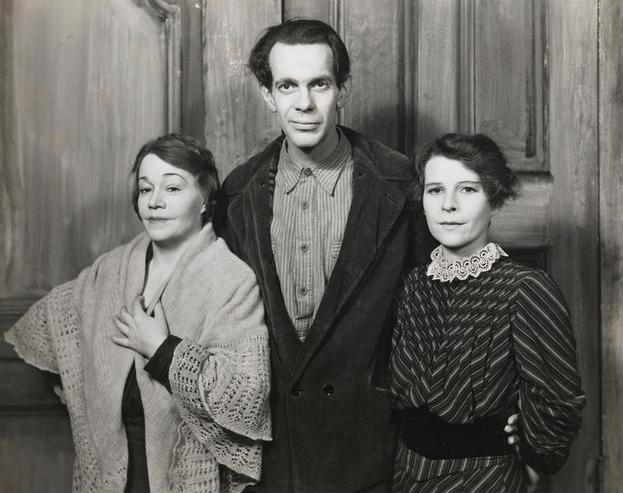
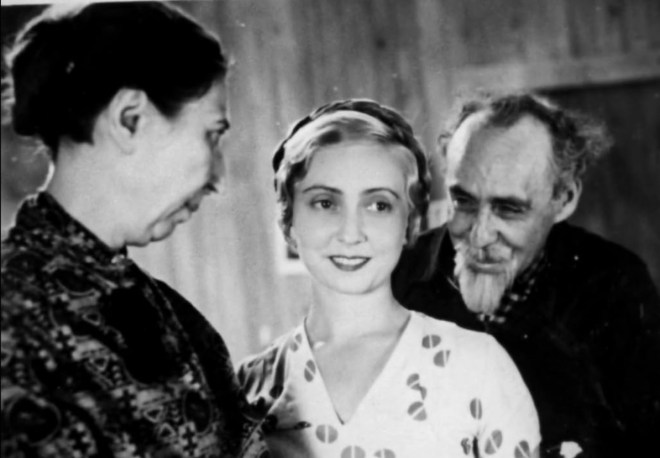
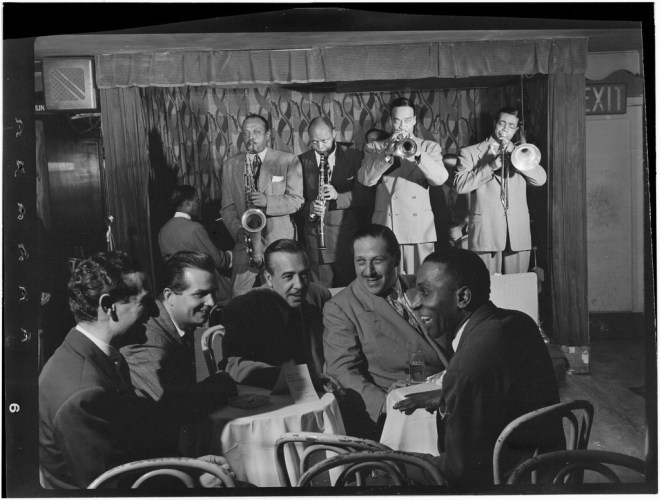
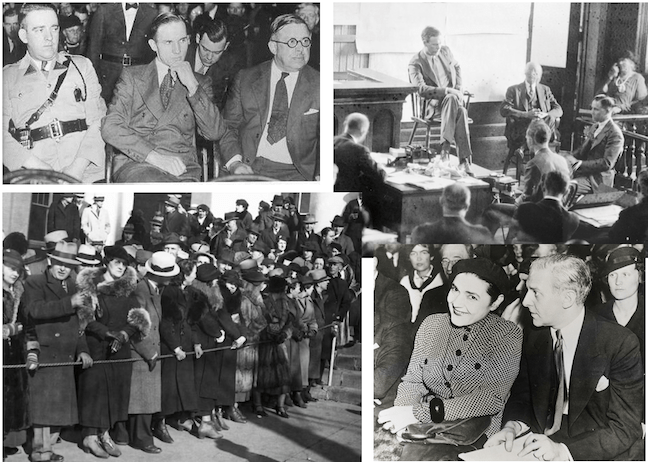
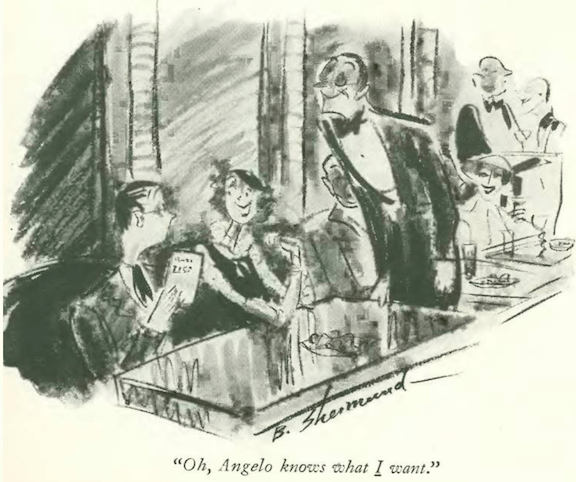Above: The 1936 Ziegfeld Follies premiered on Broadway at the Winter Garden Theatre on January 30, 1936 and closed on May 9, 1936 after 115 performances. (Hulton Archive)
Broadway impresario Florenz Ziegfeld Jr died in 1932, but his famous theatrical revue lived on for years with revivals including one in 1936 that Robert Benchley praised for being better than the originals.

