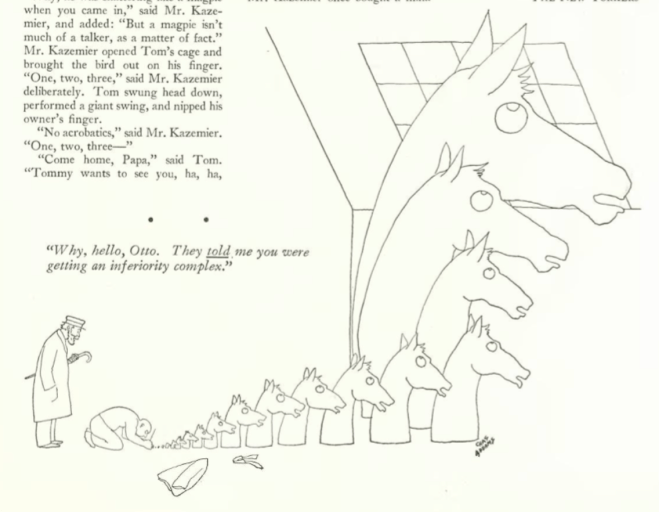
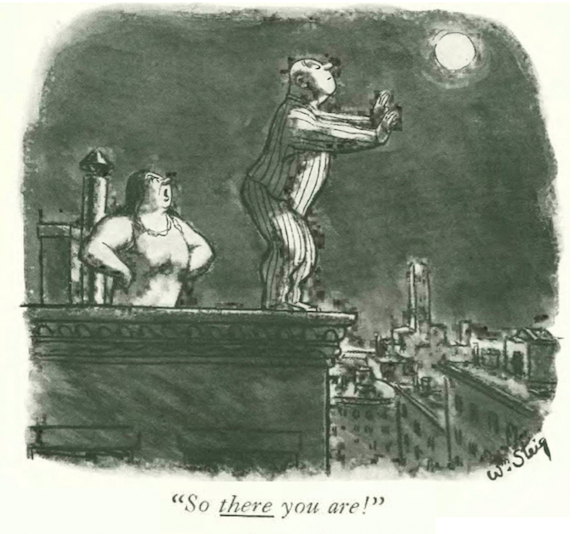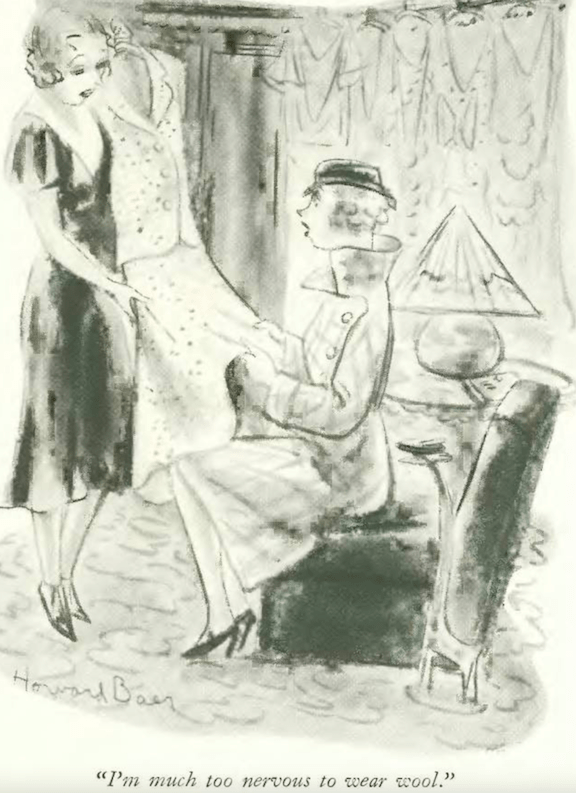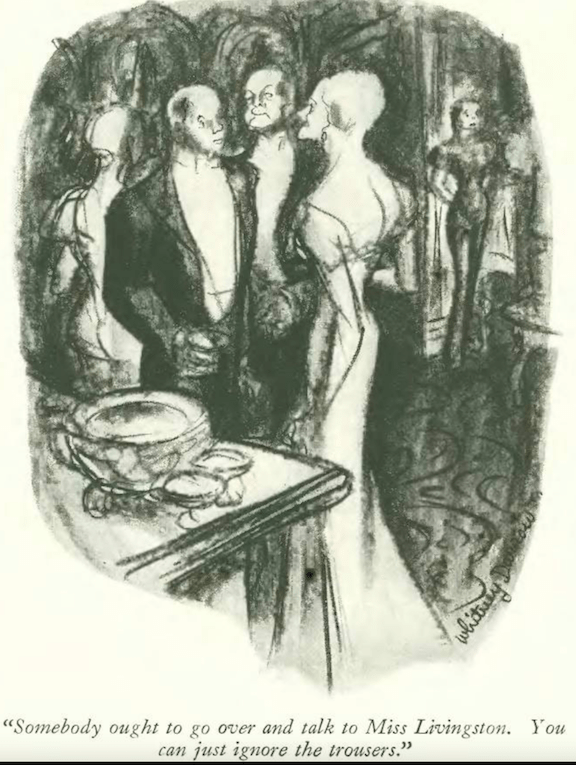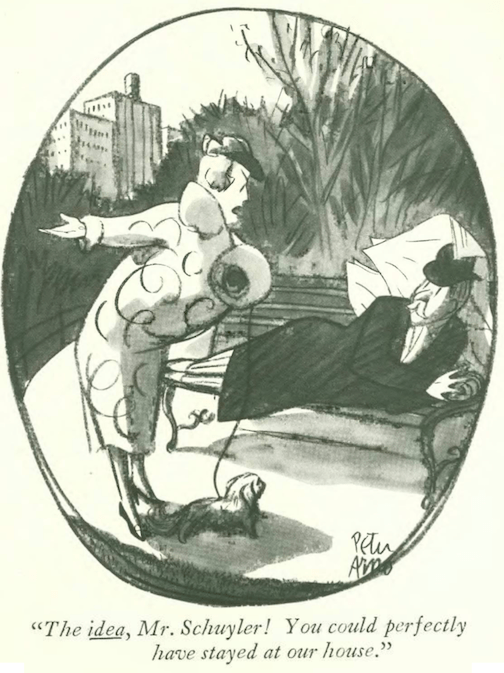James Thurber was well established as a New Yorker writer and cartoonist by 1933, but his fame would grow with the publication of the autobiographical My Life and Hard Times, serialized in The New Yorker beginning with the July 8 issue.

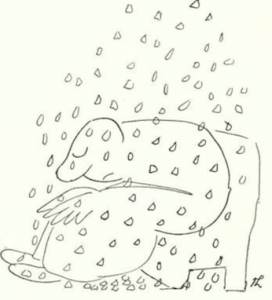
And what a beginning. “The Night the Bed Fell In” recounts the comically absurd events that took place in the wee hours at the Thurber family home in Columbus, Ohio. Beginning with his father’s decision to sleep in the attic, the story introduces a cast of characters including cousin Briggs Beall and his mother, Clarissa. Excerpts:
Briggs’ mother also had fears of impeding calamity…

Need more Thurber? Longtime New Yorker cartoonist and author Michael Maslin recounts a 1986 pilgrimage to the Thurber house in this Ink Spill entry from 2018. You should also check out Maslin’s regular Thurber Thursday feature for more insights into the world of this beloved humorist.
* * *
The Naked Truth
Once upon a time a Baptist and a Presbyterian got together and created a magazine promoting nudism. The Baptist, Ilsley Silias Boone (1879–1968), was founding father of the American Sunbathing Association—later reorganized as the American Association for Nude Recreation. His ally in advancing the cause of nudism, Presbyterian minister Henry Strong Huntington Jr (1882-1981), was the first president of the International Nudist Conference. “The Talk of the Town” laid bare the world of these randy clergymen.

