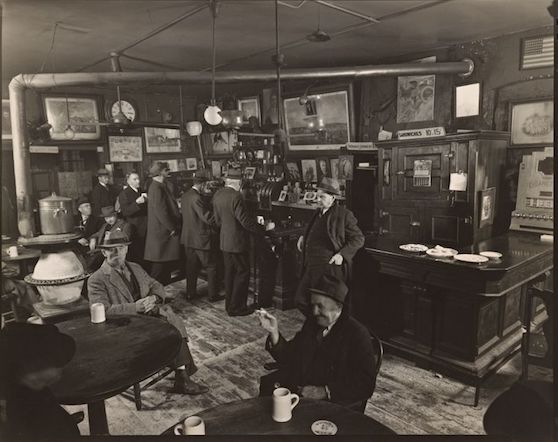
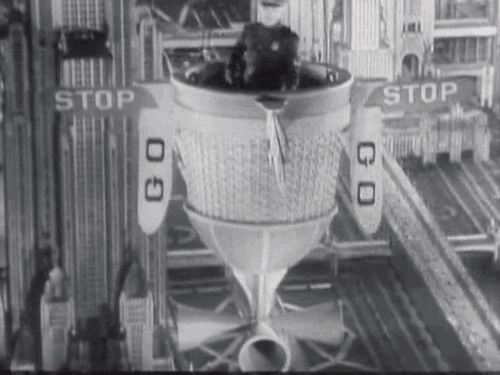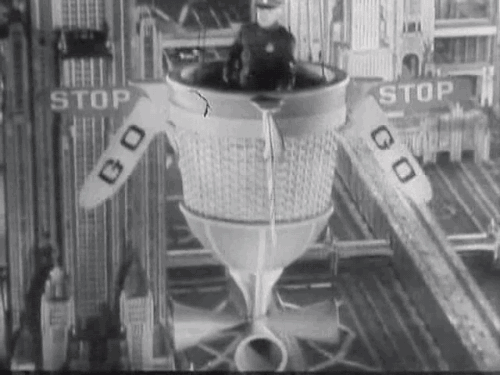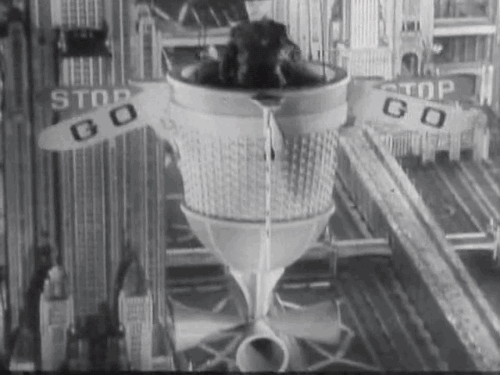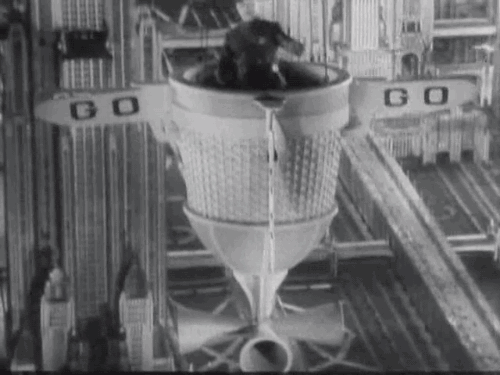
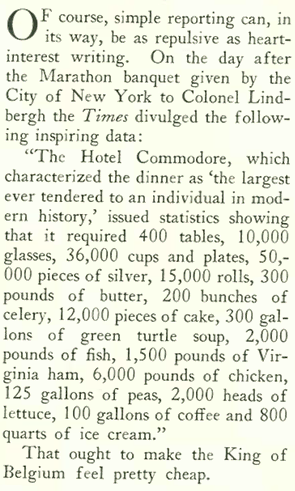Over the years Tod Browning’s 1932 pre-code film Freaks has been called everything from grotesque and exploitive to sympathetic and compassionate. Now a cult classic, the film’s closing scenes are regarded by some critics as among the most terrifying ever put to film.

