Introduce the topic of the Wickersham Commission at your next dinner party and you will most likely be answered with a puzzled silence.

However, in January 1931 it was THE topic of the month, especially among New Yorkers keen to see the end of Prohibition, which was the focus of the commission.
Established by President Herbert Hoover, the 11-member Wickersham Commission (officially, the National Commission on Law Observance and Enforcement) was not seeking to repeal the 18th Amendment, but rather to examine the criminal justice system under Prohibition, everything from police brutality and graft to the rapid rise of organized crime.

To the chagrin of many New Yorkers, the report (released on Jan. 7, 1931) called for even more aggressive enforcement of anti-alcohol laws.
This caused such a stir that The New Yorker dedicated the entire first page of “The Talk of the Town” to a satirical commentary furnished by E.B. White. An excerpt:

Humorist Will Rogers also commented on the report in this letter published on page 19 of the Jan. 26, 1931 edition of The New York Times…
…Algonquin Round Table co-founder Franklin P. Adams, on the other hand, summed up the Commission’s report with a poem:
Prohibition is an awful flop.
We like it.
It can’t stop what it’s meant to stop.
We like it.
It’s left a trail of graft and slime
It don’t prohibit worth a dime
It’s filled our land with vice and crime,
Nevertheless, we’re for it.
Back to The New Yorker, Howard Brubaker weighed in with his column, “Of All Things,” correctly noting that the majority of Americans wanted an end to Prohibition laws despite the Commission’s recommendations…
…and Rea Irvin gauged the mood of the parlor crowd in light of the report:
* * *
Polar Plunge
On to happier news, “The Talk of the Town” looked in on preparations for a North Pole trip by a refitted and renamed military submarine, Nautilus. An excerpt:


* * *
Dorothy, Abridged
Laid up with the flu, Dorothy Parker turned to some reading during her convalescence, only to find that the books provided to her (for review) were far from uplifting. One in particular, a censored version of D.H. Lawrence’s Lady Chatterley’s Lover, was downright galling. Excerpts:

* * *
Old Before Her Time
Lois Long was only 29 years old when she wrote her “Doldrums” series for The New Yorker, but the chronicler of Jazz Age nightlife who once epitomized the flapper lifestyle felt much older given how much the world had changed in just a few short years. She was particularly appalled by the younger generation’s embrace of “health and vitality” over her own generation’s lust for the party life…

…Long was mother to a toddler at the time, and would divorce husband and New Yorker colleague Peter Arno in the spring. This, no doubt, contributed to her feeling of estrangement from the younger generation:
Endnote: Bernarr MacFadden (1868-1955), referred to above, was an early proponent of body building and healthy diets that anticipated the rise of physical culture icons such as Charles Atlas and Jack LaLanne.
* * *
The Last Warrior
Paris correspondent Janet Flanner noted the passing of 78-year-old French Field Marshal Joseph Joffre, the last of the great World War I military leaders. Note that Flanner referred to Joffre’s war as “the world war,” since the next world war was still on the horizon.

* * *
From Our Advertisers
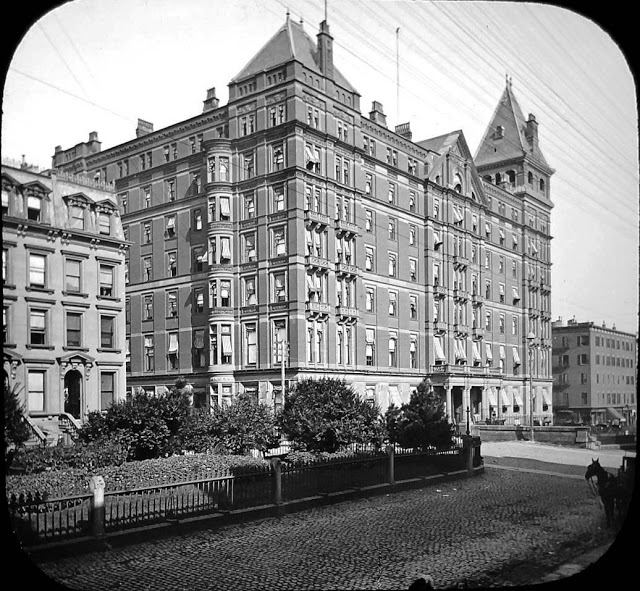
We have two of New York’s finest hotels advertised along with the newly opened National Hotel in Havana, Cuba. All three were under the same management at the time. The Cuban hotel would be heavily damaged two years later in a coup led by Fulgencio Batista. It would be restored, and eventually nationalized by Fidel Castro. The Savoy-Plaza would not be so lucky, demolished in 1965 to make way for the General Motors Building…

