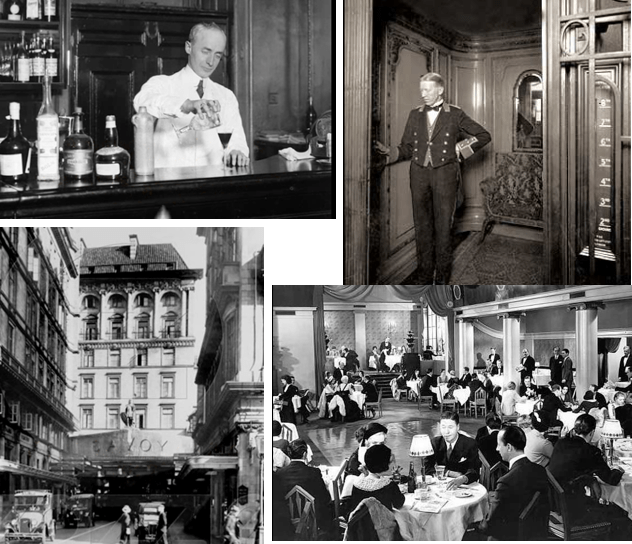
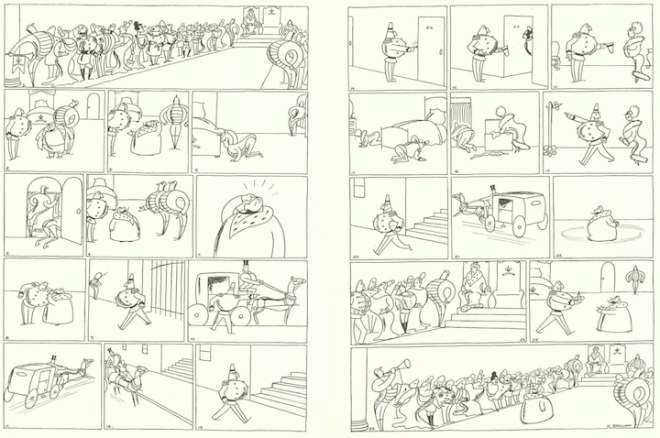
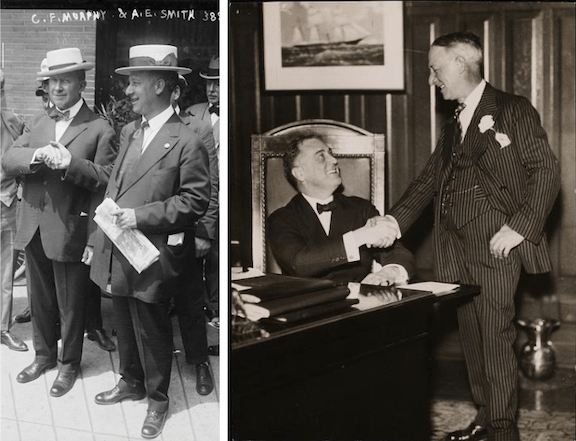
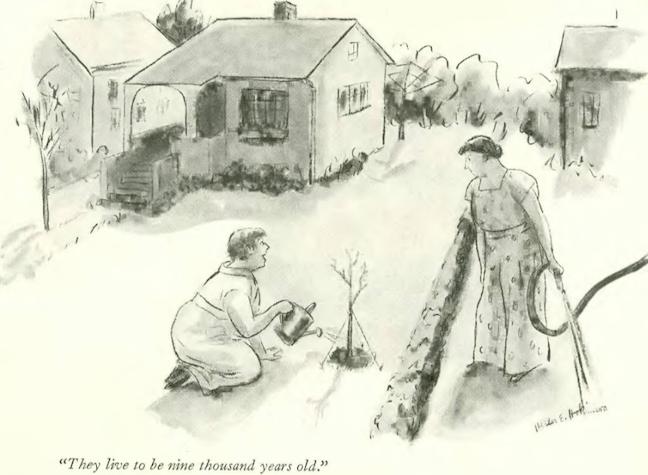Above: Al Smith waving to crowds on arrival at Chattanooga, Tennessee during his presidential campaign in 1928. (Museum of the City of New York)
It’s hard to not like Al Smith, the governor of New York from 1923 to 1928, a man who avoided the temptations of political power and stayed true to his working class roots of the Lower East Side.

The son of Irish, Italian and German immigrants, Alfred Emanuel Smith (1873–1944) was raised in the Tammany Hall-dominated Fourth Ward, and although he was indebted to Tammany’s political machine throughout much of his professional life (including stints in the New York State Assembly and as York County Sheriff, President of the Board of Alderman, and finally Governor) he remained untarnished by corruption. Smith’s unsuccessful bid for the U.S. presidency in 1928 put an end to his political life, but there was still much to do, as “The Talk of the Town” explained:

Smith first sought the Democratic presidential nomination in 1924. According to historian Robert Slayton, Smith advanced the cause of civil liberty by decrying lynching and racial violence at the 1924 Democratic National Convention, where Franklin D. Roosevelt delivered the nominating speech for Smith and saluted him as “the Happy Warrior of the political battlefield.”
Following his 1928 presidential election loss to Herbert Hoover, Smith became president of Empire State, Inc., the corporation that built and also operated the Empire State Building, which was then the tallest building in the world. Smith was also known for his fondness of animals, and in 1934 Parks Commissioner Robert Moses made Smith “Honorary Night Zookeeper” of the renovated Central Park Zoo. Smith was given keys to the zoo and often took guests to see the animals after hours. According to Rebekah Burgess of the NYC Department of Parks and Recreation, “As a resident of 820 Fifth Avenue, directly across the street from the entrance of the Central Park Zoo, Smith was known to appear with snacks for the animals or to launch into impromptu lectures for visitors. Al Smith took his honorary title to heart. Throughout the rest of his life, Smith could often be found attending to the animals at the zookeepers’ sides during open hours. At night, Smith visited with guests, or more often, one-on-one with the animals.”
Smith was also a humanitarian, and in addition to advocating for the working class, he was an early critic of the Nazi regime in Germany, vigorously supporting the Anti-Nazi boycott of 1933. Here is another excerpt from the “Talk” piece:

* * *
Culture Club
In the Nov. 9, 1929 issue of The New Yorker Murdock Pemberton hailed the opening of the Roerich Museum. For the July 14, 1934 issue, “The Talk of the Town” took another look. A brief excerpt:

* * *
Itinerant Showman
Alva Johnston filed the first installment of a three-part profile of famed sports promoter Jack Curley (1876–1937). A brief excerpt:

* * *
Over There
In his column “Of All Things,” Howard Brubaker made this brief mention of the “Night of the Long Knives;” on June 30, 1934 Adolf Hitler ordered SS guards to murder the leaders of the paramilitary SA along with hundreds of other perceived or imagined opponents.
Here is a clip from the front page of The New York Times, July 3, 1934:

* * *
Pimm’s and Soda
July in England meant Wimbledon, and The New Yorker was there to observe the “snobbish and sacred” rite…

* * *
Midsummer Dreams
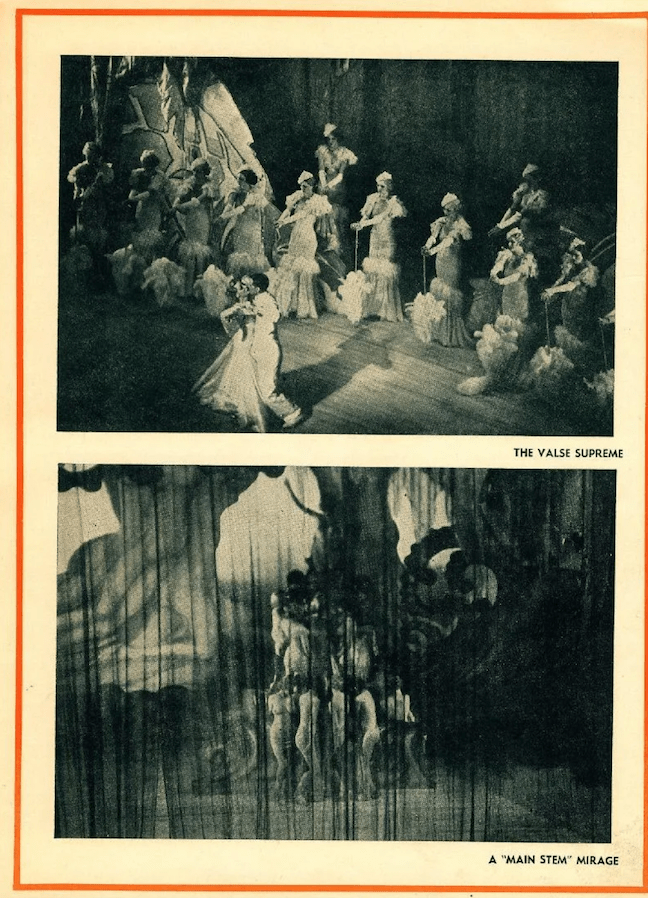
In the summertime (and before widespread use of air conditioning) stage entertainments such as theater and musical performances took to the outdoors during their off-season, seeking the evening cool of intimate rooftops or large, open venues such as Lewisohn Stadium, A brief excerpt describing a performance of Samson et Dalila:

* * *
From Our Advertisers
The folks at struggling carmaker Hupmobile took out this bold, full-page ad to tout their flashy “Aero-Dynamic” by noted designer Raymond Loewy…
…this ad from Harriet Hubbard Ayer was bold in a very different way, essentially calling some women ugly unless they used the company’s “beauty preparations”…
…consommé, a clear soup that was particularly popular among the upper classes, offered up some keen competition between two food giants…here Heinz enlisted the help of William Steig to move their product…
…while the folks at Campbell’s offered up this lovely patio setting for their “invigorating” consommé…
…meanwhile, White Rock mineral water could be found on patios all over Manhattan, as this ad attested…
…this is a reminder that most city folks had their milk and other dairy products delivered in the early part of the 20th century…by the early 1960s about 30 percent of consumers still had their milk delivered, dropping to 7 percent by 1975 and .4 percent by 2005…
…affordable home air-conditioning wouldn’t be available to the masses until after World War II…this unit (designed for a single room) from Frigidaire retailed for $340 (a little less than $8,000 today)…
…on to our cartoonists, we begin with Robert Day in the “Goings On’ section…
…Day again, exploring the baffling, glassy interiors of modern restaurants…
…the birdwatching continued with Rea Irvin…
…Alain (Daniel Brustlein) gave us a swimming somnambulist…
…Helen Hokinson explored the paranormal, via domestic plumbing…
…and we close with James Thurber, and the missing Dr. Millmoss…
Next Time: His Five Cent’s Worth…