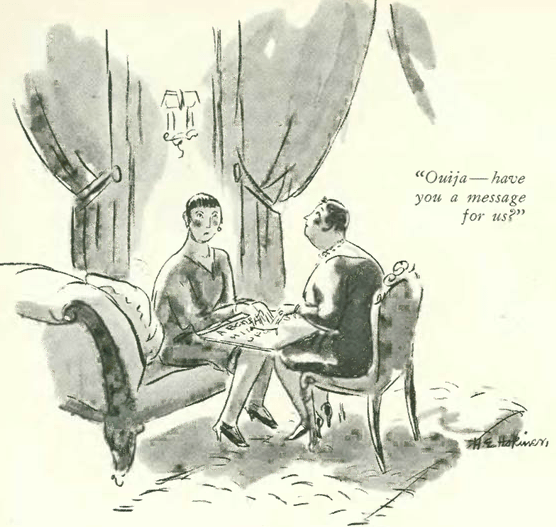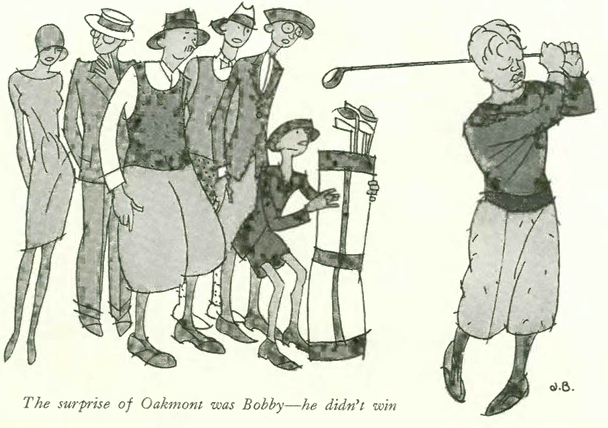Perhaps no other hairstyle has a stronger link to a historical period than the “bob cut,” associated not only with the flapper lifestyle in the 1920s but with women in general who wished to signal their independence from old cultural norms that defined femininity.

Women in Western cultures typically wore their hair long, but in the early years of the 20th century a few women of prominence began to flout convention and wear their hair in a bobbed style, including French actress Polaire, who began wearing her hair short in the 1890s; English socialite Lady Diana Cooper, who wore her hair short as a child and continued to do so as an adult; and dancer Irene Castle, who unveiled her “Castle Bob” to Americans in 1915. By 1920 the style was all the rage.

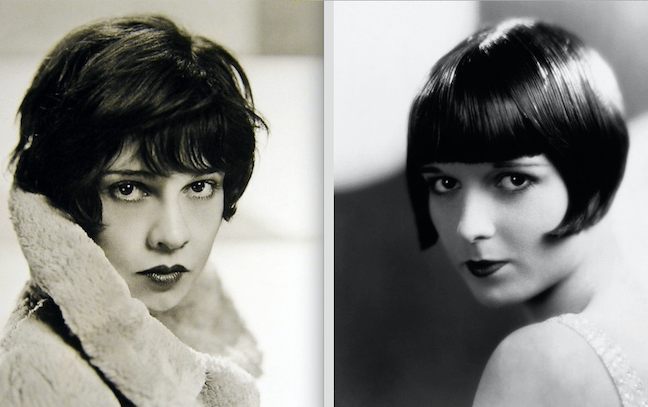
Another famous bobbed flapper of the 1920s was The New Yorker‘s own Lois Long, who wrote under the pseudonym “Lipstick” for her nightlife column “Tables For Two,” but signed her fashion column (“On and Off the Avenue”) with a simple “L.L.” Long was also a regular unsigned contributor to “The Talk of the Town,” and is credited as one The New Yorker’s early writers who gave the magazine its voice.
In the March 10, 1928 issue Long wrote in “On and Off the Avenue” about the challenges in maintaining her bobbed hairstyle:
Many women in the 1920s preferred to have a permanent wave treatment applied to their bob, which usually involved the application of high heat via a complex array of wires and hot rollers. In the March 10 issue, this ad promoted an alternative “cool method”…
…and in the March 17, 1928 issue, the Ace Comb company made a pitch to improve its market share by touting their hard rubber combs as ideal for the “ragged bob”…
…and for some further context on all things bobbed, following are some images gleaned from glamourdaze.com, including a page from a 1920s movie magazine featuring Paramount’s bobbed stars; a 1920s salon advertisement promoting bobs for all ages; and finally, a helpful reference card from the American Hairdresser, circa 1924…
* * *
A New Plot for Billy Haines
William “Billy” Haines was a top male box office draw in the 1920s, and throughout the decade was typecast in a number of comic roles as a conceited baseball player (Slide, Kelly, Slide), conceited cadet (West Point), conceited football star (Brown of Harvard), conceited golfer (Spring Fever), and conceited polo player (The Smart Set). It was that last picture that left The New Yorker wanting Haines to consider taking a different approach in his next picture:
Haines would eventually escape being typecast as a wisecracking, arrogant leading man, not by choosing different roles but by quitting acting altogether in 1935. The head of MGM, Louis B. Mayer, had demanded Haines deny his gay lifestyle (which he had lived quite openly despite the times) and marry a woman for appearances. Haines went on to become a successful interior designer, with clients ranging from Joan Crawford and Gloria Swanson to Ronald and Nancy Reagan.


In our featured cartoon from March 10, 1928, Helen Hokinson spied on her famous spinsters passing the time with a Ouija board:
Next Time: Broadway’s Soap Stars…