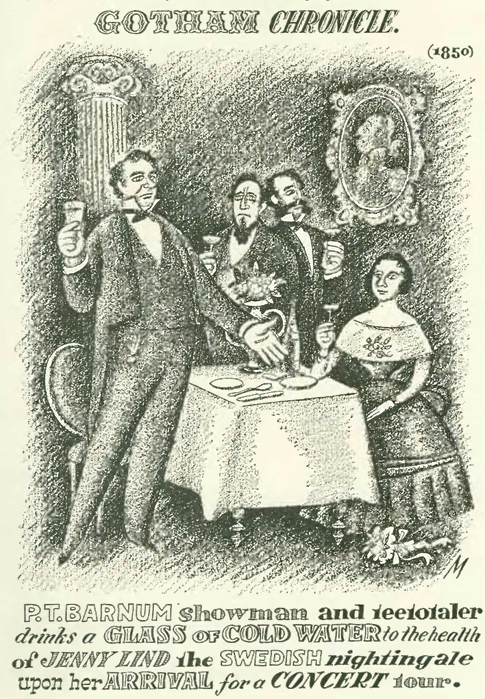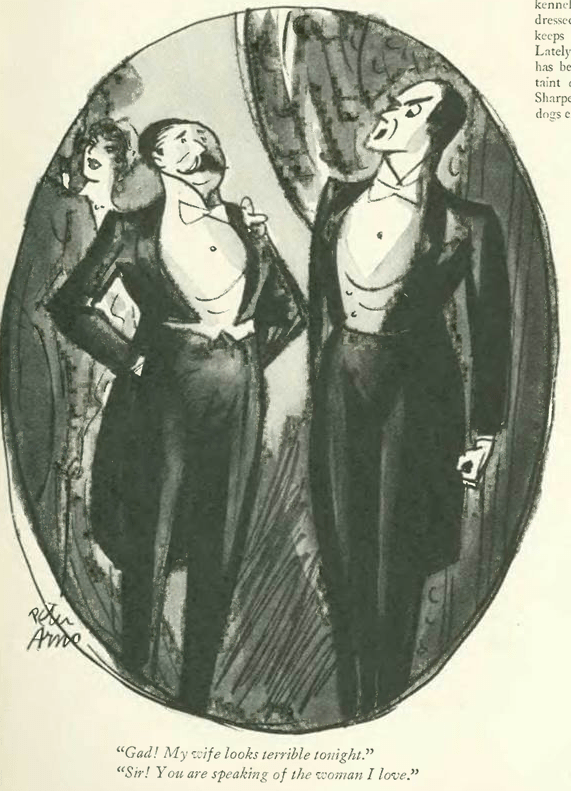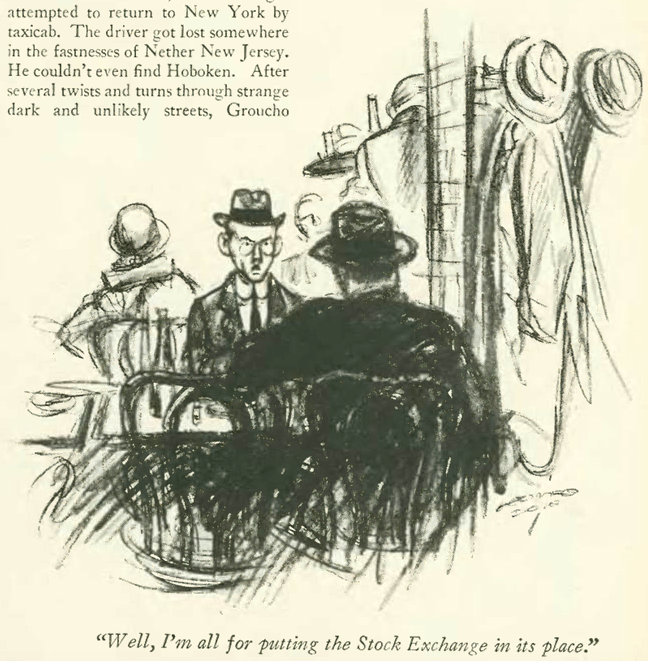The New Yorker offices at 25 West 45th Street were a long walk from Wall Street, but the panic that gripped the city beginning on Oct. 24 spread quickly through the borough. What the panic was about, however, wasn’t exactly clear.

