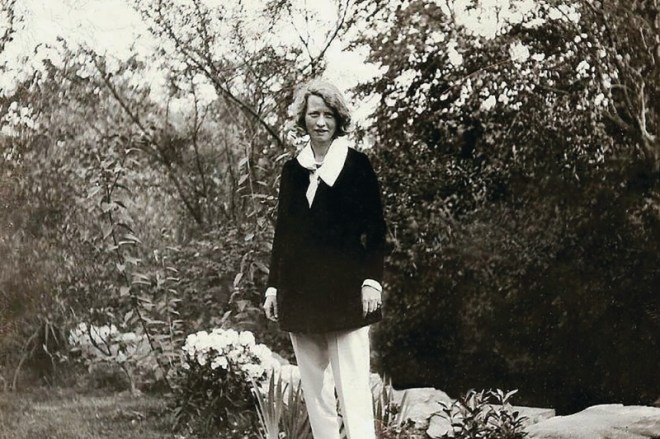
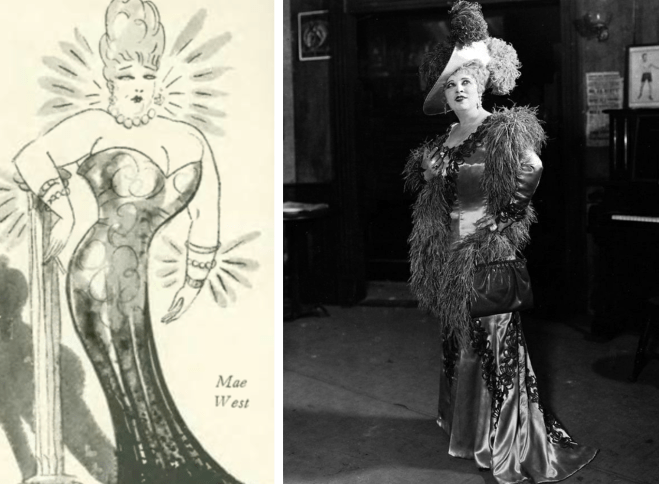
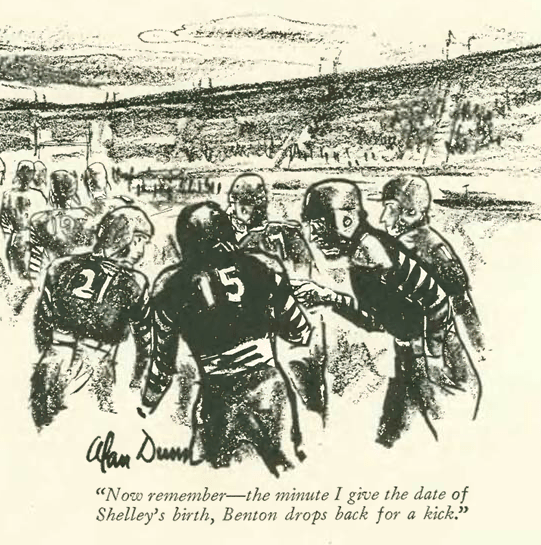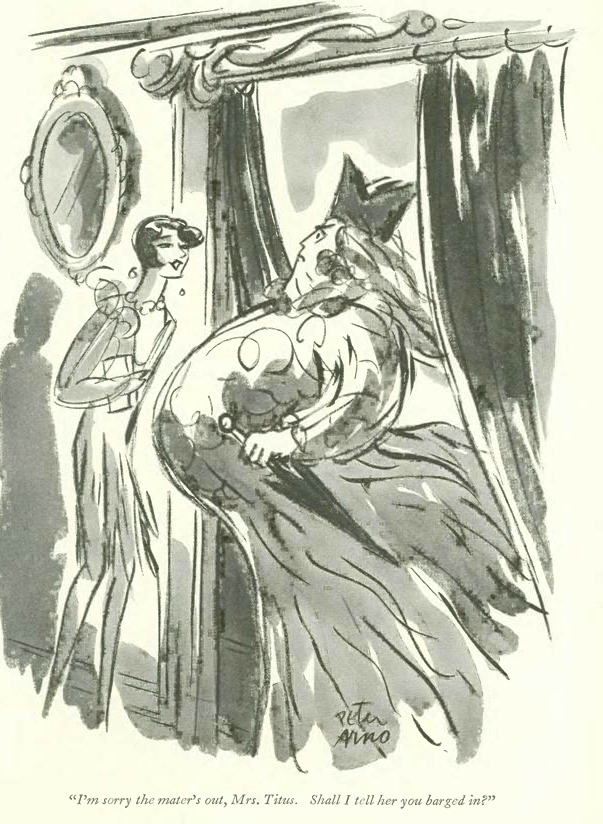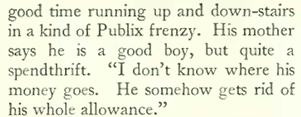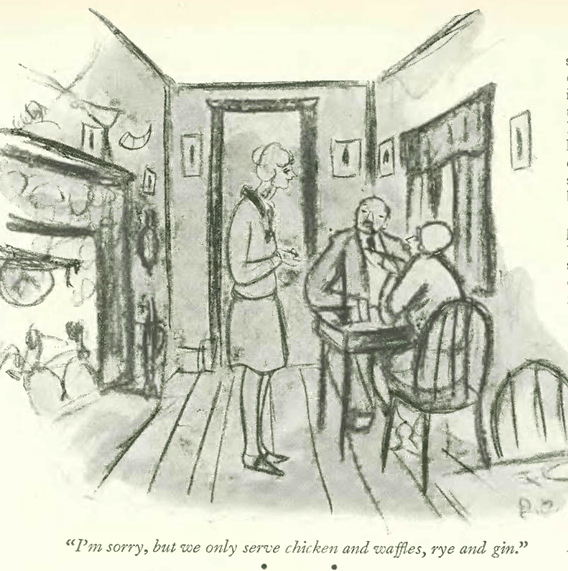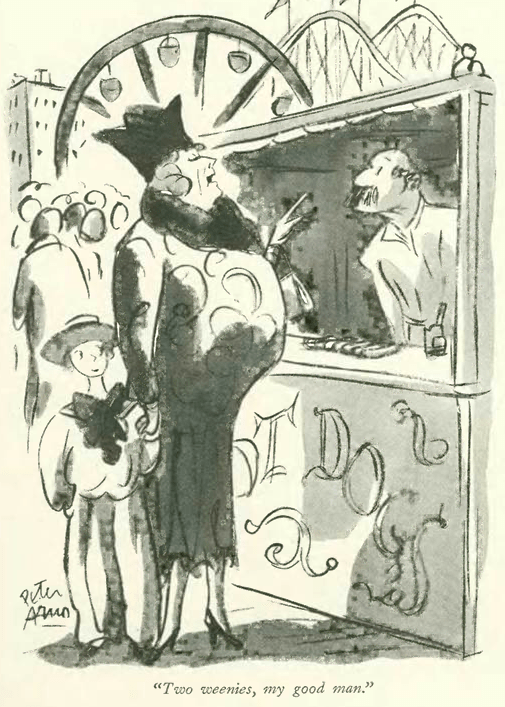Although the Roaring Twenties saw the relaxing of many moral strictures — particularly in major cities like New York — Mae West’s frank portrayals of sex on an off-Broadway stage could still create a stir in the newspapers and among arbiters of American probity.

Before she appeared in films (mostly in the 1930s) Mae West was well known to New Yorkers both in vaudeville and on Broadway. Her wider fame came in 1927, when many Americans read about her arrest on obscenity charges linked to a scandalous play simply titled Sex. A story of a Montreal prostitute, Sex opened at Daly’s 63rd Street Theatre on April 1926 to modest audiences and mostly scathing reviews. The New York Times, for example, called it a “crude and inept play, cheaply produced and poorly acted.” Perhaps because of the negative reviews, which mostly focused on the play’s morality, curious audiences flocked to see it. Ironically (at least, I imagine, to the critics), Sex was the only play on Broadway in 1926 to stay open through the summer and into the following year.

The fun ended when New York City police raided West’s production company in February 1927 and charged her with obscenity. In another ironic and hypocritical twist (many in the police department and in the city’s court system had enjoyed the play themselves, along with approximately 325,000 others during the play’s 10-month run), authorities fined West $500 and sentenced her to ten days in a workhouse on Welfare Island. Always the entrepreneur, West used the sentence to her advantage, and even arrived at the prison in a limousine. It was during her short stint in prison that she began work on her smash hit Diamond Lil.
