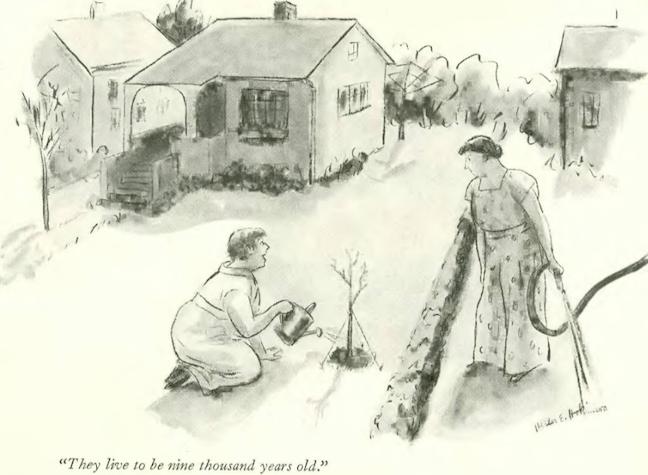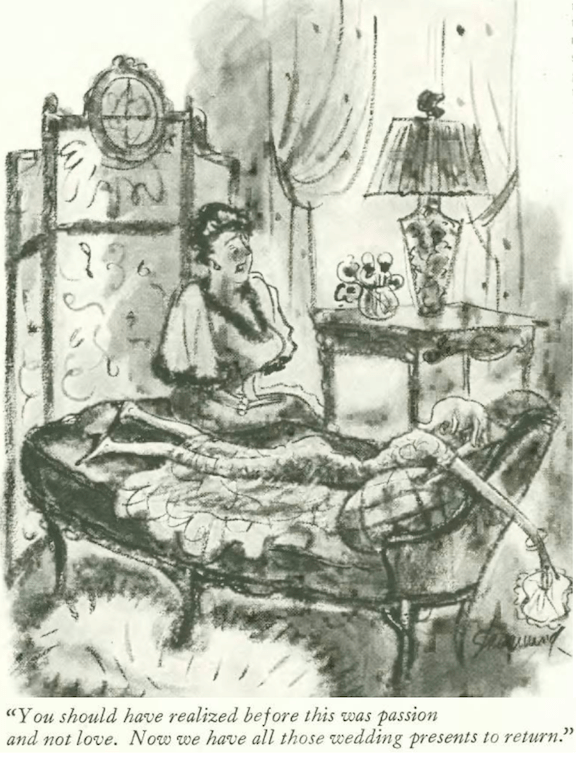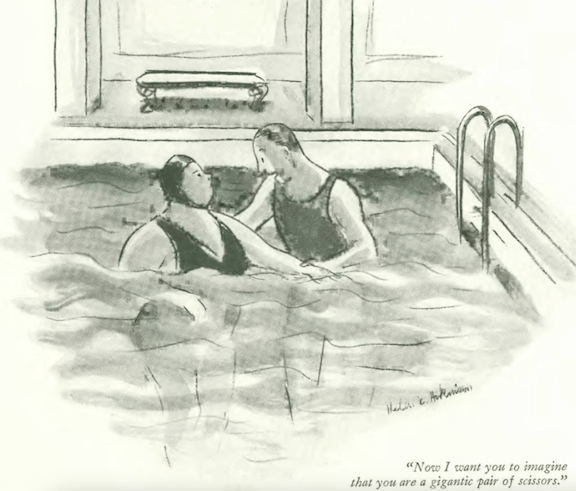Above, Stewart's Cafeteria in Greenwich Village, May 1933. (New York Public Library)
Although Sherwood Anderson is mostly known for his short story collections and novels, in the 1930s he also worked as a journalist, and for the June 9, 1934 issue of the New Yorker he explored the “centre of proletarian high life,” Stewart’s Cafeteria in Greenwich Village.

What is particularly interesting about Anderson’s page 77 article for the “A Reporter at Large” column is what it doesn’t report, namely, that Stewart’s Cafeteria (later the Life Cafeteria) was known as a popular gay and lesbian hangout in addition to being a place for gawkers, assorted bohemians, and bohemian wannabes.
Anderson was a man of the world, so he knew exactly what Stewart’s was all about. But even the New Yorker wasn’t in the business of outing anyone, and editor Harold Ross, whose eccentricities included a puritanical strain, would not have allowed anything associated with “sexual deviance” to be printed in his magazine. Here is an excerpt from Anderson’s article, “Stewart’s, On the Square,” in which he subtly hints at the cafeteria’s “third life.”

While Anderson tiptoed around the topic of homosexuality, gossip rags such as Stephen Clow’s Broadway Brevities put it front and center. Described as one of the most vicious show business gossip magazines ever published, Brevities also provided Clow with some side income: Clow and his collaborators often threatened to blackmail wealthy businesspeople and show business figures who frequented places like Stewart’s—outing them in his tabloid unless payment was made.