What disturbed so many about Freaks was Browning’s use of actual sideshow performers with real disabilities to tell the story of a conniving trapeze artist who plots to seduce and then kill a dwarf performer to gain his inheritance. The film was not well-received by audiences and many critics. The Kansas City Star’s John Moffitt wrote, “There is no excuse for this picture. It took a weak mind to produce it and it takes a strong stomach to look at it.” However, The New Yorker’s John Mosher, along several other New York critics, gave the film a rather favorable review:




* * *
Tennis Anyone?
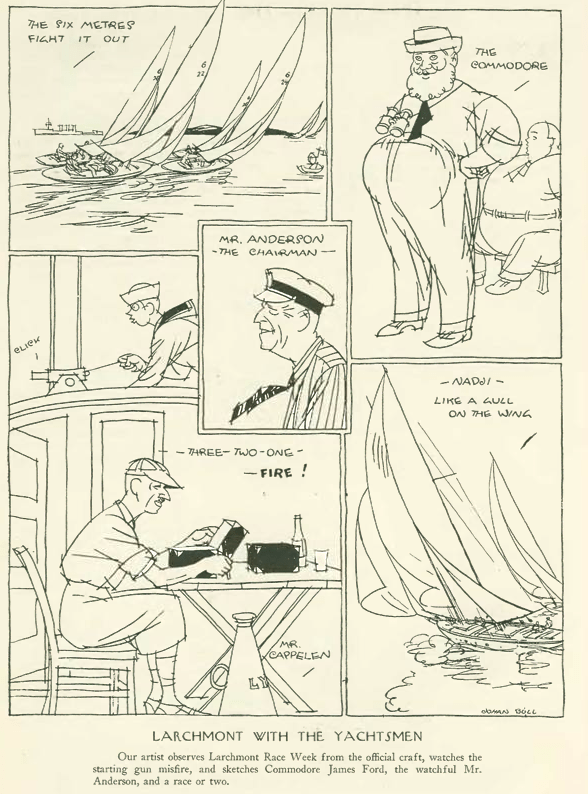
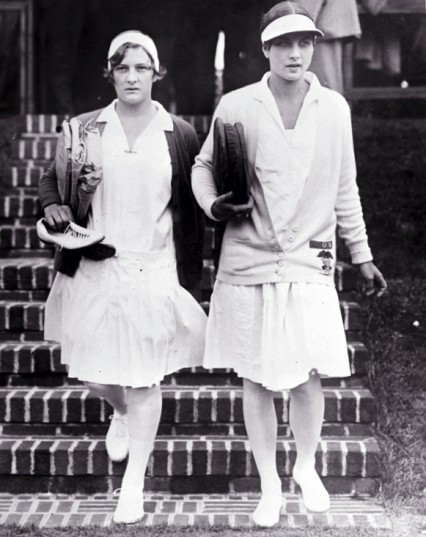
Helen Moody was the top women’s singles tennis player for nearly a decade in the 1920s and 30s, winning Wimbledon eight times, including a match in 1932 against her rival Helen Jacobs. However to sportswriter John Tunis, the women had reached such a level in their play that it had become robotic and tedious to watch. At least James Thurber livened things up with some keen illustrations.

* * *
From Our Advertisers
Sensing that the end of Prohibition was near, the makers of Budweiser reminded readers of the good ol’ days of beer drinking and such…
…if you could afford something better than beer, then you might have contemplated a trip on the SS Manhattan, which along with her sister ship SS Washington were the largest liners ever built in the US…

…if your thing wasn’t traveling to Germany to see that country being transformed into the Third Reich, you could instead become a Bermuda “Commuter”…
…back home, William Steig joined other New Yorker cartoonists who earned extra money off of the big tobacco companies…
…which segues into our cartoonists, beginning with Victor Bobritsky’s illustration for “Goings On About Town”…
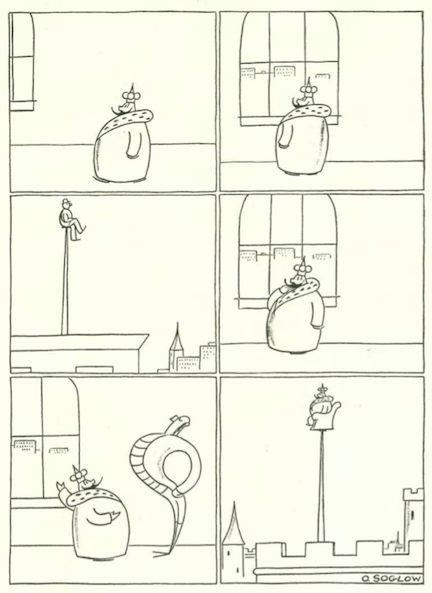
…Otto Soglow offered more Little King adventures…
…and Carl Rose gave us a man striding into a factory, apparently a rare sight in 1932…
…on to July 23…

