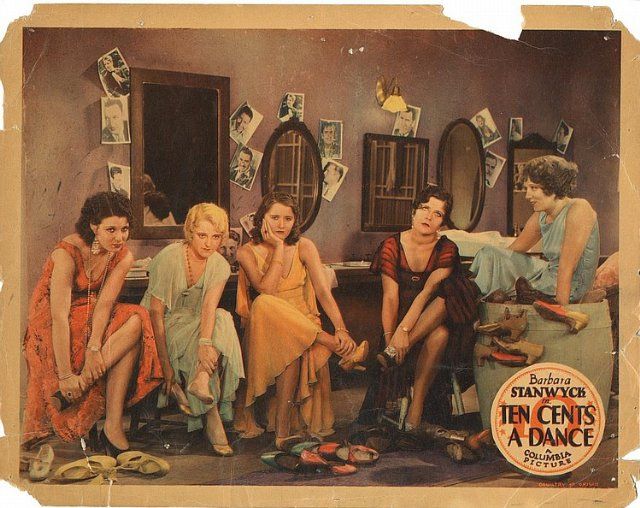As we recently saw in the 1932 film Freaks, there were some truly weird motion pictures produced in Hollywood during the pre-Code era, including four that were reviewed in the July 30 and August 6 editions of The New Yorker.

According to critic John Mosher, some of those films were not intended to be viewed as such, including Rebecca of Sunnybrook Farm (reviewed in the Aug. 6 issue), which Mosher found more gruesome than the Bela Lugosi vehicle White Zombie:


In the July 30 issue Mosher had another encounter with the strange, this time two documentaries that were very much products of their time.
In case a film about the hardships on the Alaskan tundra wasn’t enough to entice moviegoers, Universal Pictures served up this lobby card featuring a topless Nuwuk woman to promote Igloo…

…in a similar vein, husband and wife filmmakers Martin E. and Osa Johnson offered up some topless images to accompany the action promised in Congorilla. It’s a familiar National Geographic-style trope—an over-the-counter magazine or film in the 1930s wouldn’t dare show a European woman topless (there were decency laws after all!) but these folks were “primitive,” and therefore weren’t subject to the Hays Code or other “decency standards.”

The Johnson’s documentary was partly staged, including this scene with “child-like pygmies” that is just plain weird (um, didn’t “modern” jazz have its roots in Africa?):
* * *
Life of the Party
James Thurber penned this unusual July 30 profile, a parody of artistic genius- types who are loved and admired despite also being a drunken assholes. I include the opening paragraph, and the concluding paragraph, which follows a decision by Elliot Vereker’s literary friends to put him on a boat to France; during a farewell party he roundly insults them all.

