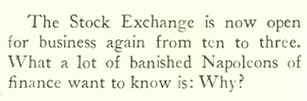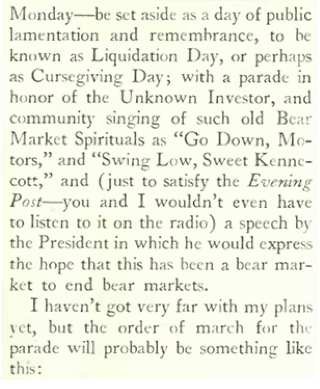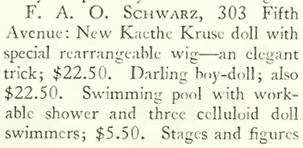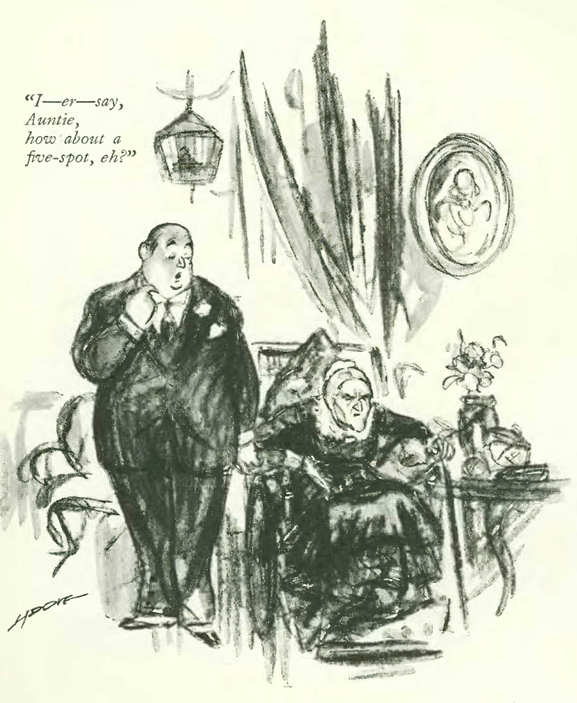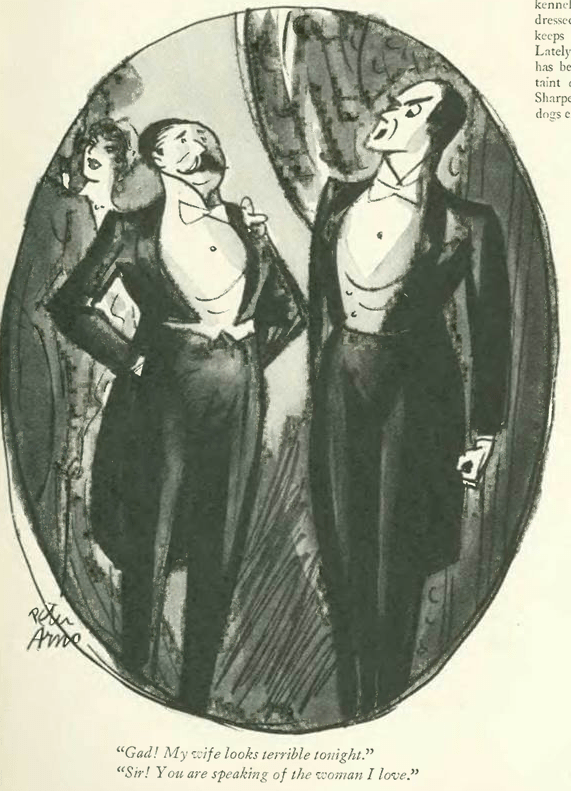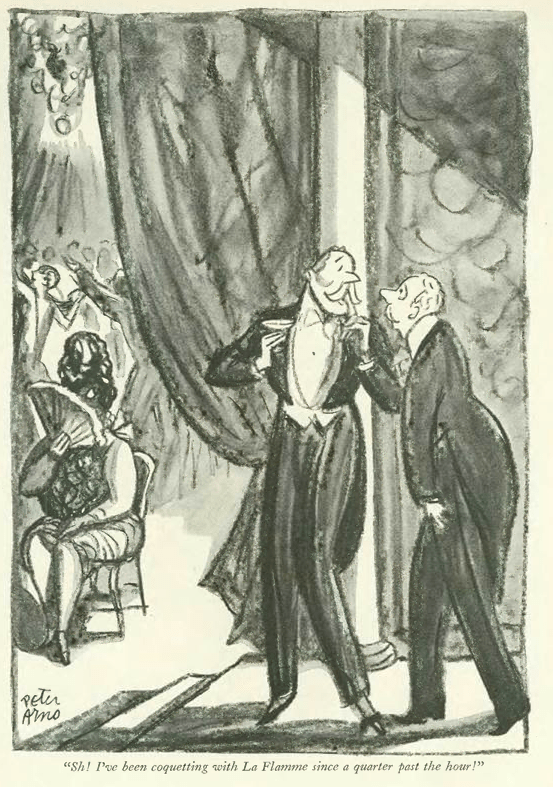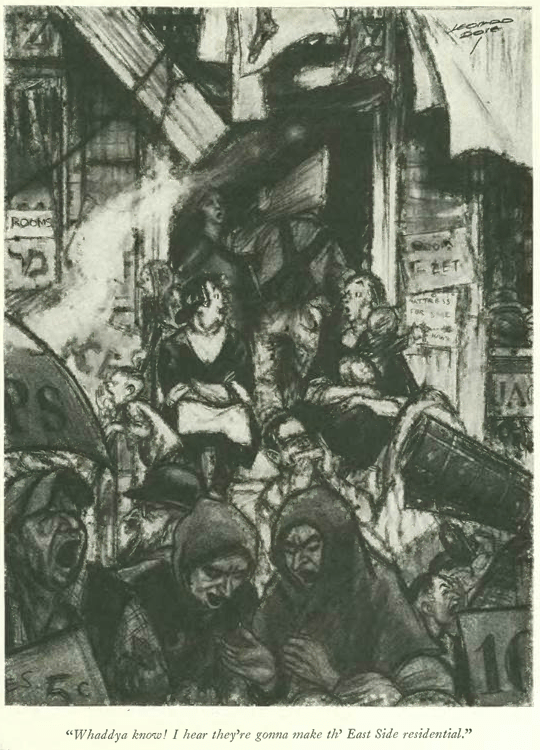The effects of the October stock market crash were finally beginning to show in the pages of the New Yorker in the last month of the 1920s.