Now on with the show. Brought back to life by Ziegfeld’s widow Billie Burke and theatre operators Lee and J. J. Shubert, The Ziegfeld Follies of 1936 was loaded with talent, with lyrics by Ira Gershwin, choreography by George Balanchine, and sets and costumes by Vincente Minnelli. What really brought people in was the star of the show, Fannie Brice, who was supported by cast members Bob Hope, Eve Arden, Josephine Baker, and the Nicholas Brothers, among others. Benchley wrote:
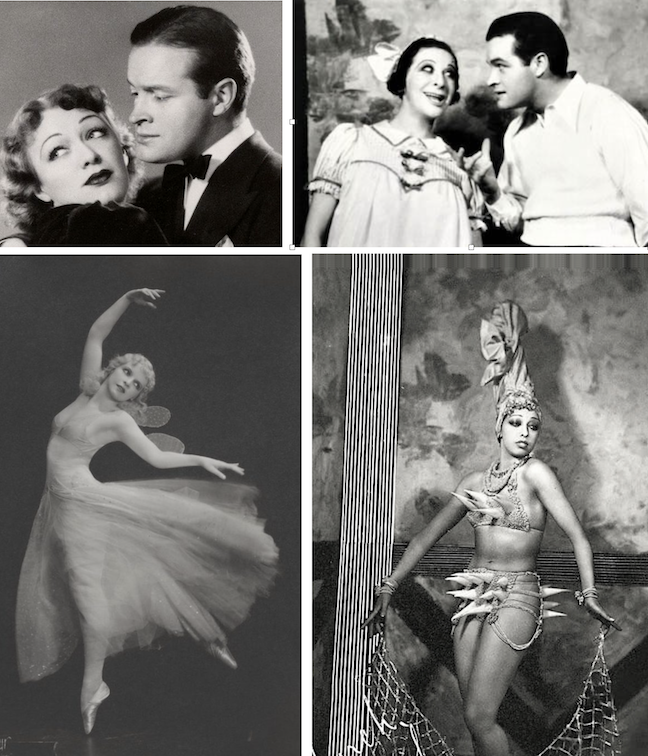

This ad for the 1936 Follies prominently featured Benchley’s endorsement:

Billie Burke (1884–1970) authorized Follies revivals with the Shuberts in 1934, 1936 and 1943, with the Shubert family producing a final revival in 1957. In 1936 MGM also filmed a Ziegfeld biopic, The Great Ziegfeld (which won two Academy Awards), casting William Powell as Ziegfeld and Myrna Loy as Burke. Burke wanted to play herself in the film, but at age 51 she was deemed too old for the part.

Fannie Brice (1891–1951) was the biggest star of the Follies and so dominated the show that when she became ill in May 1936 the production closed. Brice returned to the Winter Garden that September for 112 more performances.
Benchley also praised Call it a Day, a 1935 play by British writer Dodie Smith that ran for 194 performances at the Morosco Theatre. Benchley thought it was so good he saw it twice.

