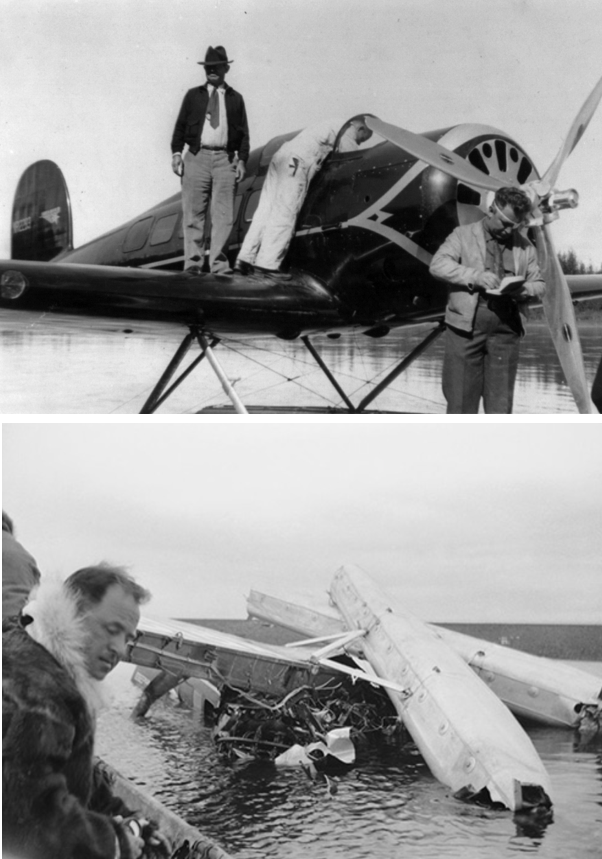
Above: Will Rogers (with hat) visits with pilot Wiley Post near Fairbanks, Alaska, hours before their fatal crash on August 15, 1935. (okhistory.org)
It would be a challenge to find a place for a multi-talented, mega-star like Will Rogers in today’s over-saturated and segmented media landscape—he was a trick roper, vaudevillian, social commentator, comedian, journalist, author, and radio and film celebrity. His early fame on the vaudeville circuit, including the Ziegfeld Follies, would spark a film career in 1918 (he would appear in 71 films), and a 1922 town hall speech would lead to a nationally syndicated newspaper column. When radio became a nationwide phenomenon his voice could heard coast-to-coast. He was seemingly everywhere.

Rogers (1879-1935) was also a big promoter of aviation, and he gave his audiences many entertaining accounts of his world travels. In the summer of 1935 he announced plans to join famed aviator Wiley Post (1898-1935) on a flight to Alaska and beyond. It appeared to be routine, making the trip’s tragic ending all the more poignant.
Although E.B. White often seemed stuck in the past—he preferred Model Ts and rattily omnibuses to more more modern conveyances—he was a flying enthusiast, never missing a chance to hop aboard an airplane and marvel at the scene far below. However, when tragedy struck, White would become circumspect. When Notre Dame coach Knute Rockne’s Fokker Trimotor crashed into a Kansas wheatfield, White expressed doubts about air safety and pondered “safer” alternatives such as autogiros (a kind of early helicopter that wasn’t so safe or practical). Such doubts returned in his “Notes and Comment” for August 31, 1935:
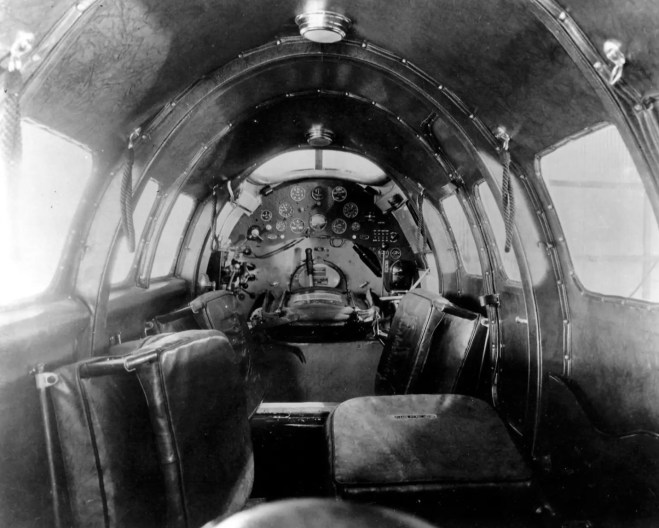
The fated aircraft, a Lockheed Orion, was heavily modified by Post into a floatplane; one wing was even salvaged from a wrecked Explorer (an older Lockheed model). The pontoon floats he attached were also designed for a larger aircraft, which made the nose-heavy Orion even more unwieldy.


