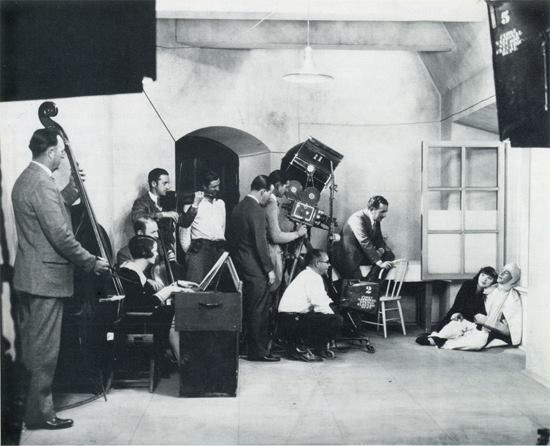
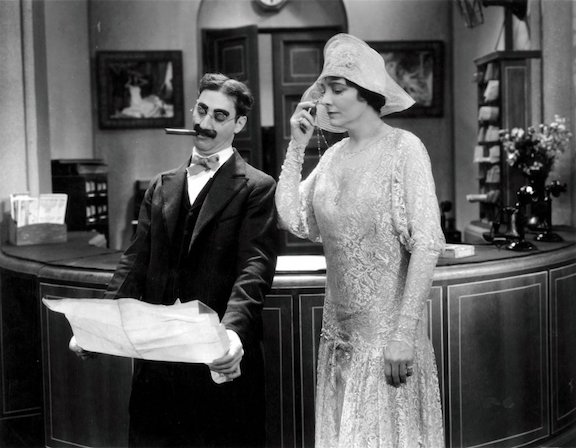
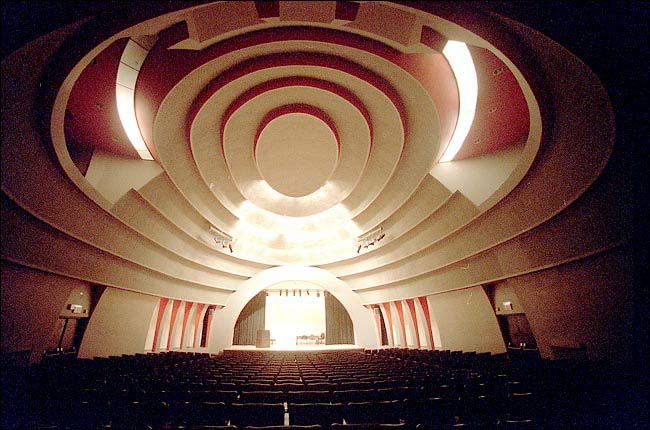
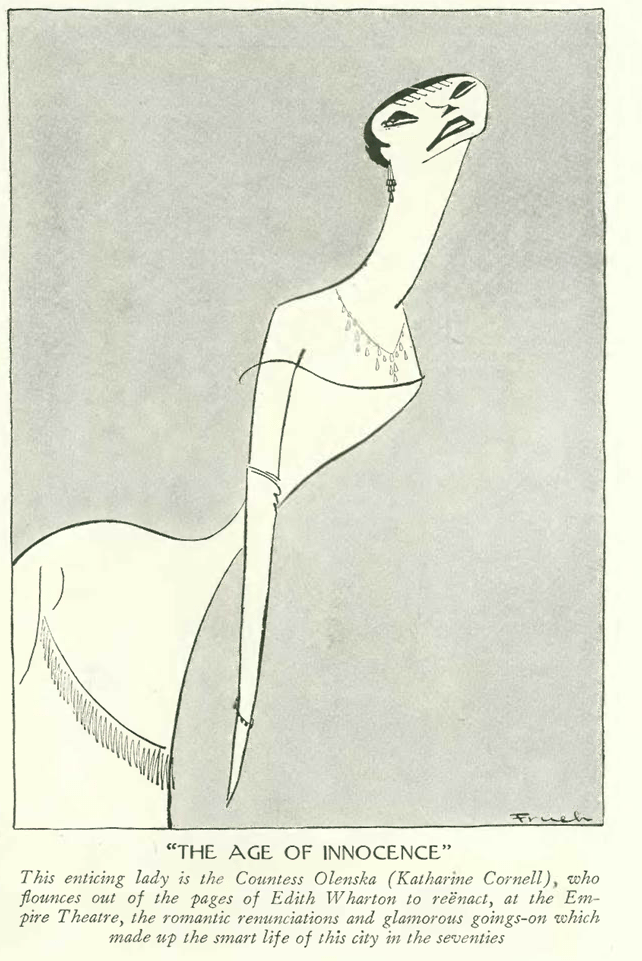
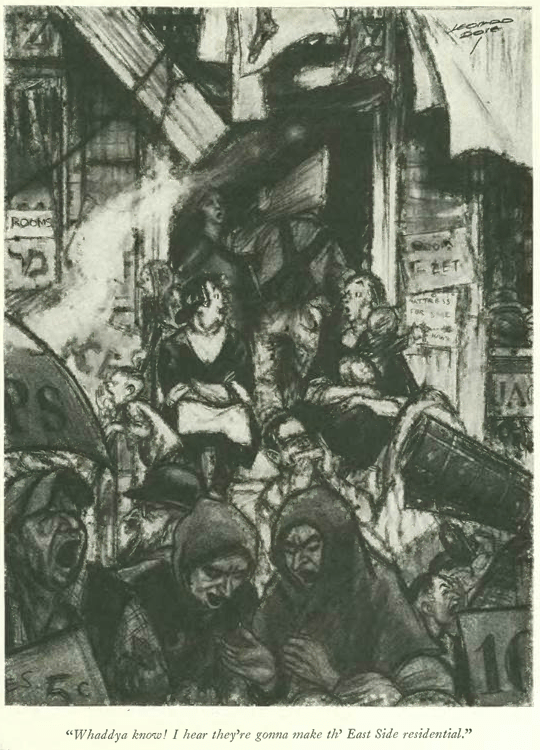MGM piled so many stars and gimmicks into the premiere of The Hollywood Revue of 1929 that even The New Yorker’s jaded film critic John Mosher had to admit he was entertained.

