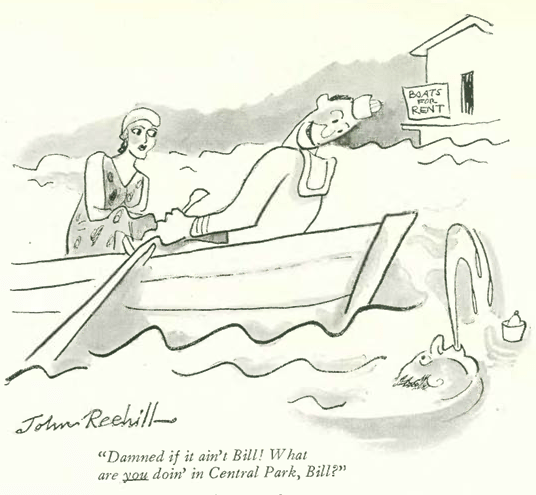
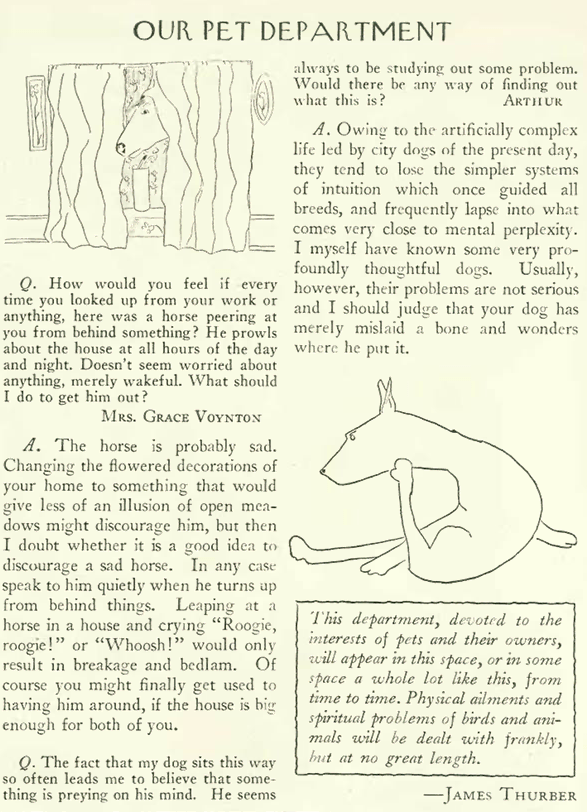
The Irish American gangster Jack “Legs” Diamond was often referred to as the “clay pigeon of the underworld” due to surviving several attempts on his life.

In his “Reporter at Large” column, Morris Markey checked up on the fleet-footed bootlegger, adored by the public for his various brushes with the law and escapes from sure death. In his opening paragraph, Markey referred to one of the attempts on Diamond’s life: On October 12, 1930, he survived being shot five times at Manhattan’s Hotel Monticello:
 Markey’s column attempted to remove some of the glamour from Diamond’s flamboyant life, a life that would be cut short about a year later in an Albany rooming house…
Markey’s column attempted to remove some of the glamour from Diamond’s flamboyant life, a life that would be cut short about a year later in an Albany rooming house…



An afternote: Enemies would finally catch up to Legs Diamond and kill him on Dec. 18, 1931. Diamond’s wife, Alice Kenny Diamond, would be shot and killed less than two years later. Diamond’s mistress and former Ziegfeld Follies performer Marion “Kiki” Roberts would return to the stage and cash in on her notoriety. In 1937 it was reported she was the big draw in a touring “Crazy Quilt” burlesque revue. And according to the writer William Kennedy, who wrote about Diamond in his 1975 novel Legs, the last record of Kiki Roberts was in Boston in the 1940s, where “she was still appearing as ‘Jack (Legs) Diamond’s Lovely Light o’ Love.’ ”
Here is newsreel footage of Diamond’s mistress Marion “Kiki” Roberts, shortly after the gangster’s death. In this brief interview with a Boston reporter (and with her mother at her side) Roberts advises girls to “live good clean lives and obey their parents wishes.” Note how it appears she is reading from cue cards.
* * *
Chitty Chitty Bang Bang
A precursor to the helicopter, the autogyro was considered by many to be the next logical step in aircraft development, and especially in the development of smaller craft that could serve as safe, affordable transportation options for commuters. The New Yorker’s E.B. White, an aviation enthusiast, demonstrated to readers the wonders of this aircraft:

* * *
Baker’s Big Show
Nineteen-year-old American-born French entertainer Josephine Baker became an instant symbol of Jazz Age Paris when she starred in La Revue Nègre in October 1925. Her erotic dance routines wowed Paris audiences, and she quickly moved on to the famed Folies Bergère. In 1930 she opened a new show at the Casino de Paris that also featured her pet cheetah, Chiquita. The New Yorker’s Janet Flanner was there to take it all in:


* * *
Grim Reminder
Despite the deepening Depression across the country, few mentions of it were made in the pages of The New Yorker. Howard Brubaker, in his “Of All Things” column, offered this not-so-gentle reminder:
* * *
From Our Advertisers
We feature Gloria Morgan Vanderbilt, a Swiss-born American socialite shilling for Pond’s cold cream. At the time of this ad she was the mother of six-year-old Gloria Vanderbilt (who would become a famous fashion designer and artist and the mother of CNN’s Anderson Cooper)…

…the makers of Ybry lipstick apparently did not have the budget to garner a patrician endorsement, so they settled for this illustration by New Yorker cartoonist Barney Tobey…
…and we have another lovely color ad from R.J. Reynolds, once again linking cigarettes to athletic prowess…
…on to our cartoons, we mark election season with Carl Rose…
…Barbara Shermund explored the generation gap…
…Peter Arno gathered his sugar daddies for a game of chess…
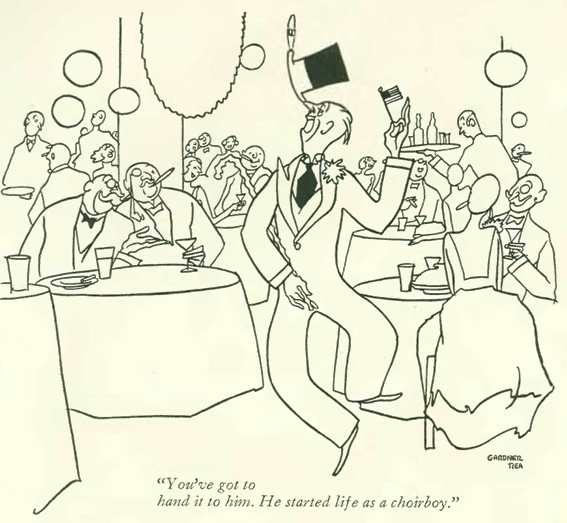
…Kemp Starrett introduced us to an unlikely life of the party…
…Alan Dunn examined the influences of popular cinema…
…Mary Petty gave us an Ivy League perspective of the Great Depression…
…and Arno again, with a cartoon that was featured along with The New Yorker’s “Wayward Press” column…
Next Time: Body and Soul…