…and we have this lovely color ad from the makers of Alcoa aluminum chairs, which bespoke “the new vogue.” Alcoa created the market for aluminum furniture in the 1920s in an effort to increase demand for its aluminum products. It obviously worked, as all kinds of aluminum chairs and desks became ubiquitous by mid-century, especially in the workplace…
…on to our cartoonists…the Jan. 31, 1931 issue marked a big moment in New Yorker cartoons, as it featured James Thurber’s very first…
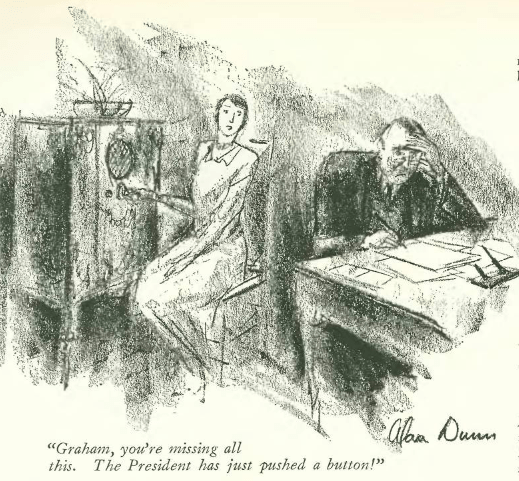
…Alan Dunn showed us a man who could not be distracted from financial woes…
…William Steig settled in as a New Yorker regular…
…Carl Rose gave us a lot of sour faces in a bank lobby…
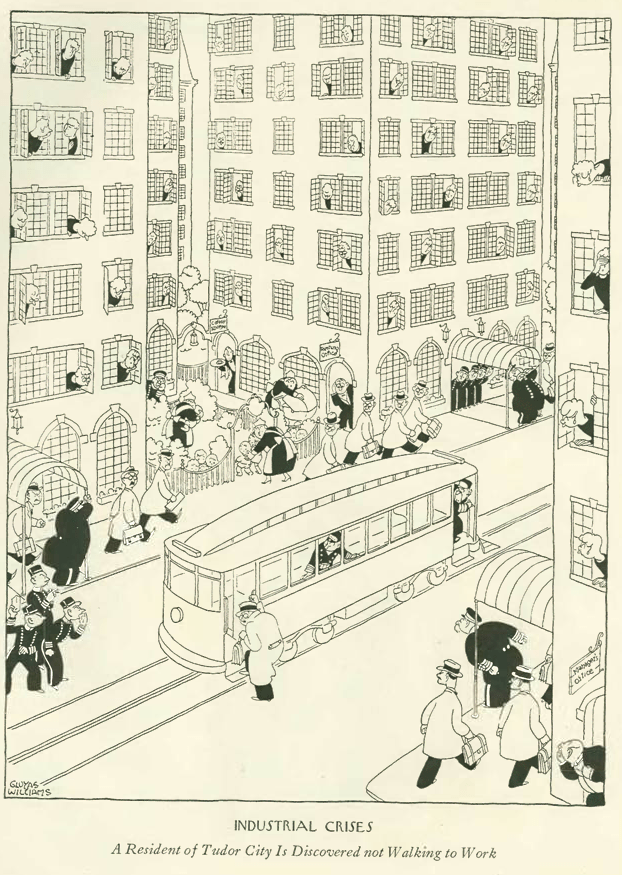
…and Gluyas Williams demonstrated the effects of decaf coffee…
…and before I go, here is a scene from the Third Academy Awards, which are referred to as the 1931 awards, although they were actually held on Nov. 5, 1930 in the Fiesta Room of the Ambassador Hotel in Los Angeles….

Next Time: And the Winner Is…