Naturally such reporting helped attract gawkers to Stewart’s and its successor, Life Cafeteria. According to the NYC LGBT Historic Sites Project, “Stewart’s closed in the mid-1930s and was subsequently reopened as the equally popular Life Cafeteria. Regulars included a young Tennessee Williams and Marlon Brando (though they didn’t meet each other until years later on a beach in Provincetown). Of the space, Brando later recalled, ‘The rednecks [on the street] were pointing at the diners like animals in a zoo. I was immediately intrigued and ventured in. Before I left that afternoon, I discovered that many of the homosexual men were actually putting on a show for the jam .'”


According to the NYC LGBT Historic Sites Project:
...in 1935 the manager of Stewart’s was convicted of operating a “public nuisance” and “disorderly house” and “openly outraging public decency” by allowing objectionable behavior in the interior and large crowds to gather outside. Specifically, the district attorney’s complaint cited “certain persons of the homosexual type and certain persons of the Lesbian type, to remain therein and engage in acts of sapphism and divers [sic] other lewd, obscene, indecent and disgusting acts” and that the cafeteria was “used as a rendezvous for perverts, degenerates, homosexuals and other evil-disposed persons.” Much of the testimony centered on the gender non-conforming dress and behavior of the patrons.
Here is another excerpt from Anderson's article, where he delves into the nighttime scene at Stewart's:
* * *
Nightlife, Part II
In my previous post E.B. White pondered the fate of the Central Park Casino, a favorite haunt of deposed Mayor Jimmy Walker and other members of the smart set who openly flouted Prohibition laws. In "Tables for Two," Lois Long made this observation (below) at the conclusion of her nightlife column, believing that Parks Commissioner Robert Moses would give the management a chance to lower food prices and allow common folks to enjoy its sumptuous atmosphere. Little did she know that Moses was feasting on a diet of revenge rather than food, and had plans to tear the place down, regardless of its lower prices.
* * *
From Our Advertisers
We kick off the ads with another Ponds celebrity endorsement from dancer and actress Francesca Braggiotti (1902-1998), who was married to actor, politician, and diplomat John Davis Lodge...

