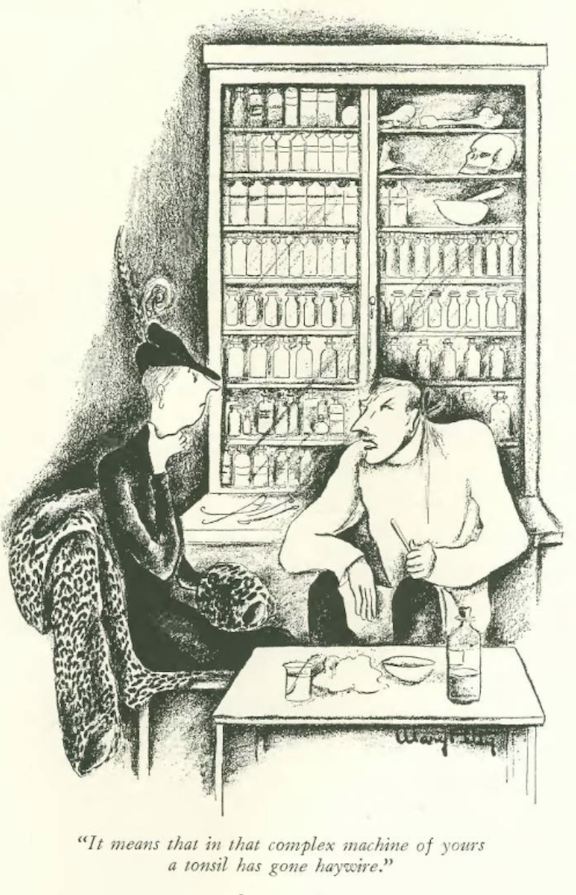
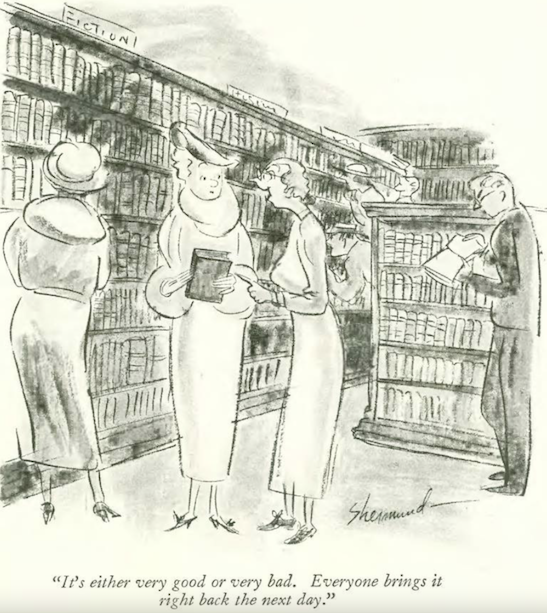
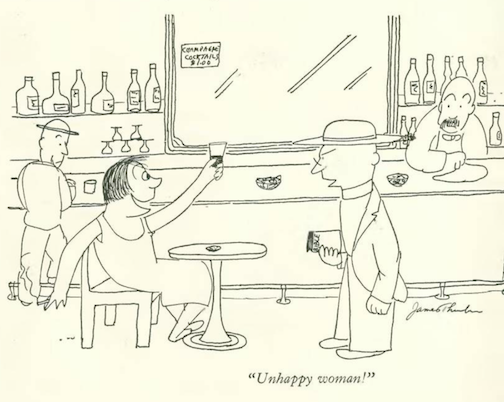
…Mary Petty gave us a straightforward diagnosis…
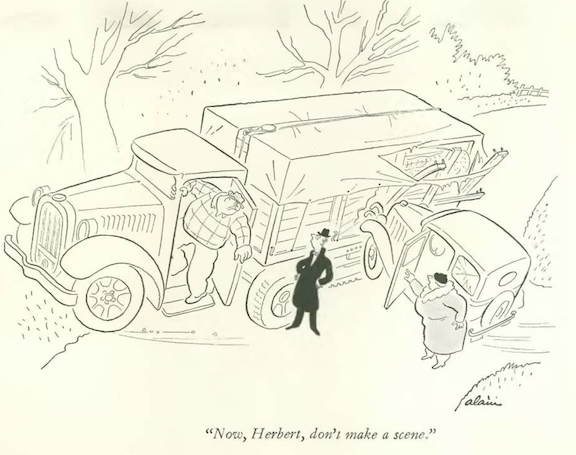
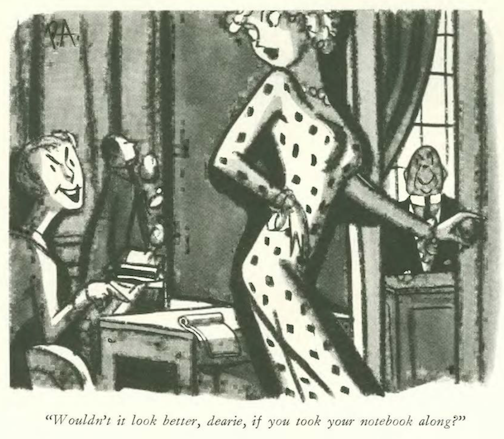
…Alain asked us to ponder the fate of one man…
…Whitney Darrow Jr eavesdropped on some child philosophy…
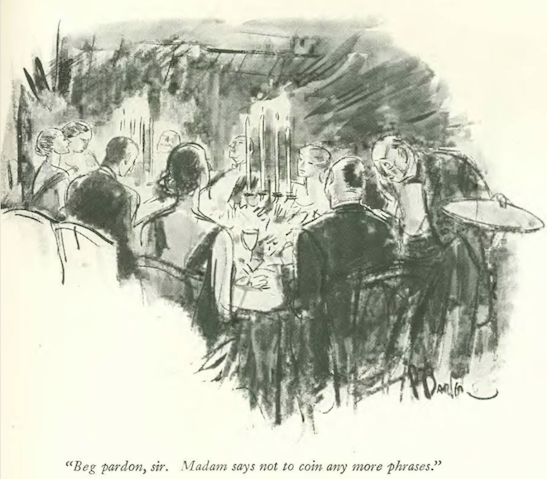
…and we close with Peter Arno, and a groom’s surprise at the altar…
Next Time: Marxist Mayhem…