When Post and Rogers arrived in Juneau, local bush pilots doubtfully regarded the Orion and asked Rogers about the flight plan. “Wiley and I are like a couple of country boys in an old Ford—don’t know where we’re going and don’t care,” he said. They were actually headed to Point Barrow, and from there planned to hop over to Siberia.
After stopping in Fairbanks they set off for Point Barrow in bad weather. Lost in the murk, they landed short of their destination in the shallow waters of Walakpa Lagoon, fifteen or so miles southwest of Point Barrow. Post and Rogers then took off—despite warnings from locals about the conditions. But the weather wasn’t the worst problem: Post had a bad habit of taking to the air in an abrupt, steep climb, which likely caused the engine to stall. Powerless, the ungainly aircraft plunged into the lagoon and landed on its top. Post and Rogers were killed instantly.

Rather than eulogize the fallen Rogers, “The Talk of Town” offered up an anecdote about his rise as a newspaper columnist, which was sparked by a backhanded endorsement speech:


* * *
Putting it Mildly
In “Onward & Upward With the Arts,” H.L. Mencken continued to explore the quirks of American language, this time looking at the pervasive (and evasive) use of euphemisms by “professional uplifters.” Excerpts:


* * *
At the Movies
We join film critic John Mosher to take a look at the latest epic from Cecil B. DeMille, The Crusades, which to Mosher’s disappointment was a rather mild epic, with little to astonish. However, our critic did find something to admire in a more recent historical drama, Diamond Jim.


* * *
From Our Advertisers
We begin with this advertisement from Lord & Taylor, featuring the latest fall fashions for young women heading to college…notable here is the inclusion of Mickey Mouse in the illustration…the animated rodent was in vogue as much the latest fashions…
…John Hanrahan, whose advertising savvy helped guide The New Yorker through its lean early years, was publisher of the richly designed Stage magazine, promoted here on the inside front cover…
…soft drink giant Coca-Cola recalled its soda fountain origins in this ad that promoted its 6.5-ounce bottled product…
…on the inside back cover Goodyear continued its series of perilous ads illustrating the dangers of tire blowouts (but not the obvious hazard of children riding untethered in a rumble seat, where they doubtless inhaled all manner of noxious fumes)…
…the majority of back covers in 1935 featured tobacco companies…here we learn that Lucky Strikes were more than cigarette; they were your “best friend”…