...Dr. Seuss was back with more ads for Flit insecticide...he was still two years away from his first children's book: And to Think That I Saw It on Mulberry Street...
...and with a splash of color, Bermuda beckoned New Yorkers to a "Real Vacation"...
...however, before you headed to Bermuda, you'd needed to do something with the kids...
...on to our cartoonists, we start with spot art from Abe Birnbaum...
...Birnbaum again with an illustration of boxer Max Baer for the profile section...
...more spot art from James Thurber in the "Goings On About Town" section...
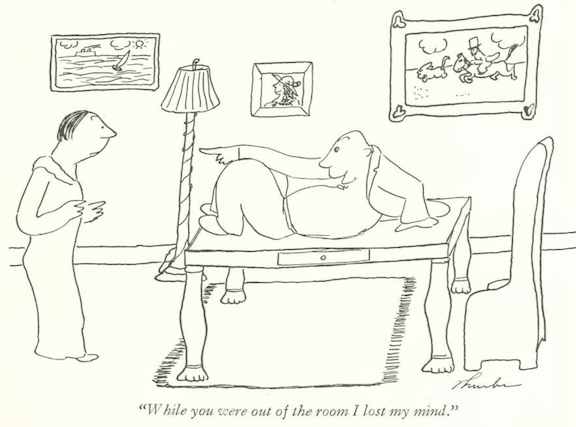
...and Thurber again with some alarming news for a potential suitor...
...Rea Irvin kicked off his series, "Our Native Birds"...
...a famed advertising agency launched a new door-to-door survey, per Perry Barlow...
...Helen Hokinson gave us a hopeful gardener...
...Barbara Shermund looked in on the "modern girl" scene...
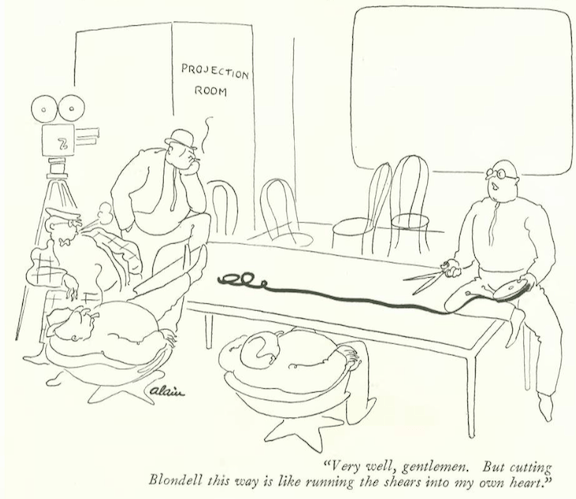
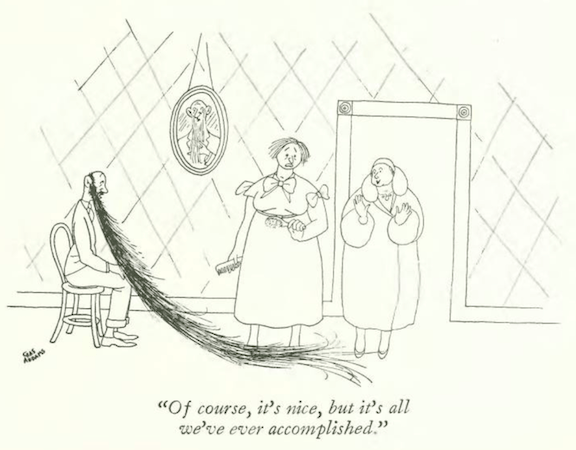
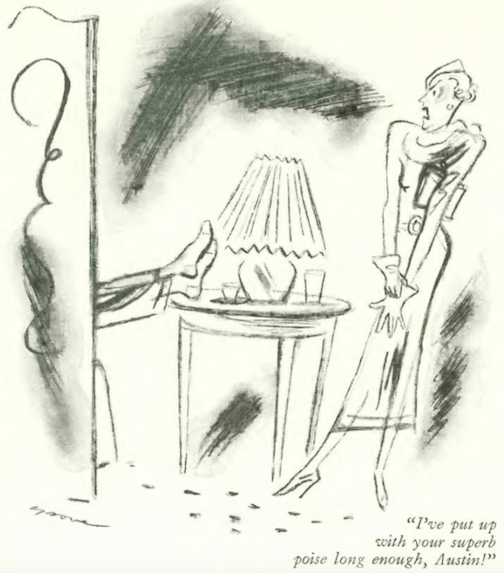
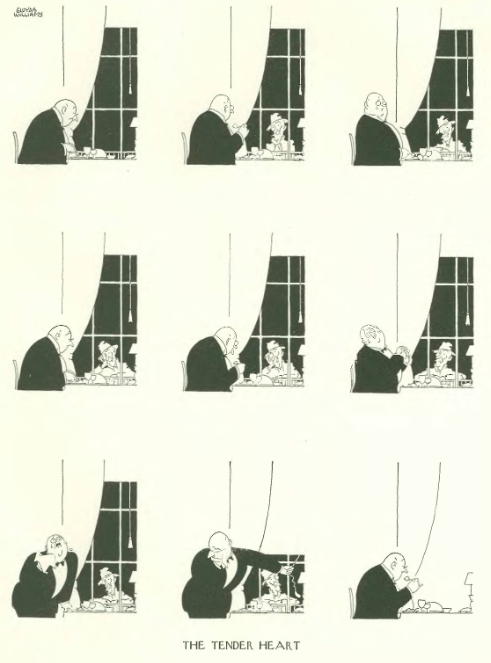
...and Peter Arno examined a sad medical case...
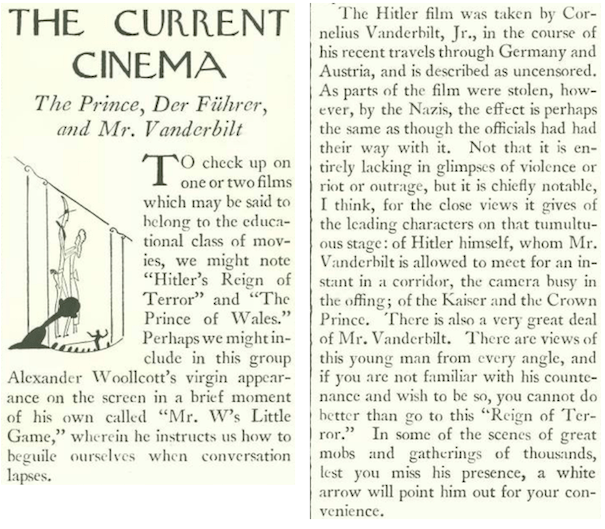
...and we close the June 9 issue with this item from E.B. White, who commented on a recent rally of American Nazis and some fighting Irish...
...the Nazi rally was also alluded to in the June 2 issue (I have the issues reversed this time to support the narrative)...