Although today’s audiences would find the film quaint and corny (not to mention its tinny sound and crude editing), it was a big hit in 1929. A plotless revue featuring nearly all of MGM’s stars (Greta Garbo said no — she had a clause in her contract exempting her from such silly things; Lon Chaney, on the other hand, was in failing health), the film followed a variety format similar to such vaudeville productions as the Ziegfeld Follies. The Arthur Freed/Herb Nacio Brown song “Singin’ In the Rain” was introduced in this film, and would inspire the Gene Kelley musical by the same name 23 years later. A rarity for the time, the Hollywood Revue included four skits in an early version of Technicolor, including an all-cast performance of “Singing’ In the Rain.” Mosher observed:
One of the film’s color skits featured John Gilbert and Norma Shearer in a Romeo and Juliet parody filled with Jazz Age slang. It would mark the beginning of the end of Gilbert’s career and, sadly, his life. He was one of the silent era’s most popular leading men, but it was purported that his voice was not suited to the talkies. What really ended Gilbert’s career, however, was studio head Louis B. Mayer, who clashed with the actor both personally and professionally…




…MGM deployed a number of stunts to generate publicity at the film’s New York premiere at the Astor Theatre, including a “human billboard” that featured scantily clad chorus girls precariously perched on a huge letters high above the theatre’s entrance. In a rather less dangerous stunt—during the movie’s “Orange Blossom Time” skit—a faint scent of orange blossoms wafted into the theatre. “The Talk of the Town” observed…



* * *
Technological Adjustments
Had you attended the premiere of The Hollywood Revue, perhaps you would have appreciated James Thurber’s observation that actors in talking pictures sound as if they are speaking into cracker boxes. In this hilarious piece (titled “The Roaring Talkies”), he proposed a solution. An excerpt:
* * *
A Happy Diversion
“The Talk of the Town” (via Theodore Pratt) looked in on the hobbyists who raced model boats at Central Park’s Conservatory Lake, a happy tradition that began in the late 19th century and continues to this day:

Pratt also described the old wooden boathouse, which was replaced in 1954 with a somewhat grander structure, Kerbs Boathouse, where model boats are still stored…