Thyra Samter Winslow, a writer who often exposed the hypocrisy and prejudice in American life in her short fiction, profiled West for the Nov. 10, 1928 issue:
Note Winslow’s surprise to find West to be much smaller than she imagined (indeed, West barely stood five feet tall). Because West preferred a curvy, buxom figure to the thin flapper look, many like Winslow assumed her to be a much larger woman. No doubt her lavish costumes also suggested greater proportions:
West explained to Winslow that she was simply giving the people what they wanted, whether it was outlandish costumes or some “dirt” in their entertainments. Behind this facade, however, was a private, hard-working woman who wrote much of her own material and had the savvy to market it.

In her profile, Winslow noted West’s marketing savvy during her incarceration, where she won many new friends along the way:
Winslow concluded her piece wondering if West had peaked in her success, and would “fade out” along with so many other vaudeville stars…
…. In less than seven years, West at age 42 would become Hollywood’s highest paid star and second only to William Randolph Hearst as the highest paid person in America. Ninety-two years after Sex, West remains an icon of popular culture around the world.

* * *
From Our Advertisers
The Nov. 10 issue featured this all American endorsement for Lucky Strike cigarettes from World Series winning pitcher Waite Hoyt…never mind that The New Yorker itself completely ignored the World Series and baseball in general.
…and Charles of the Ritz used a combination of vanity, snob appeal and class anxiety to promote their latest beauty ensemble…