There was fear in the air, and a hint of doom, when E.B. White submitted his “Notes and Comment” section for the Nov. 2 issue. Having filed his column sometime between October 24 (“Black Thursday”) and October 29, 1929 (“Black Tuesday”), he weighed the mood of his city against the reassurances offered by politicians, bankers and pundits…

…and expressed schadenfreude over “a fat land quivering in paunchy fright” and some satisfaction in confirming his suspicions that “our wise and talky friends” on Wall Street really didn’t know what they were talking about:

It seems White might have believed the worst was over, and that Wall Street would get back to its gambling spirit…

In “The Talk of Town” we find the first use of the word “Depression” in The New Yorker as it is related to the economic collapse…

* * *
Mr. Blue Sky
On the subject of stocks, “Talk” also featured this mini profile (written by Robert Coates) of Roland Mulville Smythe (1855-1930), who specialized in buying and selling old and obsolete stocks. Nicknamed “No Telephone” Smythe for his dislike of the device, he began his trade in obsolete securities and banknotes sometime around 1880…

Coates told the story of a Yonkers doctor who used what he thought were worthless stock certificates (from an abandoned coal mine) to paper the walls of his study. Thanks to Smythe’s meticulous record-keeping, when a new lode was discovered at the mine, the doctor learned his wallpaper was worth $14,000 (equivalent to about $200,000 today)…
* * *
Rise of the Machine
Ironically, the National Business Show was staging a big exhibition in Midtown while the economy was collapsing Downtown. James Thurber was on hand at the Grand Central Palace to take in the wonders of the machine age…

…Thurber seemed as impressed by the machines as by the “very prettiest girls” who were on hand to demonstrate them…


* * *
What a Strange Trip It’s Been
This brief “Talk” entry by Alfred Richman related a story from a traveling salesman just returned from Moscow. Among the highlights of his visit was a Soviet movie that “featured” America’s Sweetheart, Mary Pickford, in the title role…
In the 1920s, silent film stars Mary Pickford and Douglas Fairbanks were perhaps the most famous couple in the world. That included in the Soviet Union, where moviegoers preferred American films over their own avant-garde fare (while on the other hand, the New Yorker found Soviet films to be far more advanced than Hollywood’s). While vacationing in Moscow in 1926, Pickford and Fairbanks visited a Russian film studio with director Sergei Komarov, who cleverly captured enough footage of the two to weave them into a silent comedy titled A Kiss from Mary Pickford (Potseluy Meri Pikford). The film was a spoof on Hollywood fame, finding humor in a loveless man’s chance meeting (and kiss) with Mary Pickford, and his sudden and unexpected attractiveness to the opposite sex.

* * *
Fire and Ice
Back stateside, New Yorker film critic John Mosher took in the talking film debut of the hugely popular stage actress Lenore Ulric (1892-1970). Known on Broadway for her portrayals of fiery women, she tried, it seems unsuccessfully, to bring some of that heat to Frozen Justice, which was set in Alaska during the Klondike Gold Rush…

* * *
Right Ho, Plummie (CORRECTION: Not So, Plummie)
…thankfully, an alert reader kindly pointed out that “Ode to Peter Stuyvesant” isn’t by Wodehouse, but by another person with the initials P.G.W. — Philip G. Wylie.

* * *
From Our Advertisers
We begin with the back pages, where toaster wars were being waged by the makers of the “Toastmaster” and Thomas Edison’s “Automaticrat”…
…for some in the posh set, the days of fine dining at places like Maillard’s (with this all-French ad) would be coming to an end thanks to the market crash…actually, Maillard’s itself would come to an end in the 1930s, thanks to the Depression…
…stage, film (and later television) actress and dancer Queenie Smith was the latest celeb to tout the wonders of Lux Toilet Soap…

