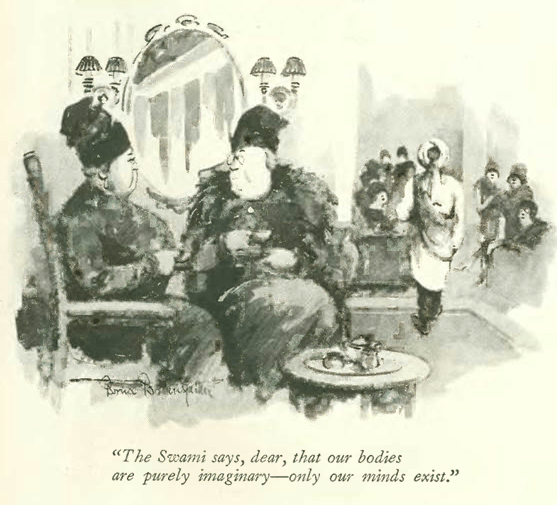
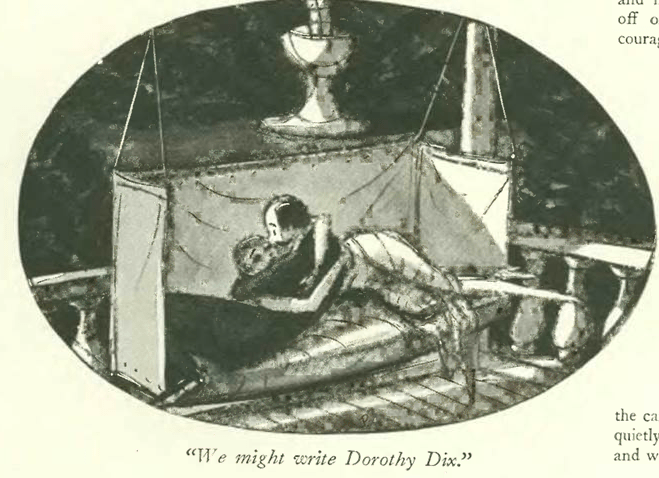
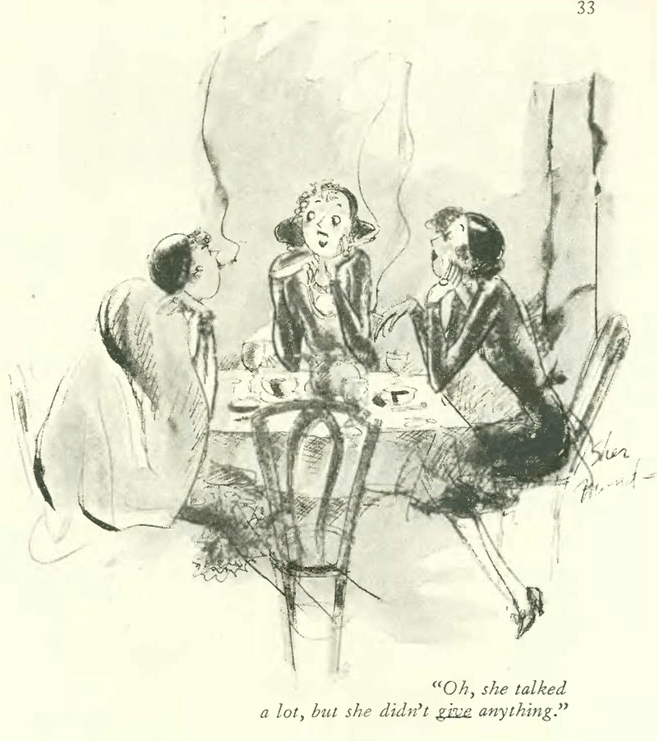The heat came early to New York in June 1933, so folks flocked to air-conditioned cinemas or sought the cooling breezes of rooftop cafes and dance floors. And thanks to FDR, there was legal beer to be quaffed at various beer gardens popping up all over town.