* * *
From Our Advertisers
William Steig continued illustrating these full-page ads for Old Gold (no surprise that tobacco companies were doing quite well during the Depression)…
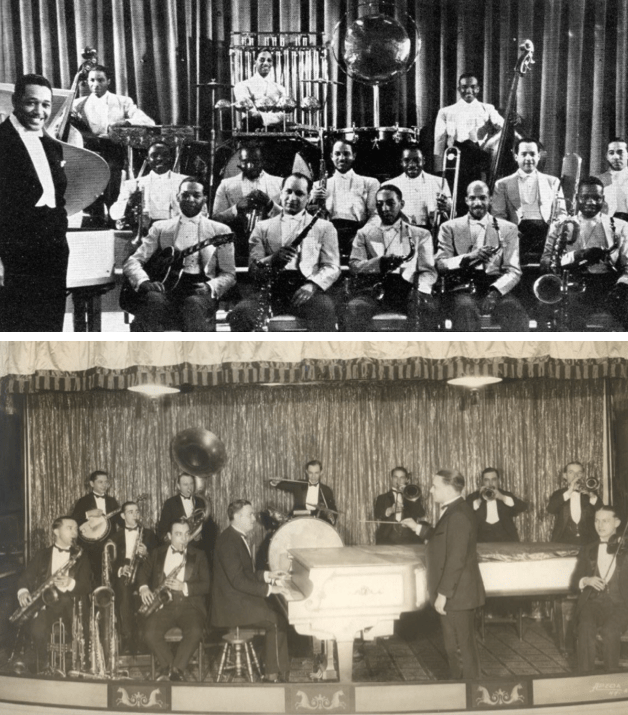
…as we’ve seen, a number of New Yorker cartoonists earned extra money illustrating ads for a variety of companies, but one cartoonist, Peter Arno, also collaborated with artists, playwrights and musicians including Paul Whiteman…no doubt this collaboration was inspired in Arno’s youth, as noted New Yorker cartoonist Michael Maslin explains in this Inkspill entry…
…and we have another in the continuing series of Lucky Strike ads encouraging smokers to inhale its “pure” tobacco, the better to draw in all that addictive nicotine…
…on to our cartoons…William Steig got a clever two-page layout with the caption, “Tell him to put plenty of sauerkraut on it”…
…Carl Rose offered his thoughts on the slate of wishy-washy candidates in the upcoming 1932 elections…
…Helen Hokinson explored the simple ways of rural living…
…Barbara Shermund looked in on the charmed lives of her modern women…
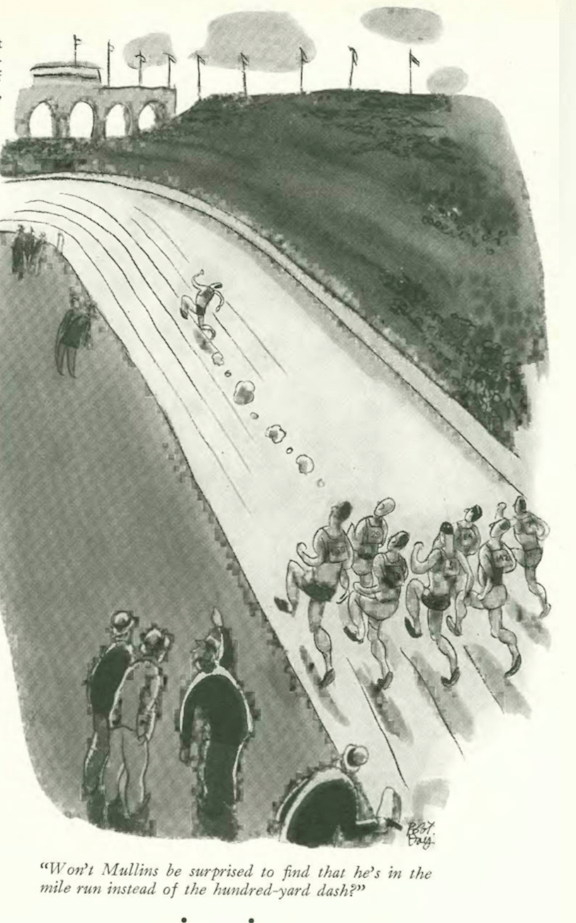
…Robert Day gave us an athlete with a big surprise ahead (and not a happy one…I made this same mistake years ago in a junior high track meet)…
...James Thurber explored the junior edition of his “War Between Men and Women”…
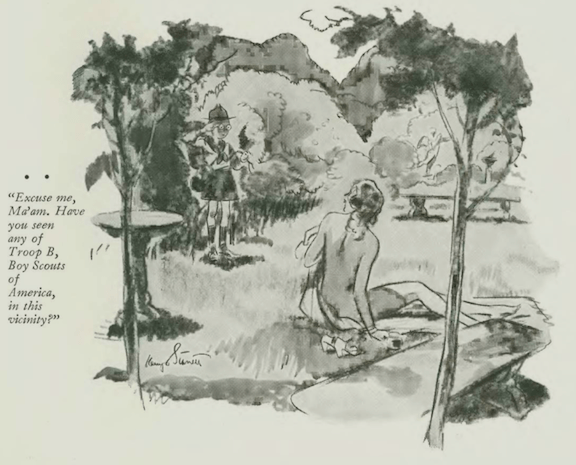
…and Kemp Starrett illustrated a Boy Scout who lost his troop along with some of his innocence…
…and we continue with the Aug. 6 issue, cover artist Constantin Alajalov choosing the 1932 Summer Olympics as his theme:

Alva Johnston penned the first part of a two-part “A Reporter At Large” feature on Knickerbocker Village. Yet to be built when this article was written (construction began in 1933 and was completed in 1934), Knickerbocker Village was the first apartment development in the U.S. to receive federal funding. It came from the Congress-authorized Reconstruction Finance Corporation (RFC), which gave loans to private developers like Fred French for the construction of low-income housing in slum-clearance areas.


* * *
From Our Advertisers
The new Waldorf-Astoria touted its Starlight Roof’s many attractions, including, no doubt, escape from the heat and dust of the city streets…