…here’s an unusual way to sell shock absorbers…I’m wondering if this is supposed to be a sugar daddy and a chorus girl trying to make hay in the back seat of a car without Houdaille shocks…
…a couple more ads from the back pages, the ones on the left appeal to women’s fitness, while the ad on the right tries its best to push a product that was fast going the way of the horse and buggy. Spats — devised in the late 19th century to protect one’s shoes and socks (then called stockings) — went out of fashion in the 1930s, no doubt because most streets were now paved and you didn’t have to worry about a passing wagon splashing mud and horseshit all over your shoes and ankles…
…and indeed, now you could have Goodrich Zippers, in smart new colors…
…and speaking of colors, a couple of richly toned ads for Arrow Shirts…
…and Camel cigarettes…
…on to our illustrators and cartoonists…spot drawings — sprinkled throughout the magazine — were often a foot in the door for aspiring contributors (Peter Arno and Charles Addams are just two examples). Below is a collection of spot drawings from the Nov. 2 issue, mostly from established artists including Barbara Shermund, Alice Harvey, Julian De Miskey, Gardner Rea, Johan Bull and I. Klein. The New Yorker also recycled old cartoons for spots, including the illustration below (third row, second one down) by Shermund of the young woman on telephone, which originally appeared in the July 16, 1927 issue with the caption, “Hold the line a minute, dear—I’m trying to think what I have on my mind.”
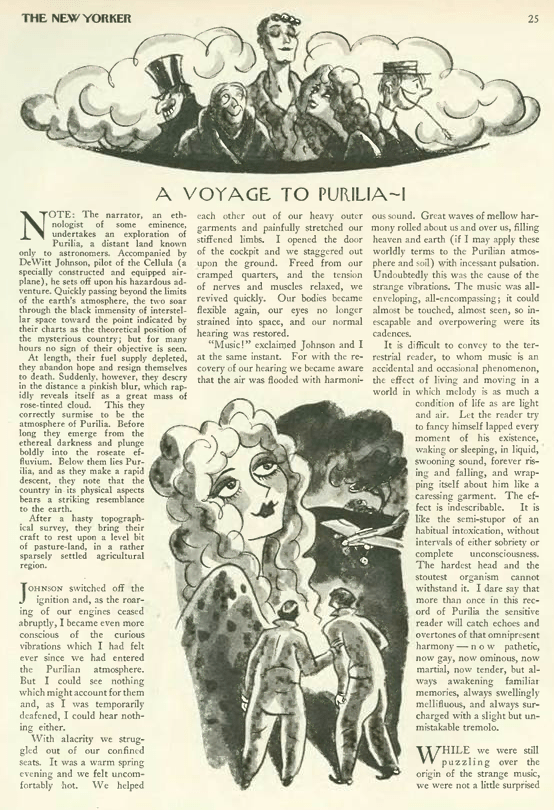
…Arno continued to provide illustrations for Elmer Rice’s serialized novel, A Voyage to Purilia…
…and Julian De Miskey illustrated G. Marston’s entry for the ongoing “That Was New York” column…
…our cartoons come from Barbara Shermund…
…Gardner Rea, having a political moment…
…for reference, a photo of Mayor Jimmy Walker…

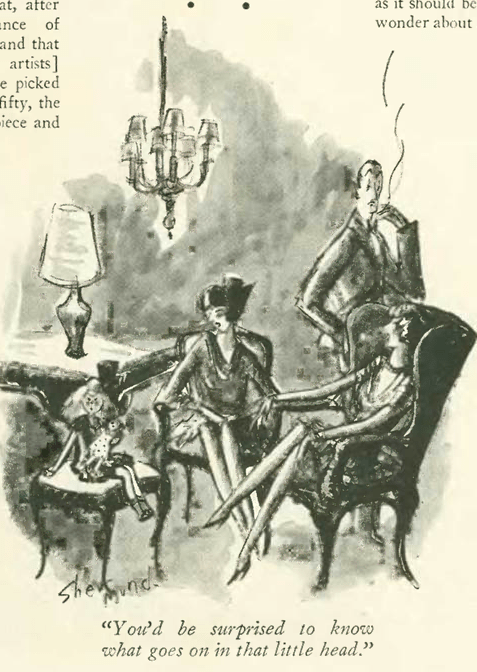
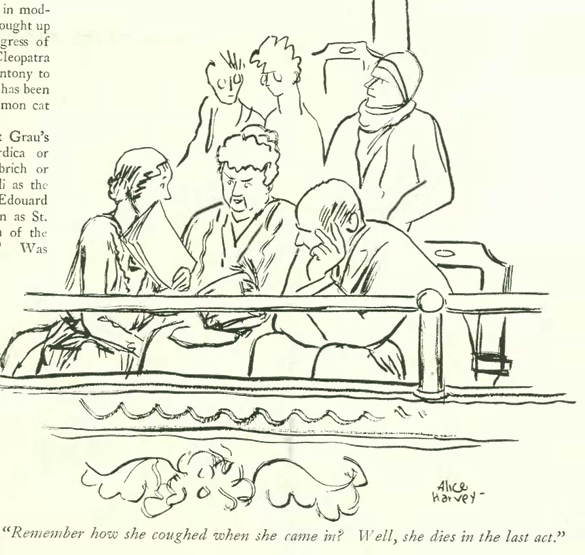
…Shermund again, on the joys of parenthood…
…Peter Arno’s take on Jazz Age chivalry…
…and perhaps the timeliest entry of all, from Leonard Dove…
Next Time: Not Much to Cheer About…