E. B. White was doing his best to keep things light, stating in his “Notes and Comment” column that despite the “time of panic,” the ad-packed Dec. 7 issue contained a whopping 176 pages…
Advertising income for The New Yorker would drop a bit in 1930 (from $1,929,000 to $1,922,000) and would continue to decline through 1932 (down to $1,448,000) before recovering slightly in 1933 and then really taking off again in 1934. And as White noted, even if they had to borrow the 15 cents, folks would still buy the magazine: circulation would top 100,000 in 1930, and except for a dip in 1932 would steadily grow past 150,000 by decade’s end.

The magazine was stuffed with ads as well as an extended “On and Off the Avenue” —which offered advice to holiday shoppers — and the continued serialization of Elmer Rice’s novel A Voyage to Purilia (installment No. 9).
But not all was sweetness and light. The biggest economic collapse in U.S. history was simply too pervasive to ignore, and even a feeling of hopelessness was creeping into magazine — here’s an observation by Howard Brubaker in his “Of All Things” column…
…and writing under the pseudonym “Guy Fawkes,” humorist Robert Benchley found little to laugh about in his “The Wayward Press” column. He chided the media for giving the public false hopes (which he labeled “propaganda”) regarding the state of the economy, and for concealing the suicide of prominent New York banker James J. Riordan, whose death announcement was postponed until Riordan’s bank closed for the weekend…

The following account excerpted from the Nov. 10, 1929 New York Times reveals how a nervous banking community responded to the market crash-related suicide of Riordan:
The popular historian Frederick Lewis Allen (1890 – 1954) offered a more lighthearted take on the events surrounding the market crash in his tongue-in-cheek casual, “Liquidation Day Parade,” in which he proposed a holiday to commemorate the end of the Big Bull Market.
Allen, who also served as editor of Harper’s Magazine, would go on to write Only Yesterday, which chronicled American life in the Roaring Twenties. The 1931 book was a huge bestseller at the dawn of the Depression, and critically acclaimed, both then and now. Writing for the Washington Post (Nov. 28, 2007), book critic Jonathan Yardley observed: “It is testimony to both the popularity and the staying power of Only Yesterday that for more than three-quarters of a century it has remained steadily in print, and to this day enjoys sales that would please plenty of 21st-century writers.”