…I find these Ethyl ads endlessly fascinating, not only for pushing leaded gasoline on the public, but for class-shaming them into using their product…
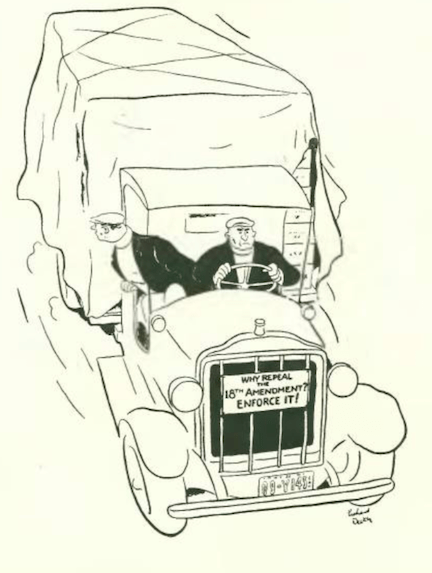
…on to our cartoons, Richard Decker showed how not all Prohibition supporters were teetotalers…
…William Steig gave us one man’s reaction to August weather…
…Barbara Shermund drew a man drawing a line on his place of birth…
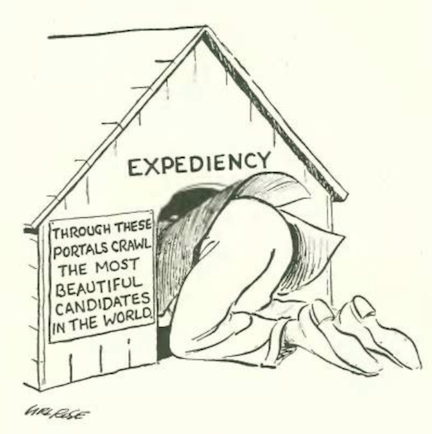
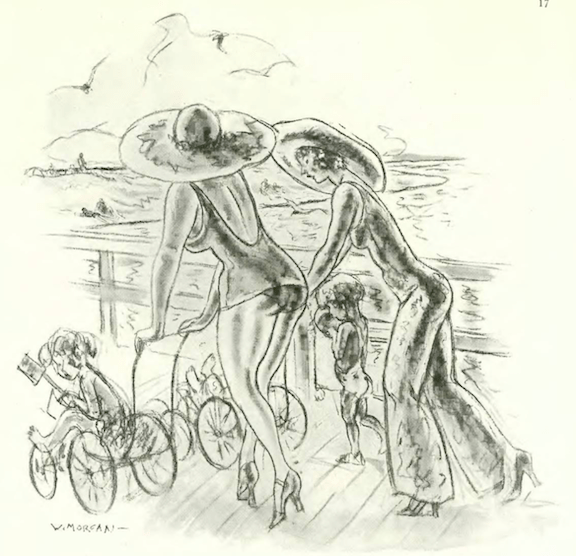
…and we end with a cartoon by Wallace Morgan…there is a joke here related to the attire of the two women, but I am at a loss (any suggestions?)…
Next Time: Silence is Golden…

















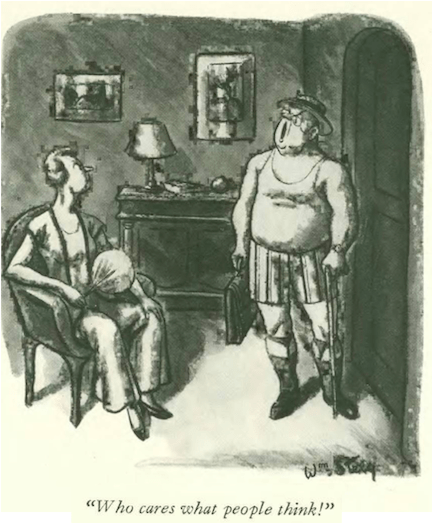






























































































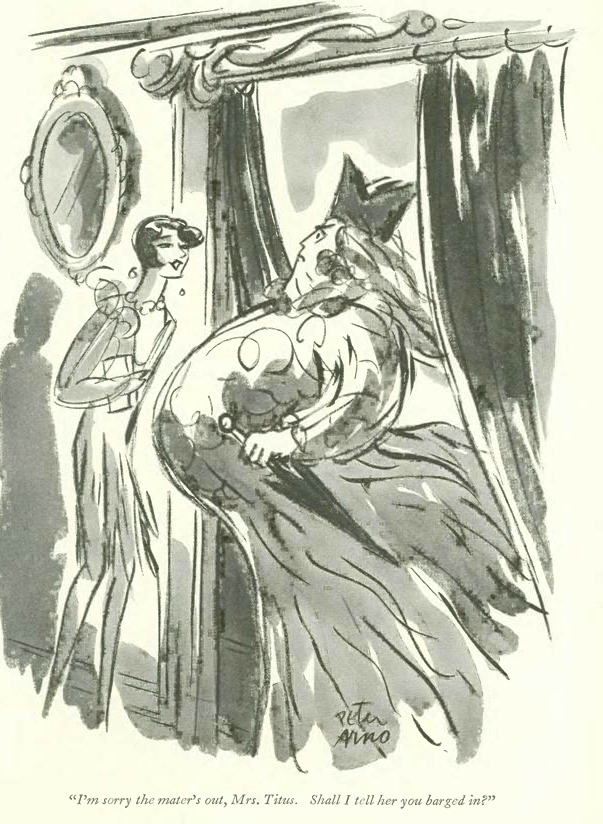











































































































 Why they called the waters “radio-active” escapes me. There were a lot of quack medical cures floating around in the 1920s—some of them quite dangerous—so I’m guessing that the proprietors of Glen Springs were adding radium to the water in some of their treatments, or maybe just claiming that radium was present in the water. Although Marie Curie (a pioneering researcher on radioactivity) and others protested against radiation therapies, a number of corporations and physicians marketed radioactive substances as miracle cure-alls, including radium enema treatments and radium-containing water tonics.
Why they called the waters “radio-active” escapes me. There were a lot of quack medical cures floating around in the 1920s—some of them quite dangerous—so I’m guessing that the proprietors of Glen Springs were adding radium to the water in some of their treatments, or maybe just claiming that radium was present in the water. Although Marie Curie (a pioneering researcher on radioactivity) and others protested against radiation therapies, a number of corporations and physicians marketed radioactive substances as miracle cure-alls, including radium enema treatments and radium-containing water tonics.