* * *
His Kind of Town
In his “Shouts & Murmurs” column, Alexander Woollcott recounted his trip to Chicago, ostensibly to see the Century of Progress (the 1933 World’s Fair) but was sidelined along the way by various diversions, including a visit with poet Edna St. Vincent Millay. An excerpt:

* * *
From Our Advertisers
Prohibition wouldn’t be officially repealed until Dec. 5, 1933, but that didn’t stop New Yorkers from enjoying their favorite adult beverage, including this pair. What on earth is that man on the left doing? It appears he’s opening a bottle of White Rock (glimpsed between his legs), but why with his back turned?…
…the folks at Packard were consistent in promoting the durability and longevity of their premium automobiles…
…and it’s no coincidence that the makers of Goodyear tires featured a 1933 Packard to tout the durability of their product…
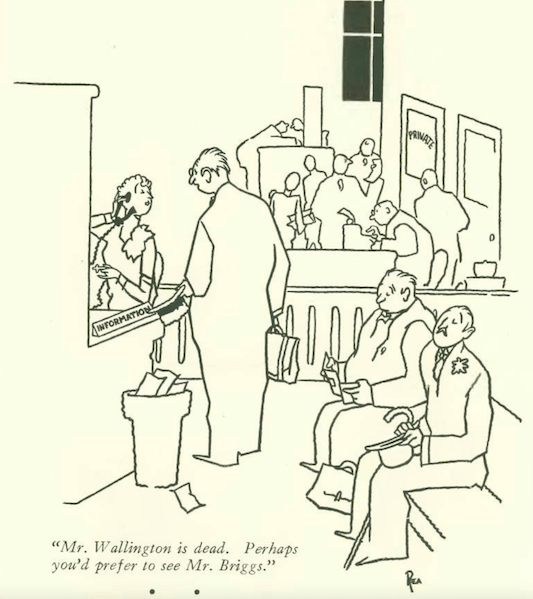
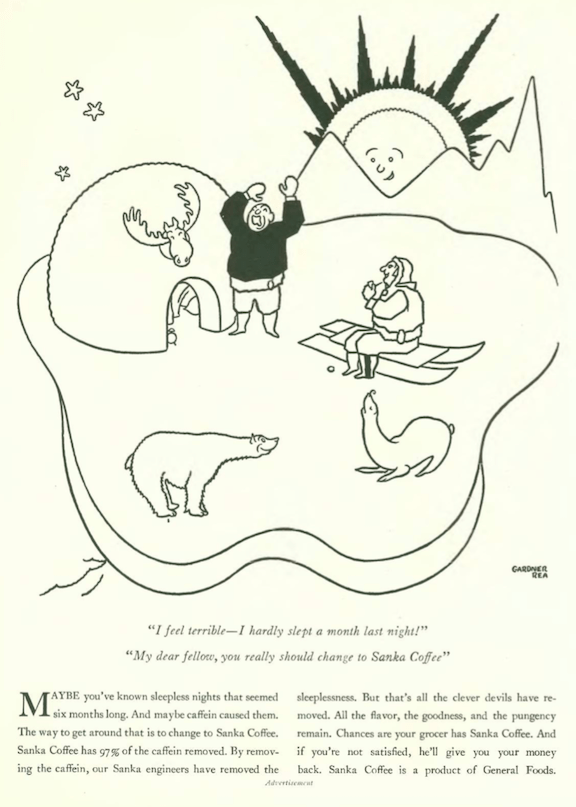
…speaking of durability, the ever-reliable Gardner Rea kicks off our cartoons…
…Mary Petty eavesdropped on the latest social event…
