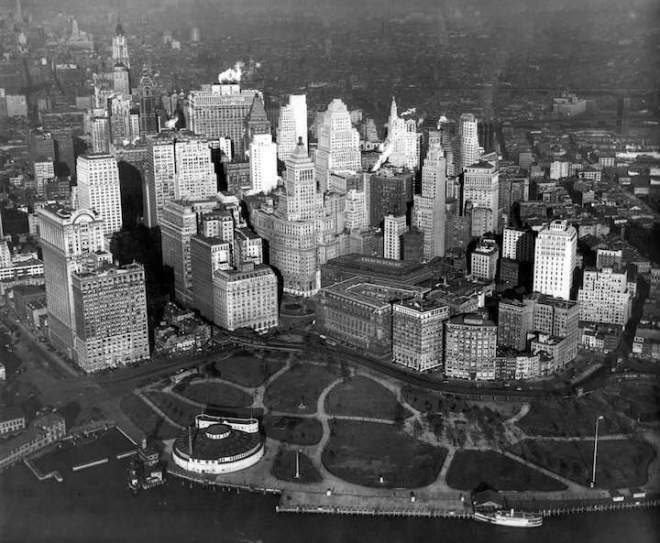
During the Roaring Twenties New Yorkers took a wrecking ball to much of their past, and at a breathtaking pace that left many residents little time to ponder what was lost.

Writer and cultural critic Gilbert Seldes succinctly summed up this spirit of the times in a tongue-in-cheek “reminiscence” of the “old” New York—that is, how the city appeared the previous fall before he left to spend the winter in Bermuda:

A member of the intellectual elite but also a strong advocate for cultural democracy, Seldes began writing for the New Yorker in late 1925 and would be a frequent contributor through 1936. In 1937 he would join CBS as its first director of television programs, and would also become one of television’s first critics thanks to his 1937 Atlantic Monthly article, “The ‘Errors’ of Television.” (Note: There were only 50 experimental TV sets in the New York area in 1937, and the first commercially available sets weren’t sold until 1939). In 1958—when there would be 42 million U.S. households with a television—Seldes would serve as the host of NBC’s The Subject is Jazz.
* * *
Peggy Bacon Did It All
Another early contributor to the New Yorker was Peggy Bacon, who displayed her sharp wit in her nearly 50 articles and poems for the magazine from 1926 to 1950. But Bacon was also well-known for displaying her talent and wit in the many paintings and illustrations she created throughout her long career. The New Yorker’s art critic Murdock Pemberton sang her praises in the March 30, 1929 issue after visiting her show at the Weyhe Gallery.


* * *
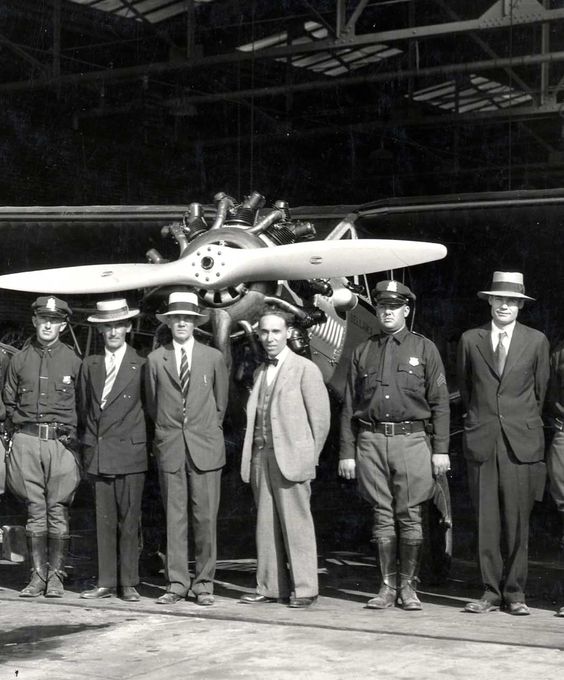
The March 30 profile featured aviation innovator Giuseppe Mario Bellanca, who in 1922 designed the first enclosed-cabin monoplane in the U.S. Perhaps even more significant, his design in 1913 of a plane with a propeller in front, a wing in the middle and tail at the end set the standard for all aircraft built since. (Before 1913 many planes were propelled from the rear, with the “tail” projected in front of the craft). The profile writer, William Weimer (with art by Hugo Gellert) admired Bellanca’s ability to stand toe-to-toe with the mighty du Pont family:
Bellanca founded the Roos-Bellanca Aircraft Company in Omaha in 1927, and was featured on the cover of Time. In 1929 he created the Delaware-based Bellanca Aircraft Corporation of America in a financial partnership with the du Ponts.