Lois Long kept her cool on the beach or at home with a cold Planters’ Punch, but one gets restless, and Ethel Waters was at the Cotton Club, so Long headed out into the night; an excerpt from her column “Tables for Two”…



* * *
From Our Advertisers
Legal beer and hot summer days combined to bring some much-needed advertising revenue to The New Yorker…
…here we have dear old dad telling the young ‘uns (all in formal wear, mind you) about the good old days before Prohibition took away his favorite tipple…
…notable about the magazine’s first beer ads was the target market…this is akin to the cigarette manufacturers, who were also targeting women as a new growth market for their products…curious how this PBR ad is illustrated…is she getting ready to drink the beer, or serve it?…
…also joining the party were the folks who made mixers like White Rock mineral water…note the reference at bottom right to the anticipated repeal of the 18th Amendment…
…the purveyors of Hoffman’s ginger ale were less subtle, encouraging drinkers to mix those highballs right now…
…you could enjoy that cool one while sitting in front of a Klenzair electric fan, which was probably nothing like riding a dolphin—a strange visual metaphor, but then again perhaps something else is being suggested here besides electric fans…
…no doubt Lois Long took in one of these breezy performances on the rooftop of the Hotel Pennsylvania…
…an evening with Rudy Vallée would have been a lot cheaper than one of these “compact” air conditioners, available to only the very wealthy…
…but you didn’t need to be J.P. Morgan to own a Lektrolite lighter, which was kind of clever…this flameless lighter contained a platinum filament that would glow hot after being lowered into reactive chemicals in the lighter’s base…
…another ad from the Architects’ Emergency Committee, which looked like something an architect would design…
…our final June 24 ad told readers about the miracle of Sanforizing, which was basically a pre-shrinking technique, like pre-washed jeans…
…we kick off our cartoons with George Price at the ball game…
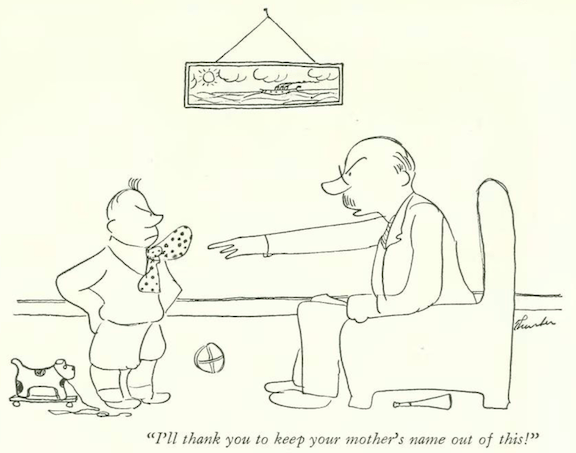
…Alan Dunn was in William Steig’s “Small Fry” territory with this precocious pair…
…James Thurber brought us back to his delightfully strange world…
…and Whitney Darrow Jr gave us a trio at a nudist colony dressing a man with their eyes…
…we move along to July 1, 1933…

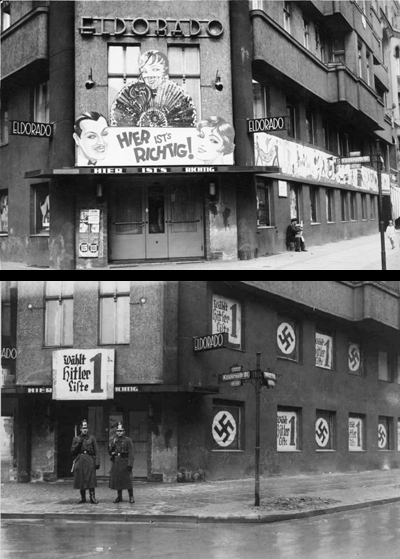
Where in this issue we find the Nazis not keeping their cool. In an article titled “Unter Dem Hakenkreuz” (“Under the Swastika”) American journalist and activist Mary Heaton Vorse commented on the changes taking place in Berlin, where the vice, decadence and other freedoms of the Weimar years had been swept away, including women’s rights…an excerpt:

* * *
Some Strings Attached
Back in the states, Alvin Johnston published the first installment of a two-part profile on John P. O’Brien (1873–1951) who served as mayor of New York from January to December 1933, the second of two short-term mayors to serve between the disgraced and deposed Jimmy Walker and the reformer Fiorello LaGuardia. Considered the last of the mayoral puppets of Tammany Hall, he was known for his brief, heartless, and clueless reign during one of the worst years of the Depression; while unemployment was at 25 percent, O’Brien was doling out relief funds to Tammany cronies. A brief excerpt (with Abe Birnbaum illustration):

* * *
That Pepsodent Smile
The author James Norman Hall (1887–1951), known for the trilogy of novels that included Mutiny on the Bounty, offered these sobering thoughts about a famed actor he spotted on a South Pacific holiday:

* * *
More From Our Advertisers
More cool ones for those hot summer days courtesy of Schaefer…
…and Rheingold, here served by a sheepish-looking woman who doubtless wished that the tray supported champagne or cocktail glasses…and leave it to the Dutch to be one of the first countries to get their foot into the import market…when I was in college this was as good as it got, beer-wise…
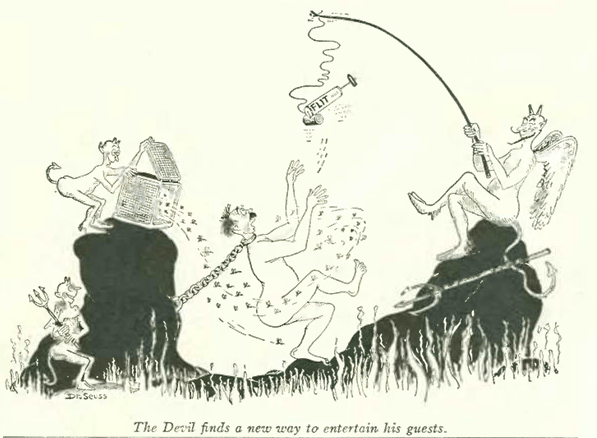
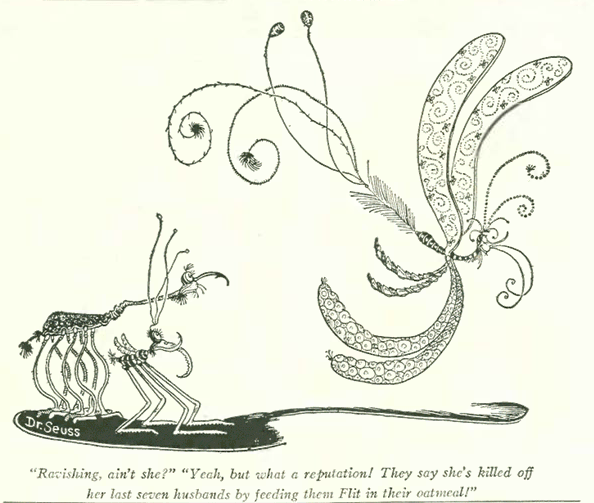
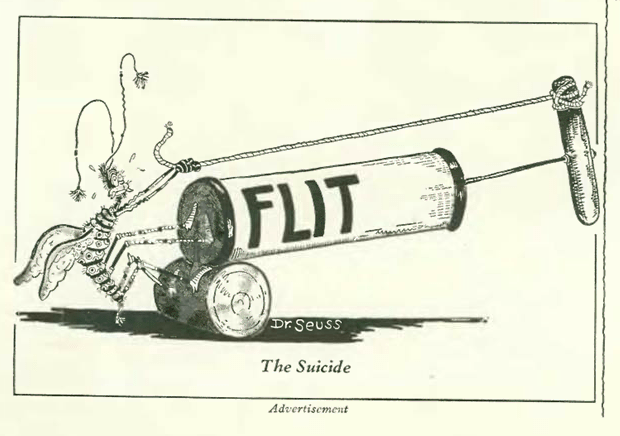
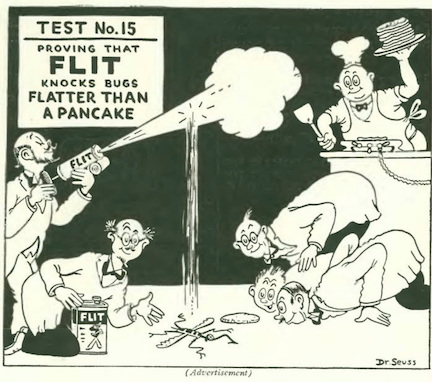
…Dr. Seuss again for Flit, and even though this is a cartoon, it demonstrates how in those days no one really cared if you sprayed pesticides near your breakfast, or pets, or kids…