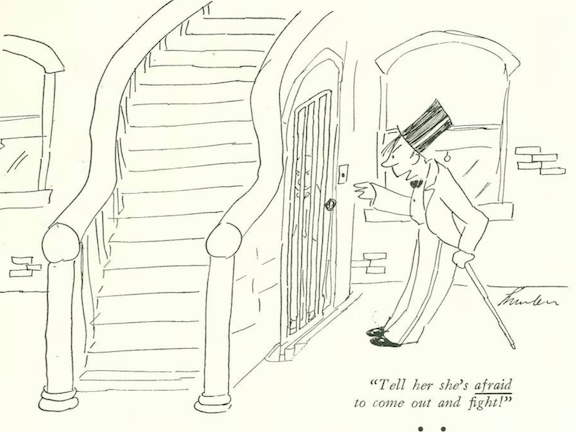
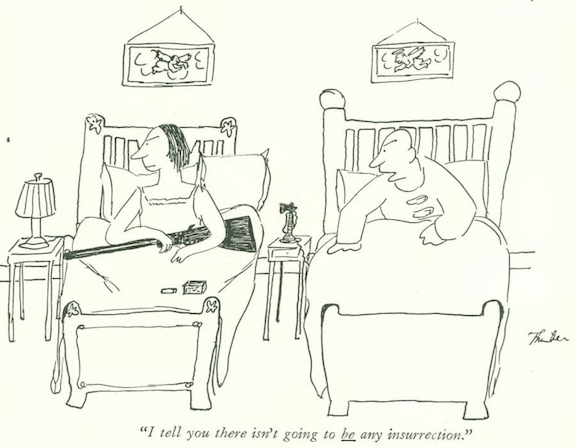
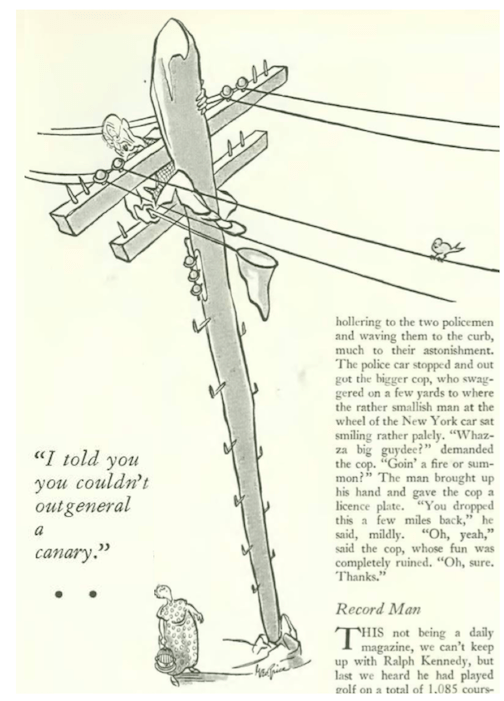
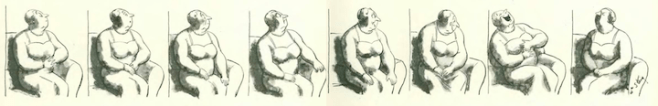
…the battle of the sexes continued in James Thurber’s world…
…Barbara Shermund shared the lamentations of a modern woman…
…and Garrett Price, likely inspired by a recent trip abroad, gave us this homesick tourist…
…and the cover of the July 15, 1933 issue…

…in which Thurber continued his tales from My Life and Hard Times with “The Car We Had to Push”…also in the issue was a profile of “Bolshevik Businessman” Peter Bogdanov, written by foreign correspondent William C. White. An excerpt:
From 1930 to 1934 Bogdanov (1882–1939) headed the Amtorg Corporation, which helped the struggling Soviet economy establish valuable business and diplomatic relations with the United States. It is no surprise that like many who helped the Soviet cause, Bogdanov was eventually arrested on trumped-up charges and executed by Stalin’s henchmen. In March 1956 he was posthumously “rehabilitated.”