…on to our cartoonists, we start with this “Profile” illustration by William Steig…the profile was a two-parter featuring a clever summons server…
…Adolph Dehn adorned the “Goings On” section with this illustration…
…unsigned, but I’m pretty sure this is H.O. Hofman…
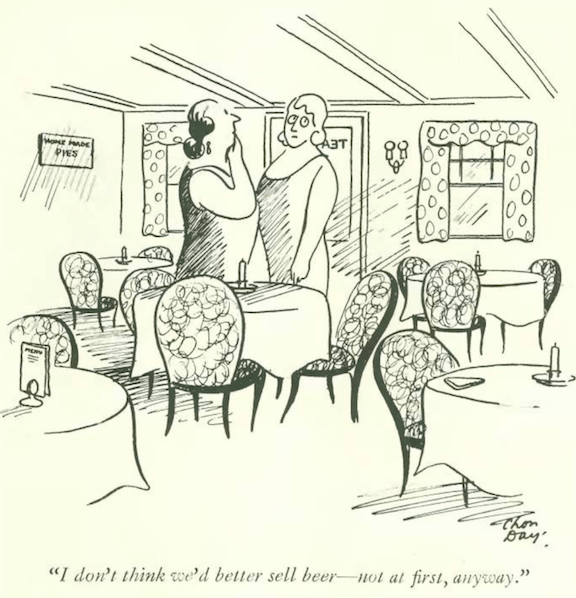
…here we get a lift from Robert Day…
…Al Frueh conjured up a nightmare of leaping sheep…
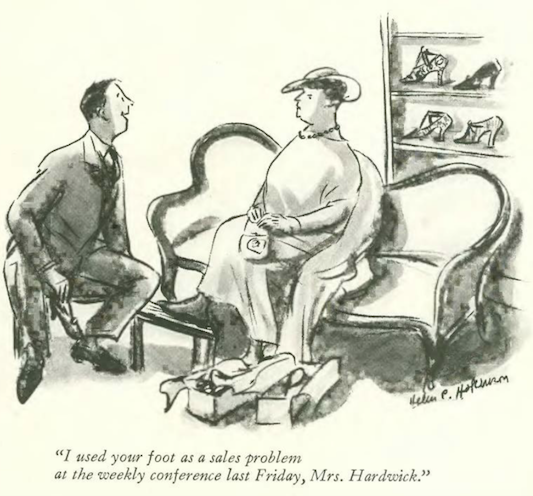
…Helen Hokinson gave us some famous footwear…
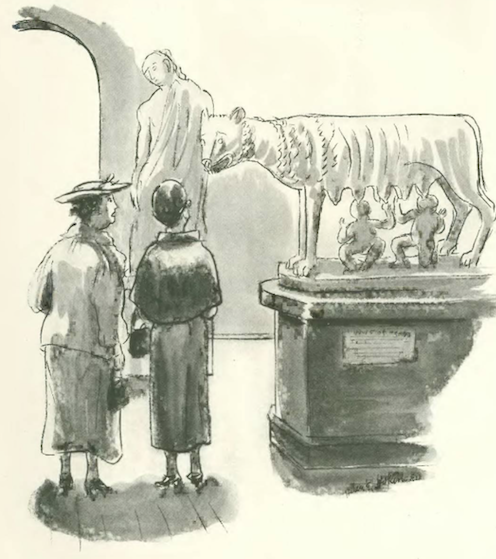
…Hokinson again, with Romulus and Remus providing a convenient metaphor…
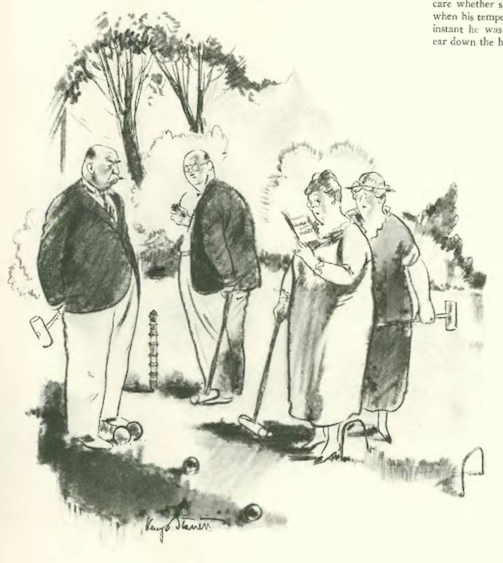
…Kemp Starrett was bogged down in the rules of a game…
…George Price discovered a budding talent…
…Richard Decker took to the back roads…(reminds me of a scene from The Long, Long Trailer with Lucy and Desi)…
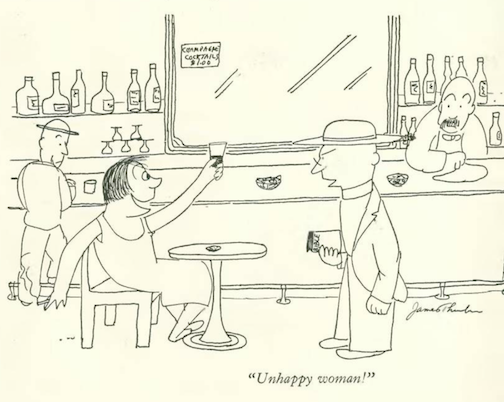
…James Thurber raised a glass to a dry do-gooder…
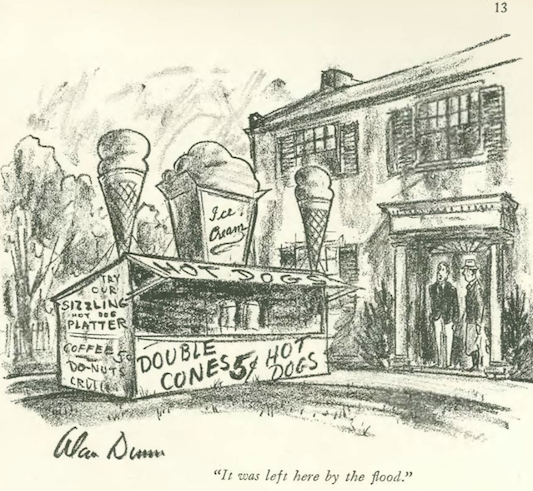
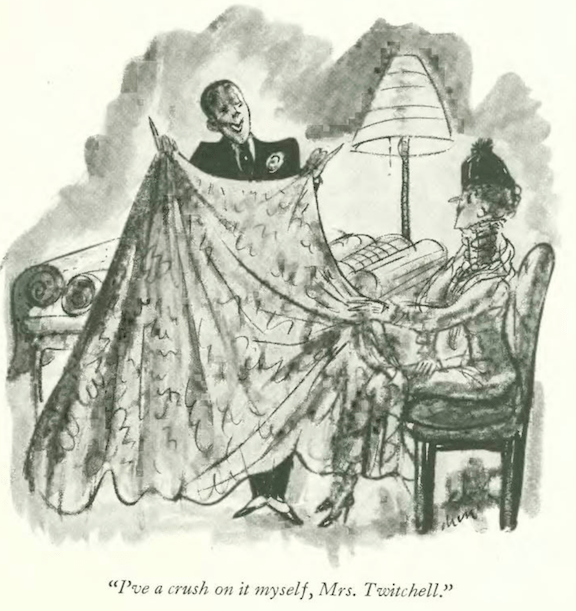
…Alan Dunn brought an unexpected windfall to Westchester…
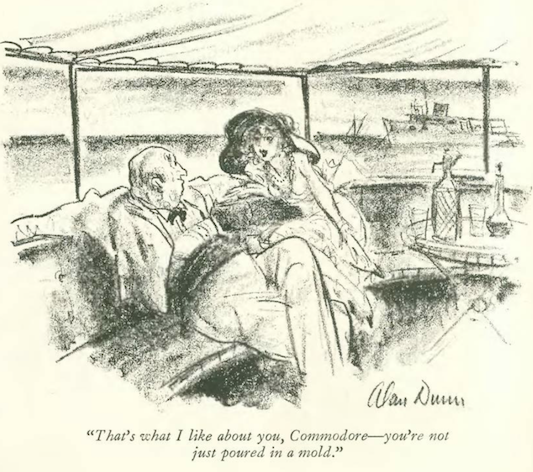
…and to close we Dunn again, and a bit of flattery…
Next Time: A Summer Night…