* * *
At the Movies
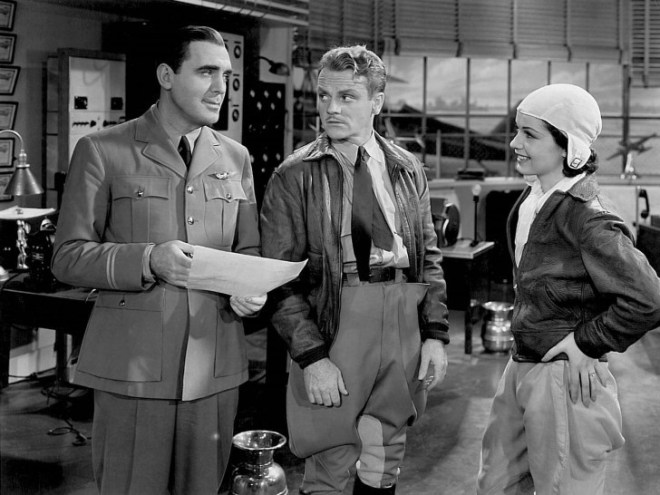
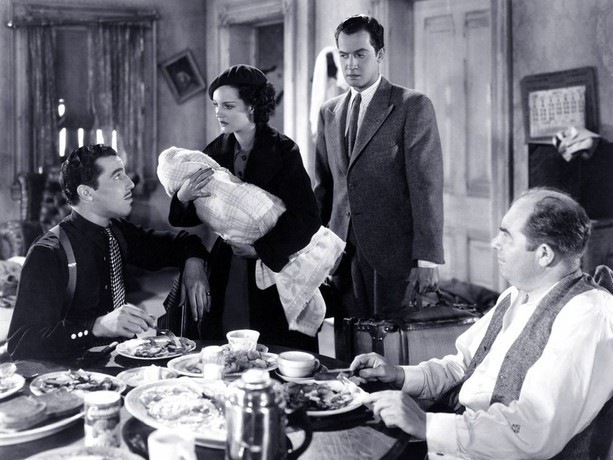
We go from the stage to the screen, where John Mosher took in Rose Marie, a musical comedy based on a popular 1924 Broadway play. The film “repolished” the old play and used it as a framework for a series of duets between Jeanette MacDonald and Nelson Eddy.

Mosher reviewed three other films that could have used some of Rose Marie’s cheer:

* * *
Miscellany
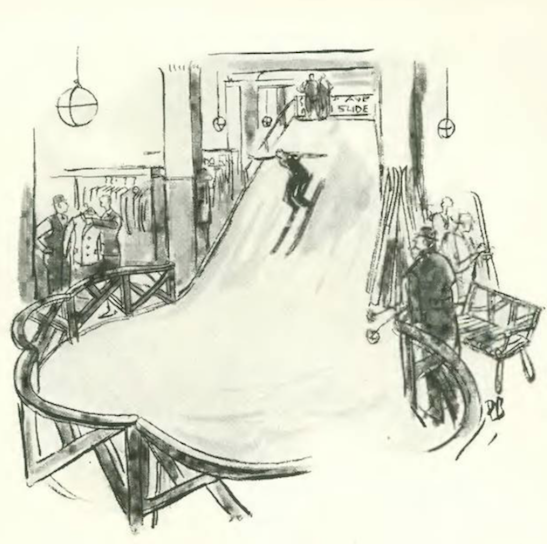
I strive to keep these posts at a readable length, and (hopefully) lively and enjoyable to read, which means that I cannot include absolutely everything that appears in each issue. For example, there are a number of regular features from the sports world—ranging from major attractions like hockey and college football (no coverage yet of baseball—which for some reason Harold Ross hated—or basketball) to more niche pursuits, such as squash (below) or indoor polo. From time to time I will include these under “Miscellany” as a way to give readers a more complete picture, and to assuage my fear that I am leaving something important out. Here is a very brief snippet of a regular feature, “Court Games,” by staff writer Geoffrey T. Hellman.