The comics glimpsed the foibles of the upper classes, including this terrific entry by 22-year-old Ben Hur Baz, a Mexico-born artist who would go on to become famous for his pin-ups in the 1940s and 50s, many of them appearing in Esquire:
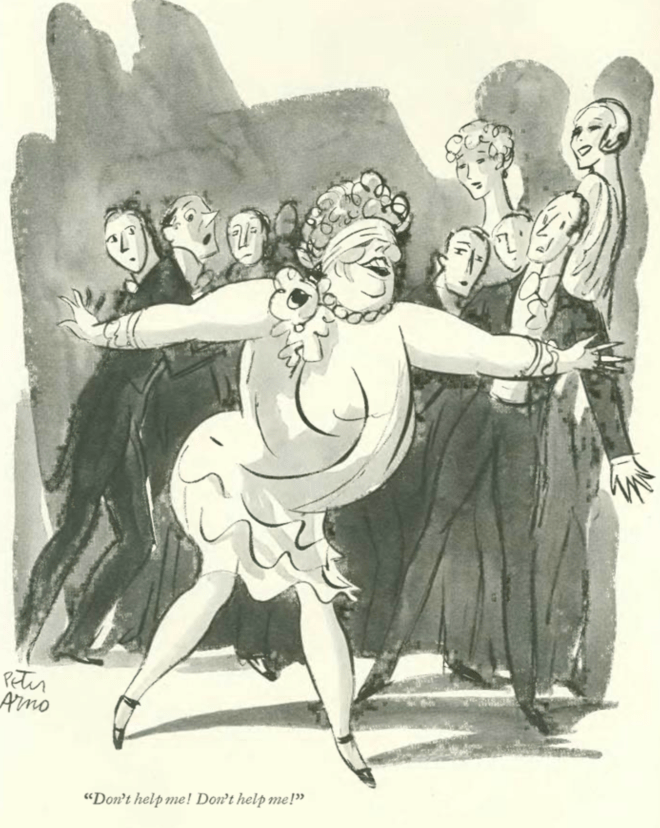
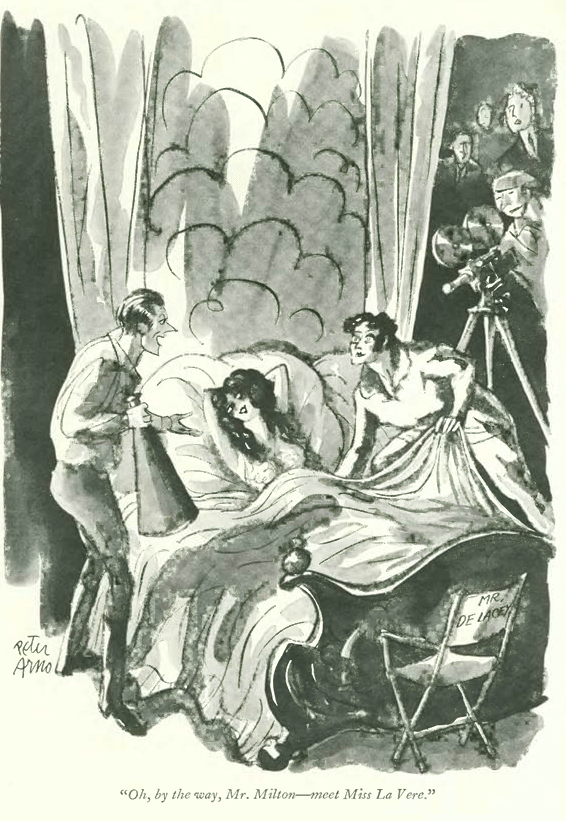
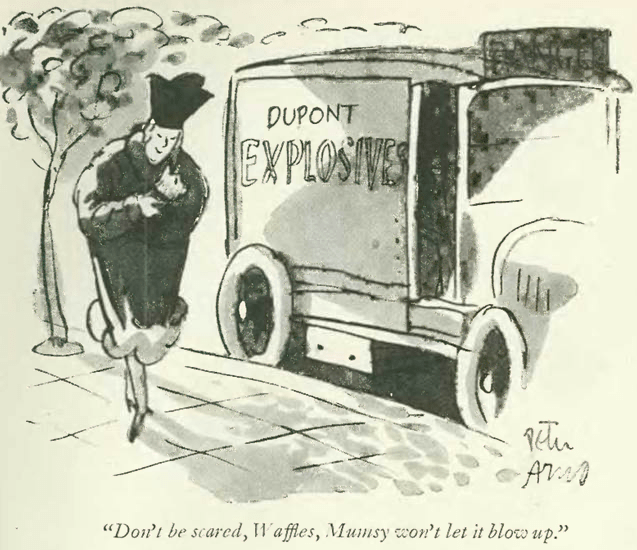
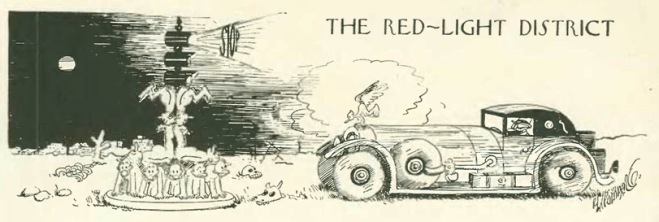
…and a game of blind man’s bluff (or some say ‘buff’) as rendered by Peter Arno:
* * *
The Nov. 17 issue featured an unusual entry by E.B. White, who, like many of his New Yorker colleagues, found many reasons to be critical of the media, including the dumbing down of newspapers that increasingly favored trivia, sensation and promotion over serious discourse.

White skewered the news of the day in this two-page spread that parodied the look and language of contemporary newspapers (click to enlarge):
* * *
The issue’s “Talk of the Town” featured a lengthy entry on Notre Dame football coach Knute Rockne, a figure greatly admired and generally lauded by the magazine’s sportswriters. A brief excerpt:
The Nov. 17 film reviews gave a rare thumbs up to an American movie, Show People, which starred Marion Davies.

* * *
From Our Advertisers
Although you couldn’t legally procure a drink in 1928, you could (unlike today) legally purchase of box of Cuban cigars for you special someone:
…or if you preferred, a carton Chesterfields. Apparently someone in marketing thought conjuring up the horrors of trench warfare would help sell some smokes…
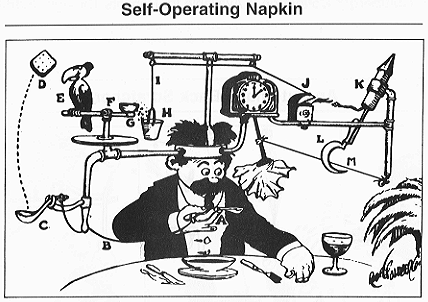
And finally, Peter Arno found out what’s for dinner at the table of a great outdoorsman:
Next Time: What Santa Brought in 1928…