* * *
Clipped Wings
We turn back to E.B. White, The New Yorker’s most enthusiastic proponent of the aviation age. In the previous issue (Nov. 30) White had rhapsodized about a flight he took on a huge, new Fokker F-32. In the Dec. 7 “Talk of the Town” White reported that the very same plane had crashed and burned (and also noted that another plane on which he had been a passenger, a Ford Trimotor, had crashed earlier that year in Newark). White speculated that aviation would soon head in a different, safer, direction along the lines of the autogyro, a flying contraption that was widely favored by futurists of the day:

* * *
Wonders Never Cease
“Talk” also reported the growing popularity of newsreel theaters, and marveled at the speed with which camera crews could deliver their finished product to movie screens. An example was the crash of a small plane onto the side of a YMCA (an incident also noted by White in the previous issue); a newsreel crew was able to go from scene to screen in about four hours:

* * *
High Wire Act
The artist Alexander Calder was already well known for his wire sculptures (his colorful mobiles would come later) when he embarked on his Cirque Calder in Paris in 1926. He brought “the show” to New York in 1929, where he used everything from eggbeaters to balloons to bring his wiry performers to life. Presumably art critic Murdock Pemberton wrote this account for “Talk of the Town”…

And we also have Pemberton over at his art column, where once again he tried to make sense of the new upstart Museum of Modern Art. He seemed to be surprised by the large crowds drawn to the new museum as he pondered its next show…

Pemberton had yet to see MoMA’s stunning second exhibition, Paintings by Nineteen Living Americans, but had to (grudgingly) conclude that the museum was filling a need…
* * *
The Toy Bazaar
From its beginnings in 1862 until the end of the 19th century, the F.A.O. Schwarz toy store was known to New Yorkers as the “Toy Bazaar,” and by 1929 was something of an institution. As part of a lengthy column featuring ideas for Christmas shoppers, The New Yorker offered some tips on what shoppers might find at the famed toy store:

Some of the toys mentioned in The New Yorker article, from the 1929 F.A.O. Schwarz Christmas catalog. There’s nothing plastic here — plastics as we know them, such as polypropylene, would be developed in the 1950s:
The 1929 F.A.O. Schwarz Christmas catalog also featured a color spread of its stock of Lionel Electric Trains:
If you want to look at the entire 1929 F.A.O. Schwarz Christmas catalog, you can find it at this terrific site.
The column also offered advice on “gifts for servants,” at least for those who weren’t getting laid off due to the market crash. Note the somewhat patronizing tone, especially the final paragraph regarding nurses and governesses:
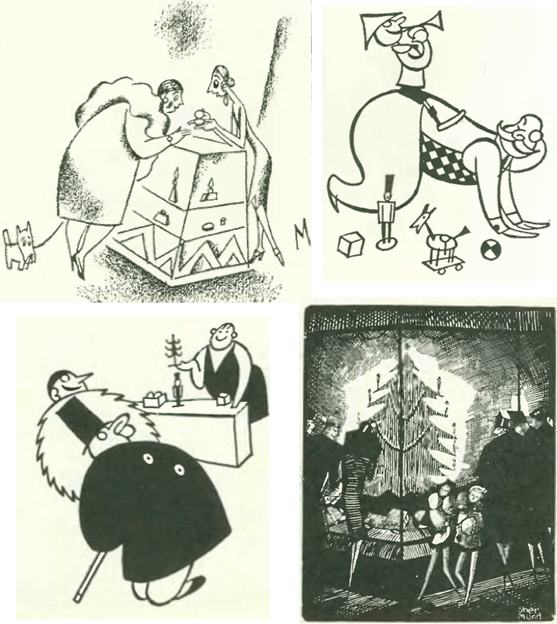
As usual, the shopping column was sprinkled with spot drawings celebrating the season: here are three from Julian De Miskey and one from Barbara Shermund:
* * *
The Bard Does the Talkies
At the movies, critic John Mosher found much to like at the Rivoli, which was screening The Taming of the Shrew featuring the husband/wife team of Douglas Fairbanks and Mary Pickford:

* * *
Somerset Saga
When I first spotted this I thought it was an early edition of The New Yorker’s famed Christmas poem, but those were started by Frank Sullivan in 1932. Nevertheless, here is a clever “Saga of Somerset County” from our dear E.B. White:
* * *
From Our Advertisers
For men who hadn’t lost their shirts and had an “ingrained taste for luxury,” here was a men’s toilet set from Coty featuring a talcum shaker that would have doubled as a fine whiskey flask…
…did the folks at Bergdorf Goodman miss the news of the market crash? Read the fine print about the coming “revolution in fur fashion”…
…Helen Hokinson illustrated another ad for G. Washington instant coffee…
…Atwater Kent offered up this sumptuous appeal to holiday shoppers…
…at first glance I thought this was an ad for a luxury apartment…the copy is almost identical, save for a couple of words like “death” and “crypt”…
…on to our artists, here is a spot by Constantin Alajalov that ran along the bottom of “Talk of the Town”…
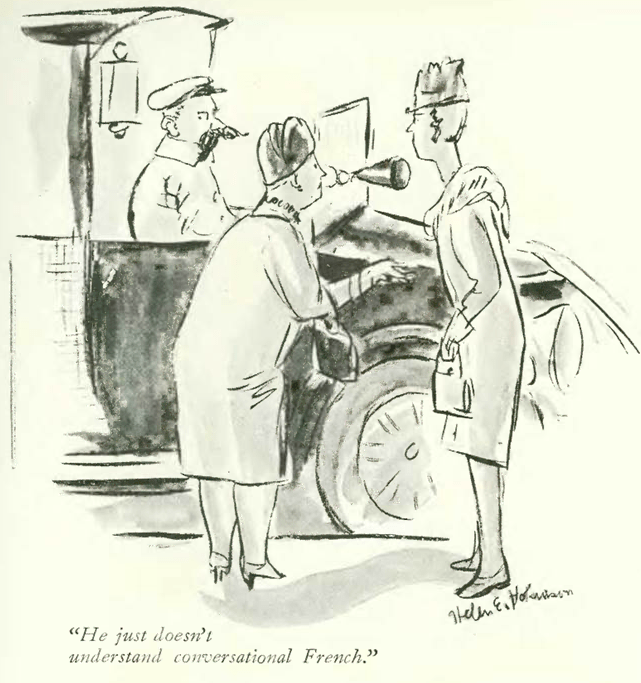
…and a sight that would become more familiar as the Depression deepened, a look at an estate sale, courtesy Helen Hokinson…
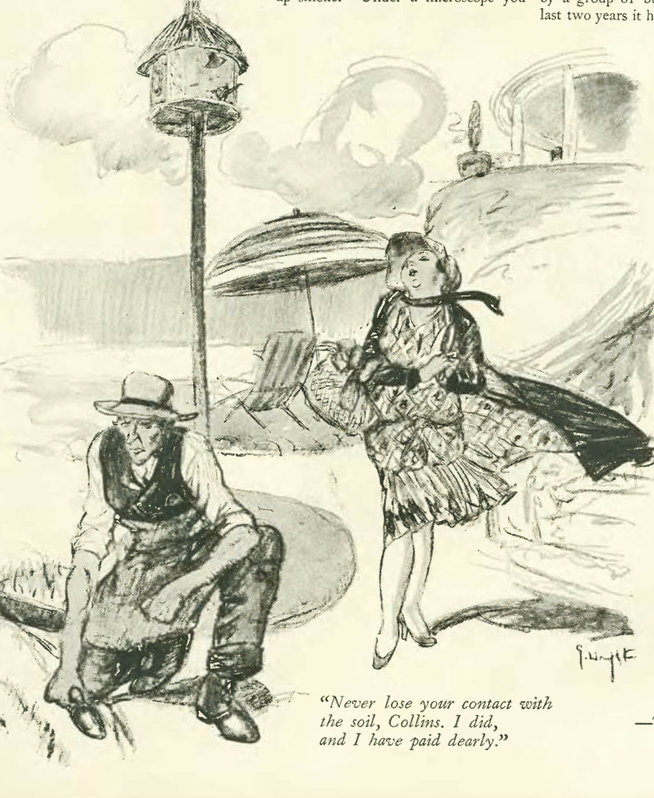