* * *
On the Lighter Side
While millions in the Soviet Union were dying of famine and other Stalin-inspired atrocities, Americans were keeping their Depression-era spirits up at the movies, including critic John Mosher, who called the latest Mickey Mouse cartoon “a beautiful thing”…

* * *
More From Our Advertisers
I once had a relative in New Jersey who drank a tall can of Schaefers every day, on orders from his doctor…
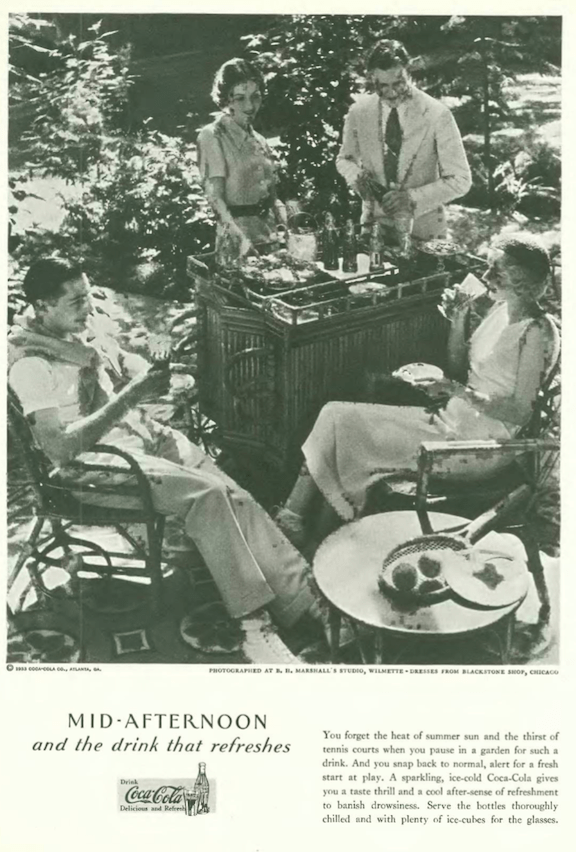
…the makers of Coca-Cola continued to tout their product in full-page New Yorker ads…
…recalling the Packard ad from the previous issue, the cheapest Packard model would set you back $2,150…you could instead get this swell Plymouth Six for just $455 and head down to the waterfront, where, according to this salesman, “men are men”…