* * *
Showing Some Restraint
In his “Sky Line” column, the New Yorker architecture critic George S. Chappell (aka “T-Square”) praised an award-winning 1928 apartment at 3 East 84th Street for its contemporary charm and “fine restraint.” Designed by Raymond Hood and John Mead Howells, the 9-story building was commissioned by Joseph Medill Patterson, owner of the New York Daily News. The design would be influential in Hood’s much more ambitious projects two years later—the Daily News Building (1930) and Rockefeller Center (1931).

* * *
Advertisers in the March 30 issue offered various garments for the gentleman, including this sports-country ensemble at left from Finchley and a custom lounging robe from Macy’s…
…and for fashionable, amusingly mischievous woman there was the new “Scalawag” hat by Knox (ad illustrated by the great Carl Erickson)…
…Blue Moon’s blonde fairy girl was one of the Jazz Age’s most recognizable labels…here she is matched with an Art Deco-inspired spectrum of stocking colors…
…Ligget & Myers Tobacco Company joined the ranks of sophisticated advertisers who touted a product—in this case Fatima cigarettes—without actually showing the product…
…on the other hand, American Tobacco Company, the makers of Lucky Strike, made doubly sure you wouldn’t forget that bright red bullseye, or Rosalie Adele Nelson, “The Original Lucky Poster Girl”…
Nelson’s image for Lucky Strike was almost as ubiquitous as the fairy in the Blue Moon ads. Apparently she was also a member the Nelson family of circus acrobats and performed her own signature act with baby elephants:

Philip Morris took an entirely different (and unusual) approach to selling its relatively new brand of Marlboro cigarettes by touting the achievements of Gretchen Colnik, winner of the “1928 Marlboro Contest for Distinguished Handwriting….”
Like Rosalie Adele Nelson, Gretchen Colnik would go on to minor fame of her own. She was managing editor of the Great Neck, NY, newspaper before returning to her hometown—Milwaukee, Wisconsin. From 1952 to 1966 Gretchen was the Martha Stewart of Milwaukee, hosting a TV show that provided advice on interior design, food and crafts. “The Gretchen Colnik Show” was sponsored by Mrs. Karl’s Bread.
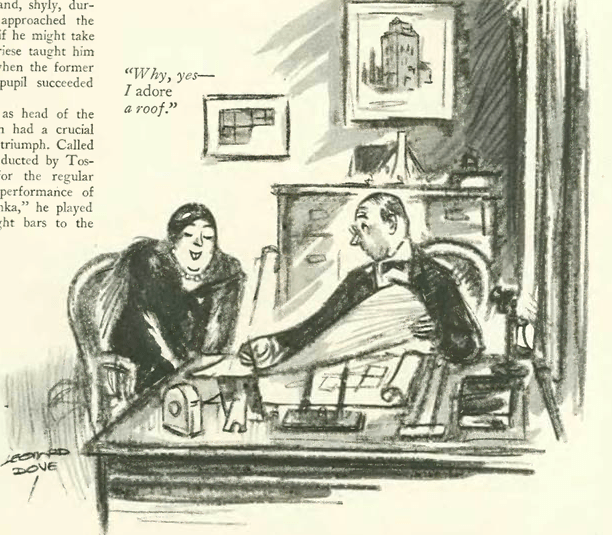
Our cartoon is by Leonard Dove, who looks in on an architect at work:
The Cruelest Month
The film reviews for the April 6, 1929 issue found the New Yorker once again at odds with Hollywood and favoring cinematic products from the Old World.

In the case it was a French film, The Passion of Joan of Arc, which even today is regarded as a cinematic landmark.

The New Yorker review praised the film as “one of the few of the year which merit serious attention”…
On the other hand, there were the latest products from Hollywood, which stood on the other side of a “vast abyss” from the French film:

* * *
From Our Advertisers
The April 6 issue found Charlie Chaplin getting in on the action of Old Gold cigarette endorsements…
…while Curtiss Flying Service thought it might interest some of the more well-heeled New Yorker readers in the purchase of an airplane…
…a couple weeks later, in the April 20 issue, the New Yorker would make this observation about the ad in “The Talk of the Town”…
…and finally, our cartoon by R. Van Buren, looking in on yet another sugar daddy and his much younger companion on a night out…
Next Time: Generation of Vipers…