* * *
From Our Advertisers
Let’s start with the inside front cover…advertisements from Dorothy Gray salons were all about the restoration of youth in older women…apparently the treatments were so successful that “Mrs. M” was a bigger attraction at a Ritz-Carlton debutante party than her society-bound daughter…note the young gents at right checking out mom, and not the deb…
…opposite Dorothy Gray was this elegant appeal from Bergdorf Goodman…ads aimed at more refined tastes almost always featured these attenuated figures (whether they were people or luxury automobiles)…I guess I would hold onto something too with stilts like those…
…here’s a Steinway grand for less than a grand…$885 in 1936 is roughly equivalent to $20,000 or so today, but that’s still a bargain—Steinway grand pianos currently start at around $85,000…
…speaking of bargains, you could own “The Most Beautiful Thing on Wheels” (according to this ad) for a mere $615…

…the folks at Chrysler were doing everything they could to get people interested in buying their Airflows—despite its technological advances, the car’s streamlined design (toned down in later models) was just too radical for mass market tastes…note how the ad draws attention to the work of “Artist Floyd Davis”…
…here’s a photo of Floyd Davis…

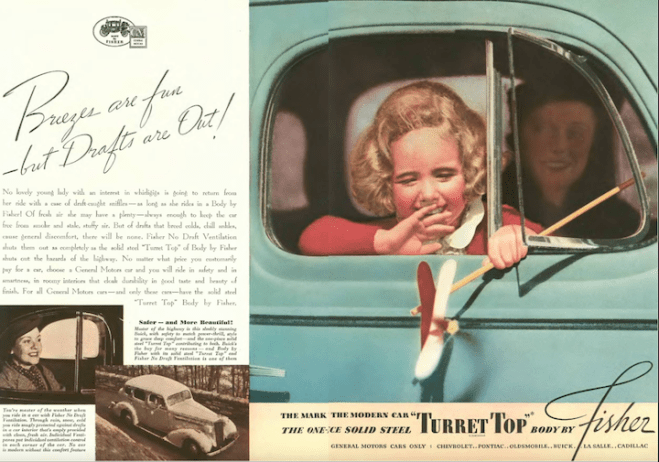
…the Fisher company, makers of car bodies for General Motors, liked to emphasize the safety of their “Turret Top,” although it didn’t seem to occur to anyone that a child dangling from a car window was problematic…
…actress Lupe Vélez made the unlikely claim that flying on a 1930s airliner was “as comfortable as a private yacht”…