…and while on the waterfront you might be able to bum a smoke and maybe some caviar from a sailor named Hugh…
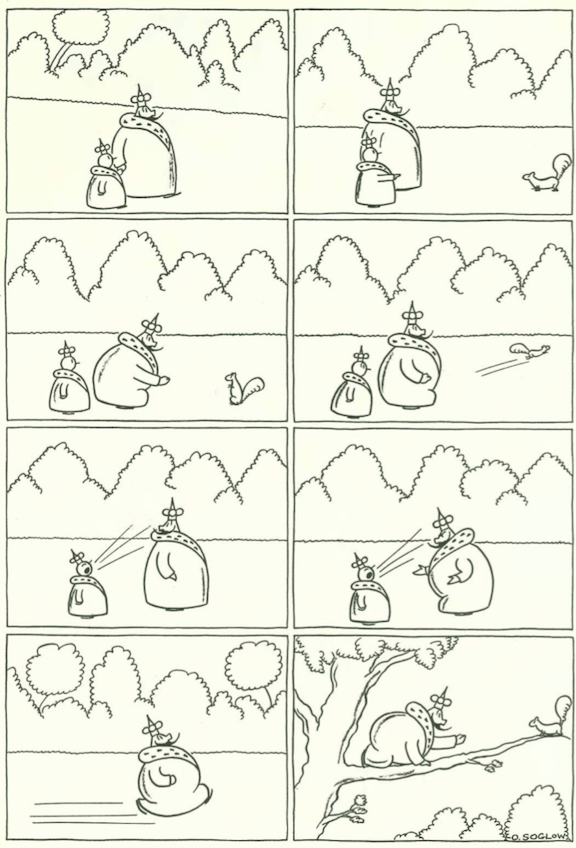
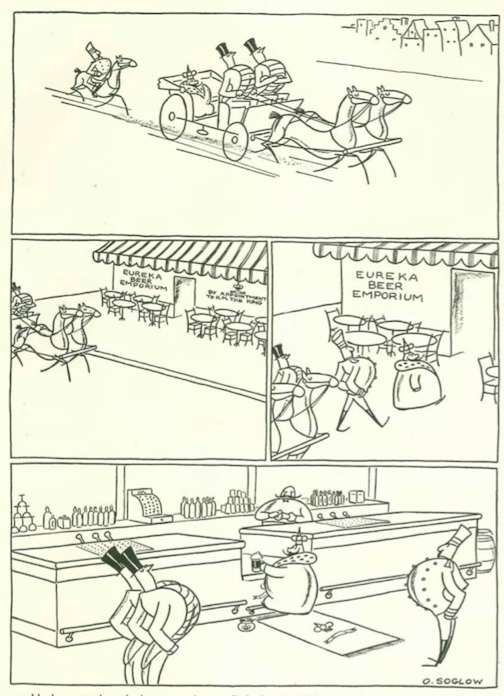
…and now we take a stroll in the park with Otto Soglow’s “Little King”…
…and find romance along with other hot dishes at the automat, courtesy Whitney Darrow Jr…
…adrift with Carl Rose, and a man unlucky in love…
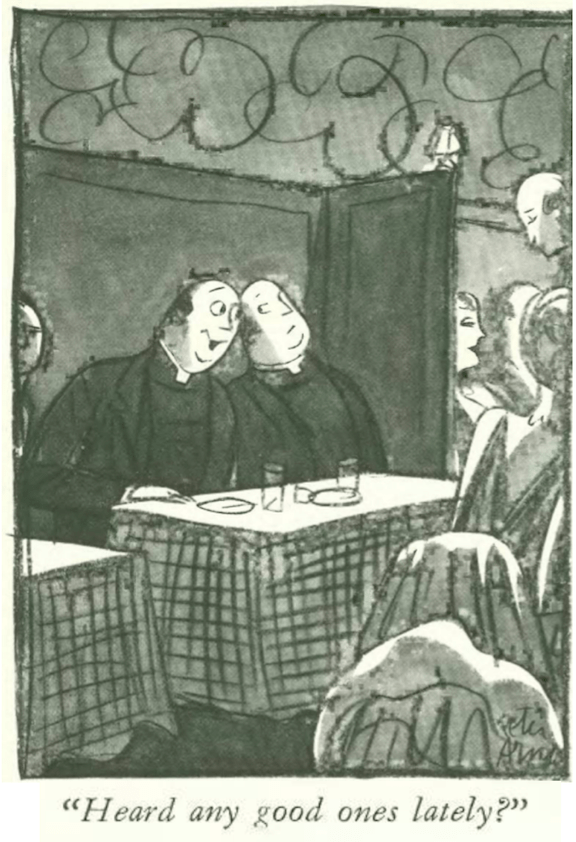
…Peter Arno played hide and seek with an escaped con…
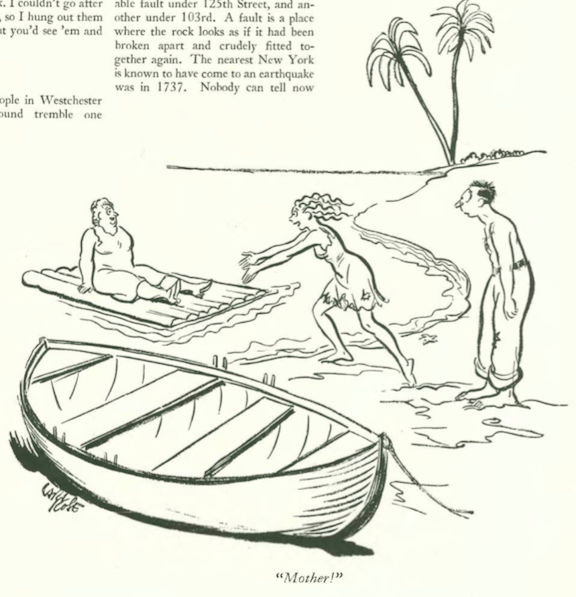
…and we end where we began, with James Thurber at his best…
Next Time: She Wore the Pants…