* * *
On the Other Hand…
Leaving the cool and quiet of the park brought one quickly back into the dust and clamor of the metropolis. Pratt observed that the summer season lasted two weeks longer in the city than in the country, thanks to the city’s heat island effect— perhaps an unwelcome observation given the usually hot summer of 1929. Not only did the city’s heat extend the season, but it also kept the city enveloped in “an enormous cloud of dust”…

* * *
Already Feeling Old?
I found this “Talk” item curious for exploring the sentimental attachment some folks had developed for old cars from the 1910s, given those cars were barely twenty years old and cars in general hadn’t been in common use much longer…
…as for another “Talk” item, I doubt modern New Yorker readers would find any humor in this observation:
* * *
On to sillier things, Robert Benchley turned in a casual titled “Boost New York!” Benchley ridiculed a promotional brochure from the New York Merchants Association that touted various statistics in a manner reminiscent of the fictional George Babbitt. Benchley imagined how an Iowa couple might respond to such dazzling numbers:
* * *
A Drinking Life
Occasionally I like to feature infrequent or one-time New Yorker contributors who are nearly lost to history. Frank Ward O’Malley (1875-1932), a reporter for the New York Sun from 1906-19, was known for his humorous stories. In 1928 he published a book titled The Swiss Family O’Malley. In this casual (titled “The Fatty Degeneration of Broadway”) from the Aug. 24 issue, O’Malley described an alcohol intervention of sorts and then his fall off the wagon. Here are the opening and closing paragraphs, along with his photo circa 1910s.

* * *
From Our Advertisers
This week we have an advertisement for the Drake Apartment Hotel, claiming to be the “smartest” in New York. Note how they employed what seems to be the same pointy-nosed, haughty couple that we saw last week (below) who endorsed the Park Lane (I want to believe there is a subtle joke here)…
…just 25 years removed from the Wright Brothers’ flight at Kitty Hawk, advertisers were treating flying as though it were routine…

…and this young woman seemed to think flying was nothing more than “playing ring around the rosy with the clouds”…
…I like the reviews included in this bookseller’s ad, especially the first one for the book Ex-Wife by Anonymous (it was written by Ursula Parrott, a writer of romantic fiction)…
…our illustrations include Abe Birnbaum’s contribution to the casuals section (breaking up the copy of one of Josie Turner’s Elsie Dinsmore parodies)…
…Reginald Marsh illustrated the late summer beach scene at Coney Island…
…and for kicks this nice little filler by Constantin Alajalov…
…thanks to the skills of The New Yorker’s first layout artist, Popsy Whitaker, we have this whimsical pairing of Otto Soglow and Dorothy Parker…
…Mary Petty contributed a cartoon that looks contemporary…
…Peter Arno paid a visit to the doctor’s office…
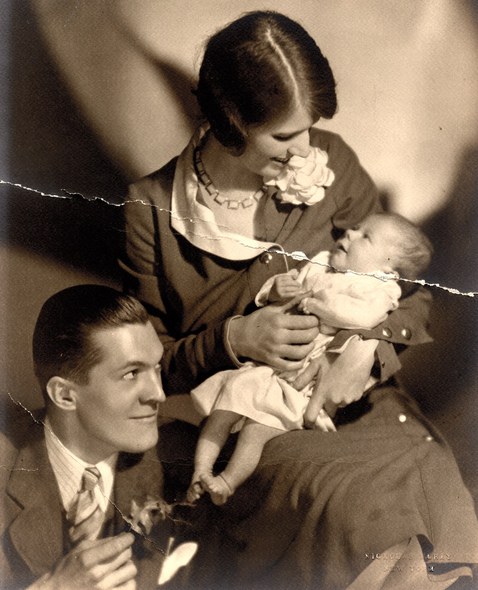
…and commented on his life as a new father…the woman holding the baby was doubtless inspired by his wife, New Yorker columnist Lois Long…
…for reference, Peter Arno and Lois Long are pictured here with baby daughter Patricia Arno in 1928…Lois clearly had a better grasp on the situation than Arno had imagined…

…Alice Harvey eavesdropped on a conversation between teenagers…
…and like Arno, Leonard Dove had two cartoons in this issue…here an editor finds the former Prohibition enforcer no longer newsworthy…
…and over on the East Side, rumors of gentrification…
Next Time: A Carnival in the Air…