…ads for White Rock were among the more colorful found in the early New Yorker…
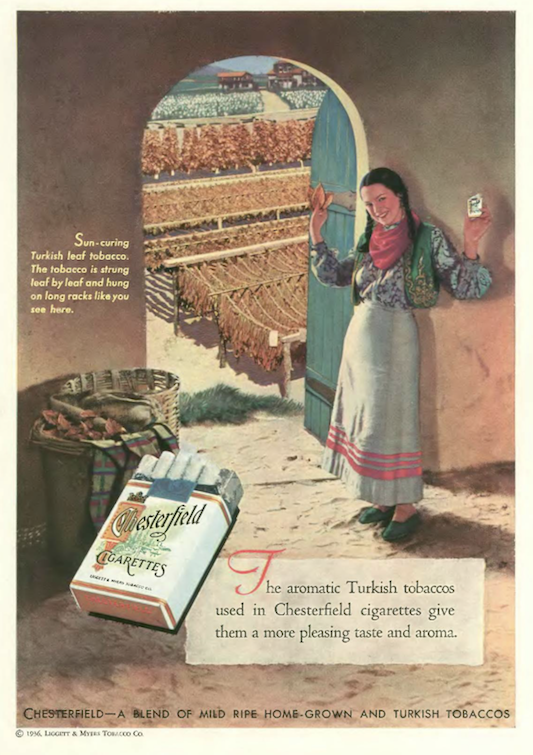
…on the back cover, Liggett & Myers tobacco company shifted gears from elegant to homespun with an ad that emphasized the high quality of Turkish leaf tobacco…
…the folks at Coty hired two New Yorker contributors, poet Arthur Guiterman and illustrator Constantin Alajalov, to promote their line of lipsticks…
…which brings us to the cartoonists, beginning with Al Frueh…
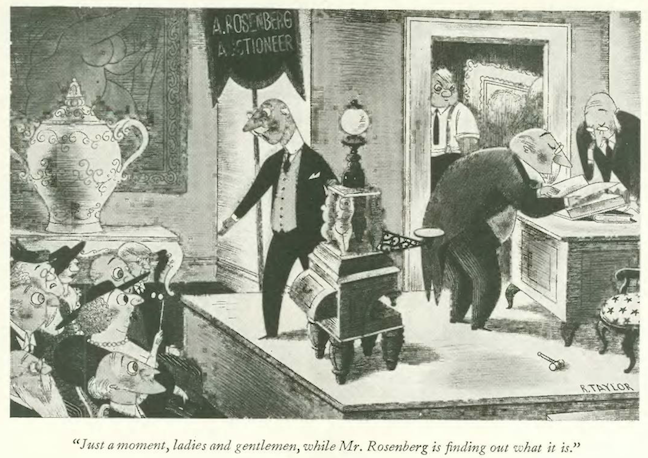
…Richard Taylor opened things up in “Goings On”…
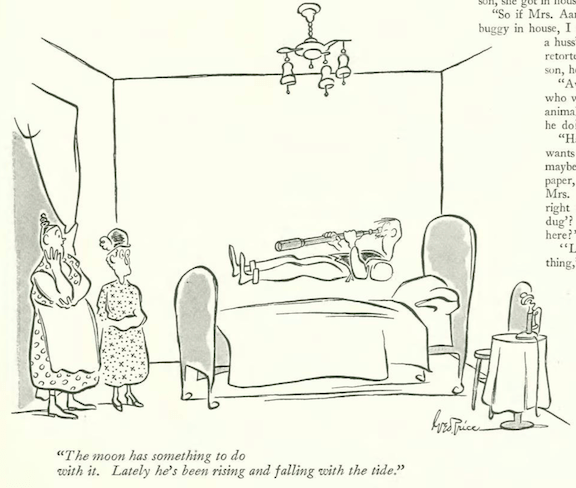
…and George Price added this bit of action to the calendar section…
…Abe Birnbaum contributed this delightful spot drawing…
…the Westminster dog show was the talk of the town, and at Grand Central, per Perry Barlow…