…signs of the economic collapse were starting to creep into the cartoons, including offerings by Raeburn Van Buren…
…Leonard Dove…
…and Paul Webb…
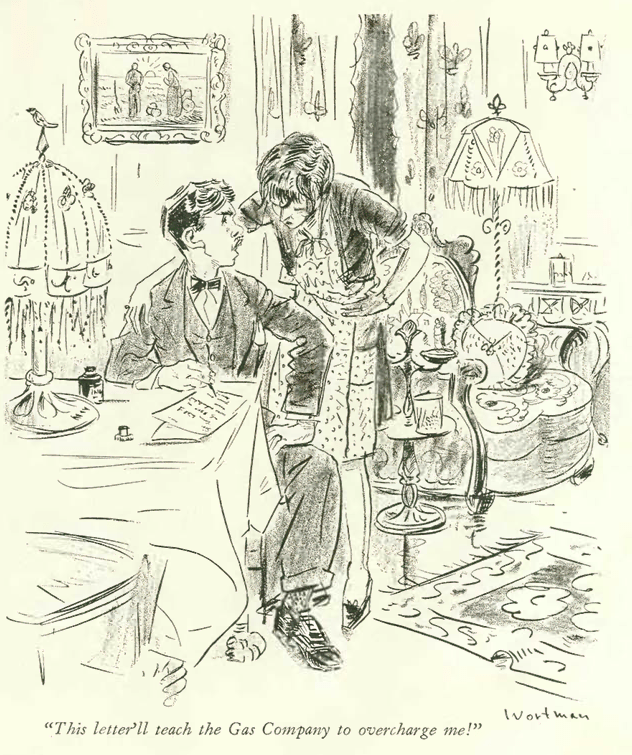
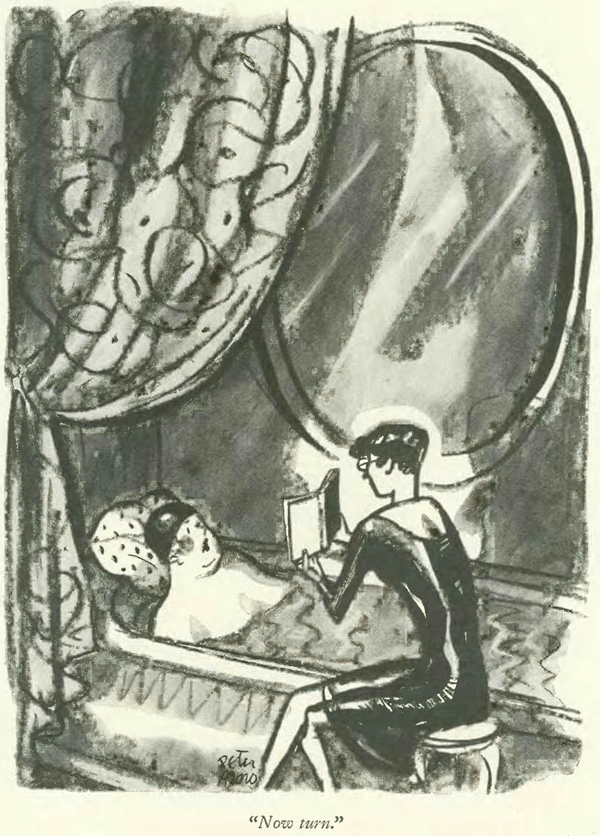
…while the economy was headed into the pits, cartoonist Peter Arno saw his fortunes soaring as he headed into a new decade. In his excellent 2016 biography, Peter Arno: The Mad Mad World of The New Yorker’s Greatest Cartoonist, Michael Maslin writes, “By the time The New Yorker’s December 7, 1929 issue hit the newsstands, its readership had, within the year, seen three Arno covers and fifty-seven of his drawings.” Maslin notes that drawing number fifty-eight, which appears below, “ended the 1920s with a bang (so to speak).” The drawing, writes Maslin, “became a lightning rod for two New Yorker camps: the (James) Thurber camp, who chose to believe Harold Ross (the magazine’s founding editor, who forbade sex as a subject) was naive in sexual matters, and the (E.B.) White camp, convinced Ross would never have let the drawing appear in the magazine if he hadn’t understood its meaning.” If you enjoy Arno’s work, or are a fan of The New Yorker, Maslin’s book is a must-read…
Next Time: In Search of Holiday Cheer…