…and we have another John Mosher film review, in which he refers to Freaks as a “dainty prelude” to another film about the lives of entertainers, in this case George Cukor’s What Price Hollywood, a pre-Code drama starring Constance Bennett and Lowell Sherman with a storyline that anticipated 1937’s A Star Is Born—namely, a famous but fading male star who helps an ingénue rise to stardom while he descends into a pit of alcoholic despair.

* * *
From Our Advertisers
Originally published by Adam Budge, Inc. in 1910 and later by Joseph Judd Publishing and others, Arts & Decoration magazine hoped to stay alive in the Depression with a promise that its August 1932 issue would be “compellingly readable”…
…and here is the cover of that issue…Arts & Decoration would hang on for another ten years before folding in 1942…
…one of the stars of Ziegfeld Follies of 1931 was actress and dancer Patricia “Boots“ Mallory (1913 – 1958), who posed for this portrait to demonstrate the wonders of color reproduction…
…and here’s Boots Mallory in a scene from the 1932 film Handle With Care with comedian Elmer “El” Brendel (standing) and actor James Dunn…
…not everyone could be a movie star, but you could pretend to be one in this swell new (and low-priced) DeSoto…Walter Chrysler must have laid out some big bucks for this two-page color spread…
…for those with greater means you could skip the roads altogether and fly the friendly skies of Ludington Airlines…the airline was founded by wealthy New York socialite Charles Townsend Ludington and his brother Nicholas…
…founded in 1929, Ludington Airlines was the first airline with flights every hour on the hour and the first to carry passengers only (others carried mail, an important source of revenue). The airline offered service between Washington, D.C. and New York City—with stops in Philadelphia, Baltimore, Norfolk, Virginia, Nashville and Knoxville, Tennessee—using seven Stinson tri-motor 6000 aircraft in its fleet, each carrying up to ten passengers…the airline went bankrupt in 1933 (mostly due to the lack of mail revenue) but left behind an astonishing record—in its first two years it flew more than 3.4 million miles and carried 133,000 passengers, a record at the time…

…back to earth, sort of, we have this Lucky Strike ad with the famed “Do You Inhale?” campaign that oozed innuendo and no doubt prompted a few young men to take up the habit posthaste…
…on to cartoons, beginning with this spot art by James Thurber…
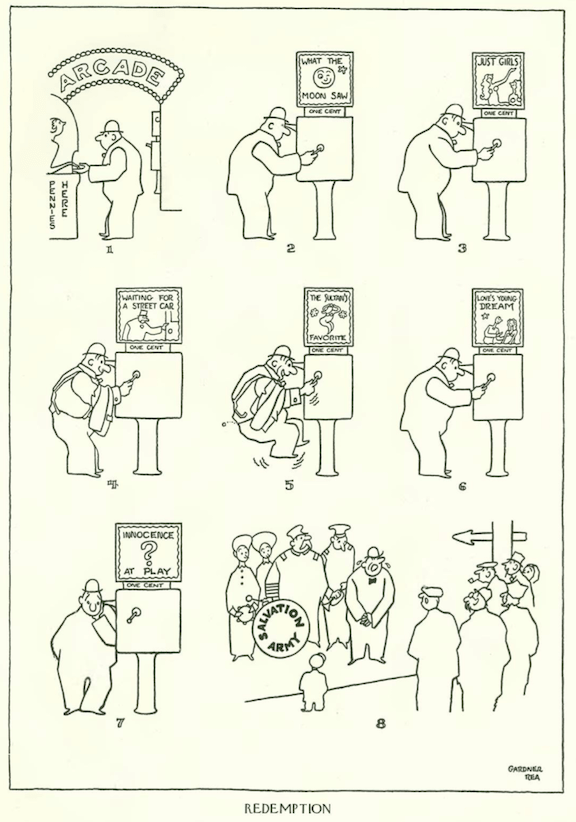
…Gardner Rea showed us a man getting his nickel’s worth of sin and repentence…
…and we end with the delightfully unrepentant Peter Arno…
Next Time: Rebecca and the Zombies…