…Robert Day had a fight on his hands…
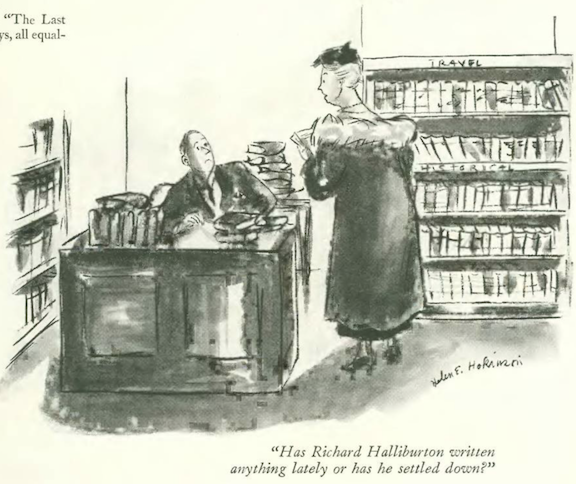
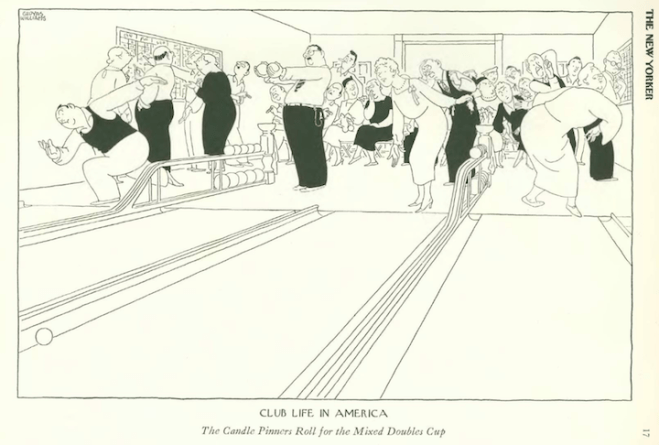
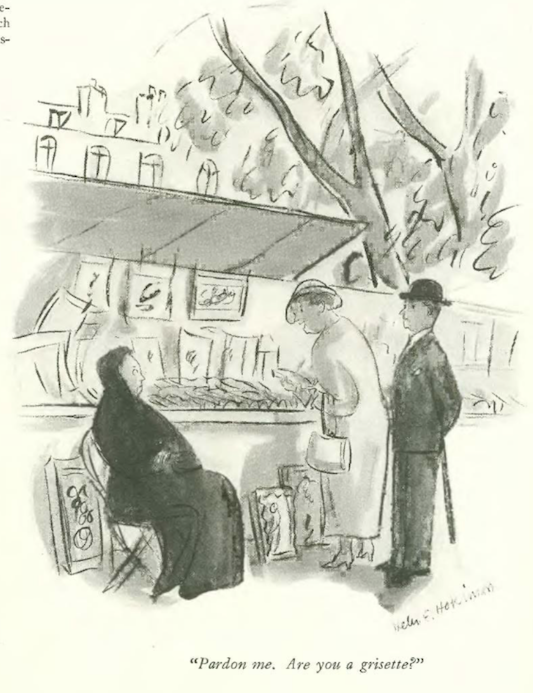
…Helen Hokinson’s “girls” were out to snub the sanitation department…
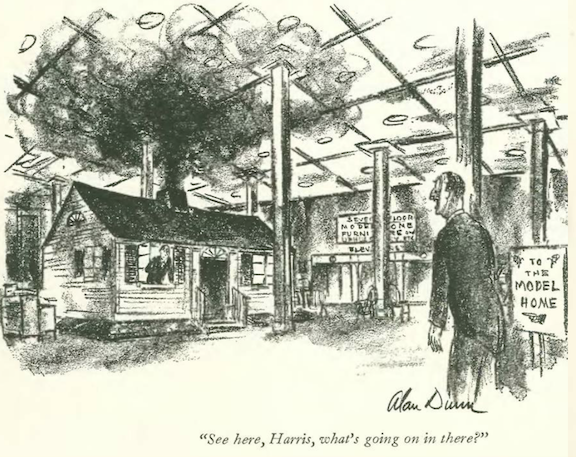
…Rea Irvin drew up the literal downfall of one business…
…Eli Garson had us seeing spots…
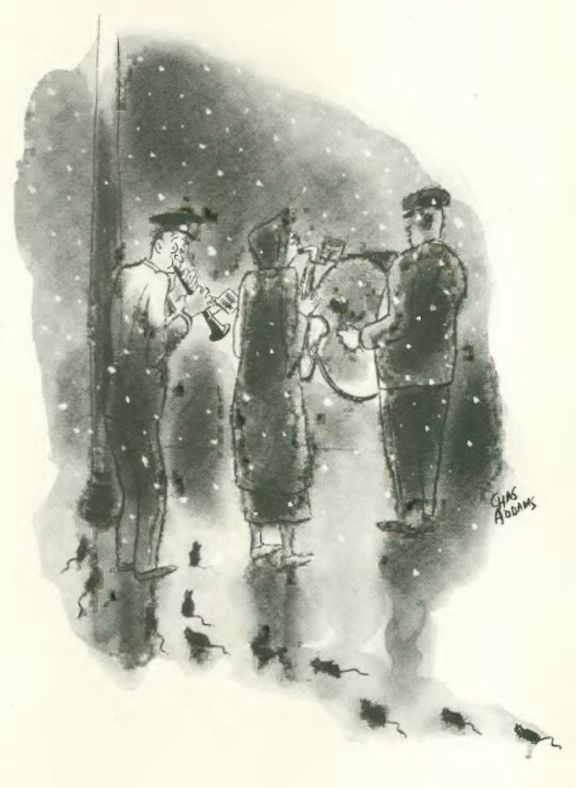
…Charles Addams found the Pied Piper in a Salvation Army band…
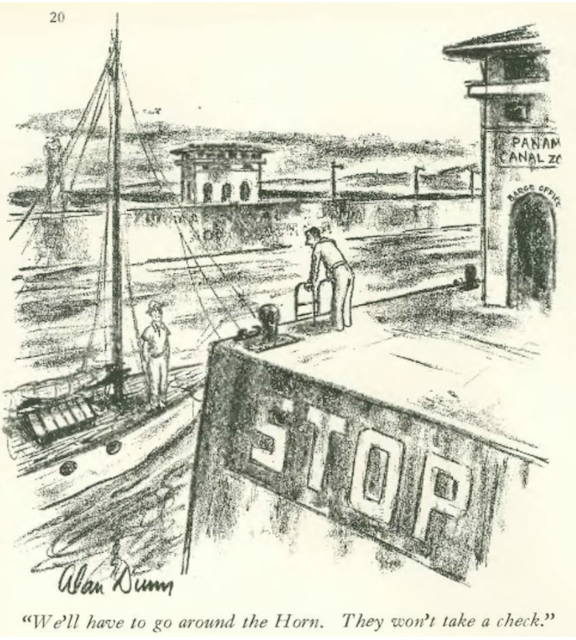
…Alan Dunn gave new meaning to “taking a detour”…
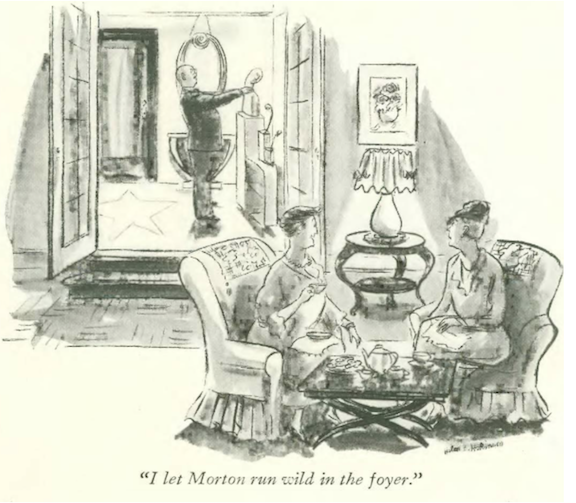
…Barbara Shermund illustrated one of the perils of cocktail parties…
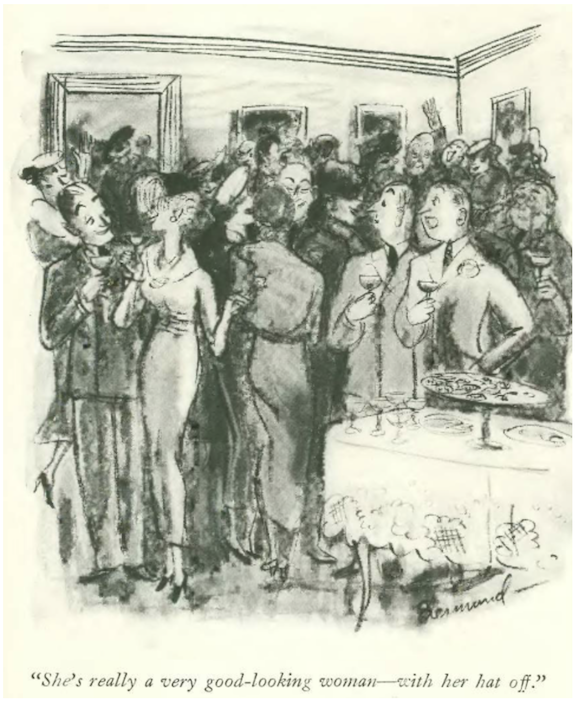
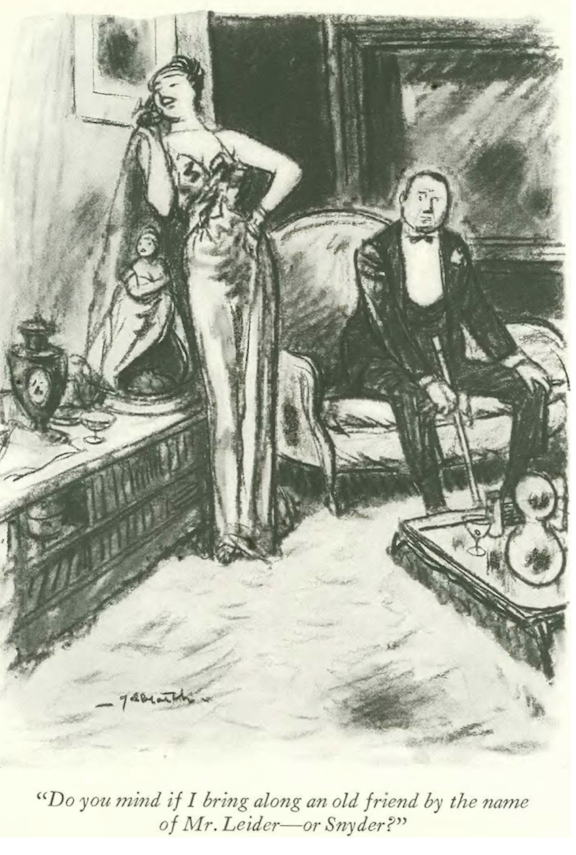
…and we close with Peter Arno, and the sinister world of taxi dancers…
Next Time: Modern Times…