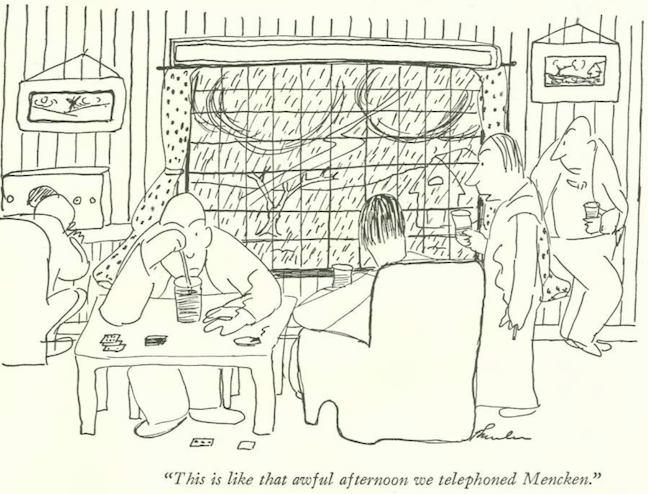
...where Howard Brubaker was keeping things light in his column "Of All Things." I was surprised how little was mentioned in either issue about the meeting of 20,000 Nazi sympathizers on May 17, 1934, at Madison Square Garden.
Let's explore further: According to the Jewish Virtual Library, America's first established anti-Nazi boycott group was the Jewish War Veterans (March 19, 1933), followed by the American League for the Defense of Jewish Rights (ALDJR), which was founded by the Yiddish journalist Abraham Coralnik in May 1933. By 1934 the ALDJR was led by Samuel Untermyer, who changed the organization's name to the "Non-Sectarian Anti-Nazi League to Champion Human Rights." Nazi sympathizers targeted Untermyer as the face of boycott efforts, and at the May 17 rally the mere mention of his name prompted shouts of "Hang him!"

This excerpt from the May 18, 1934 edition of The New York Times gives some idea of what transpired at the rally:

* * *
Dueling Muses
Film critic John Mosher always seemed upbeat about anything involving Disney, but given that animation was still in its infancy (its plastic trickery still rather novel), it didn't take much to outshine the otherwise drab fare (the "Grim") being coughed up by Tinseltown.

The grim included the Pre-Code drama, Upper World, about a rich, married man who falls to his ruin via a romance with a stripper (don't they always?), and Now I'll Tell, another Pre-Code drama, this one loosely based on the doings of racketeer and crime boss Arnold Rothstein.

* * *
More From Our Advertisers
We cool off by a taking a dip in the pool...er, rather by enjoying the "No Draft Ventilation" of a car body by Fisher...the model might want to stay in the pool, since air-conditioning in cars was still a good twenty years away...
...and yes, this is also a car-related ad, if you can believe it, the bride looking forward not to years of wedded bliss but rather her new La Salle (a Cadillac product)...
...another bride, and a car...is that a car body by Fisher? Who cares, the wedding is over and its time to fire one up...
...this woman seems to have it all thanks to Daggett & Ramsdell of Park Avenue, who are prepared to coat her in a "complete range of all the essential creams, lotions, face powder...cold cream soap, dusting powder" etc. etc....
...Dr. Seuss again for Flit, with baby in tow...
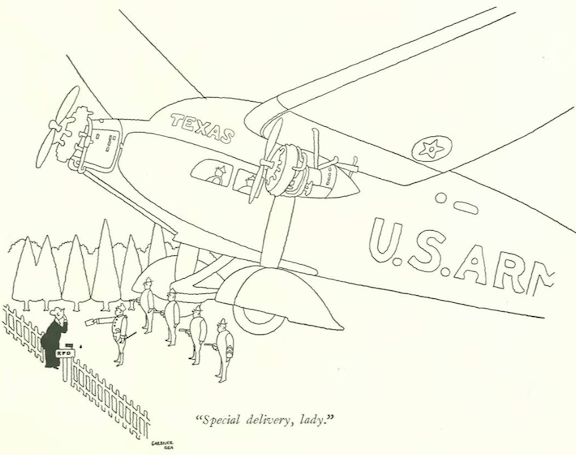
...on to our cartoons, we have Robert Day checking on the progress at Mt. Rushmore...
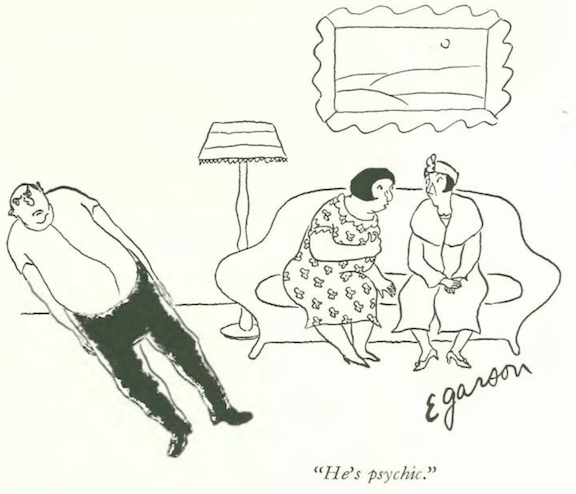
...Alan Dunn reveals pandemic worries of a different nature...
...and we close with Helen Hokinson, and a sudden change of mood...
Next Time: Coney Summertime...