…here’s one of just four cartoons contributed to The New Yorker in the early 1930s by Walter Schmidt…
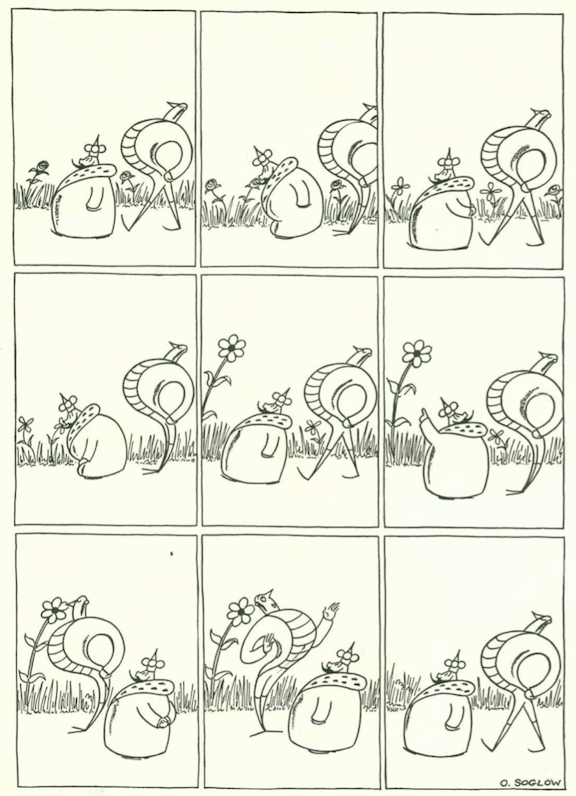
…Otto Soglow’s Little King found an opportunity to stop and smell the flowers…
…Mary Petty gave us two examples of fashion-conscious women…
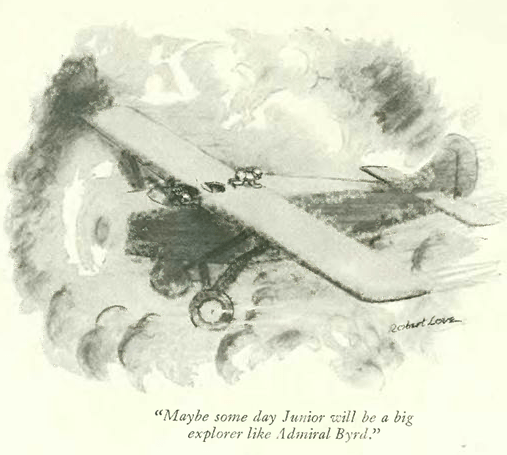
…James Thurber explored the nuances of parenting…
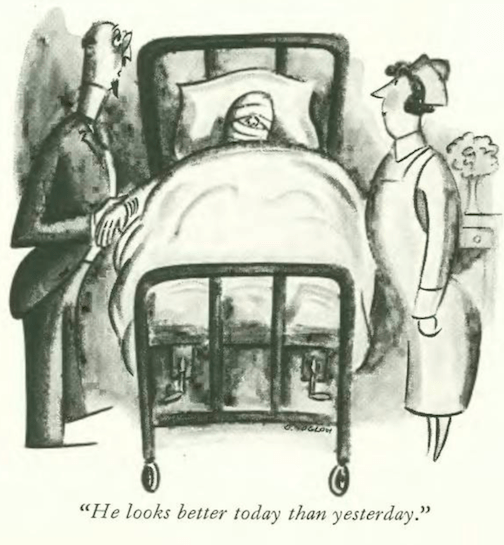
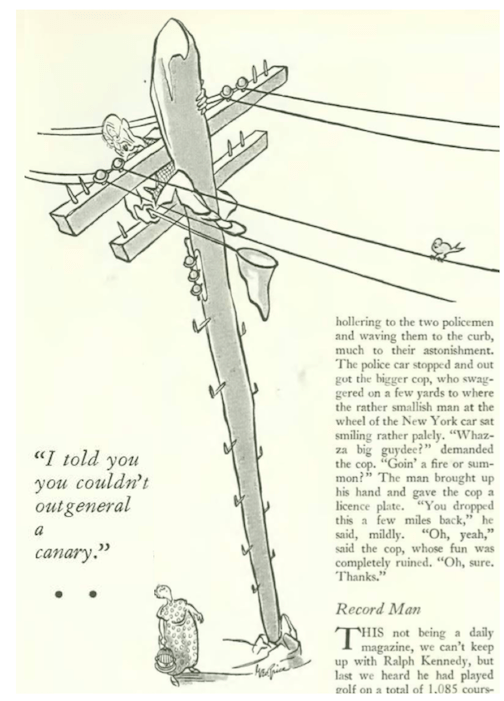
…and we close with George Price, master of oddities…
Next Time: The Night the Bed Fell…































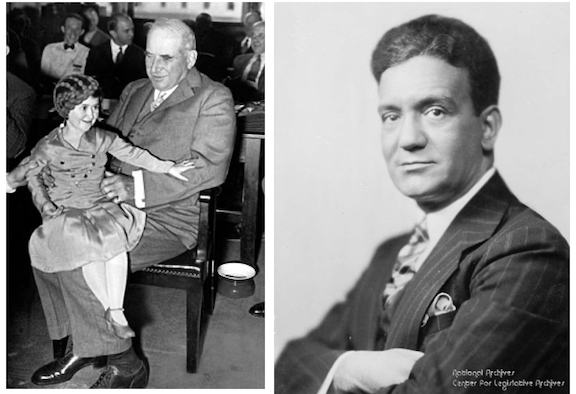






































































































 “
“