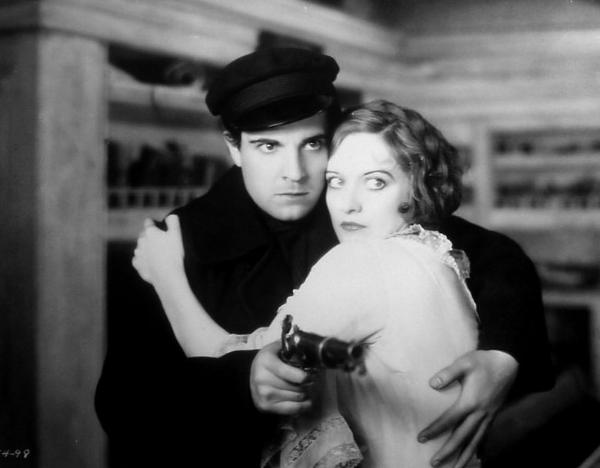
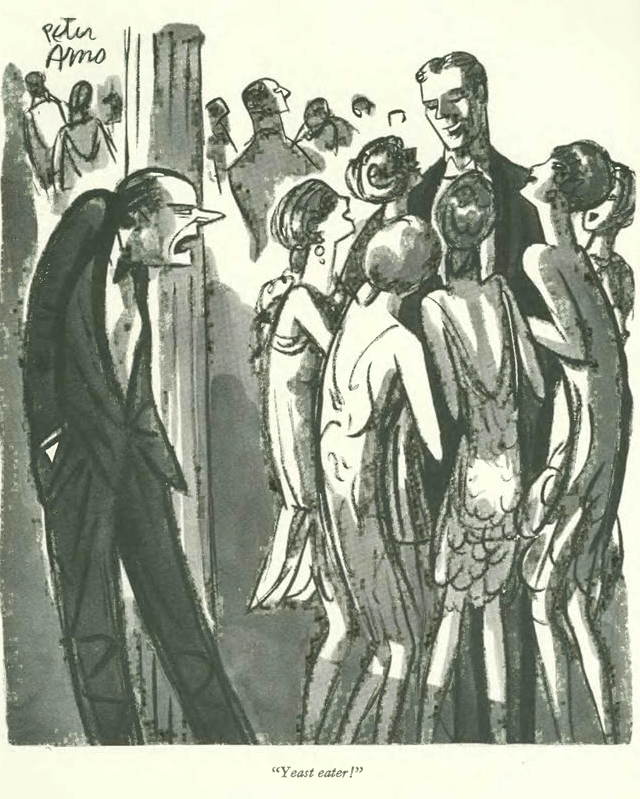Lights of New York would be a forgettable film if not for the fact it was the world’s first 100 percent talking motion picture. Yes, it was a bad film, but…

…even the July 14, 1928 New Yorker had the foresight to note that the film was destined to be a “museum piece.” Despite the corny plot and bad acting, the magazine’s critic “O.C.” had to concede that the film offered proof that sound would improve the motion picture experience.



The Jazz Singer (1927) launched a “talkie revolution” that would culminate nine months later in Lights of New York, and by the end of 1929 Hollywood was almost exclusively making sound films. But studios still released silent films into the 1930s, since not every theatre in the country was wired for sound.
The New Yorker had been slow to embrace sound in motion pictures (see my previous posts). What helped to win them over was the further refinement of the Movietone process, in which the sound track was printed directly onto the film strip (The Jazz Singer used Vitaphone, which essentially synched a record player with a film and provided a sporadic rather than continuous sound track).
In the same issue, writer Robert Benchley also predicted (in “The Talk of the Town”) that sound in movies would challenge actors whose voices weren’t as attractive as their screen images:


The New Yorker also noted that sound pictures would prove to a great “bonanza” to voice teachers:
 Transition to sound in the late 1920s would later provide the theme for the 1952 musical Singin’ In The Rain, in which Jean Hagen portrayed silent film star Lina Lamont, whose voice was ill-suited for talking pictures.
Transition to sound in the late 1920s would later provide the theme for the 1952 musical Singin’ In The Rain, in which Jean Hagen portrayed silent film star Lina Lamont, whose voice was ill-suited for talking pictures.

The New Yorker also noted that the advent of sound in motion pictures would put an end to many theatres operating on the vaudeville circuit:
In his regular column, “Of All Things,” Howard Brubaker gave his two cents about the new world of talking movies:
Paving Over Paradise
The July 14 “Talk of the Town” offered more bittersweet commentary on the city’s rapidly changing landscape. This time it was a famous stretch of lawns on West 23rd Street—London Terrace— that were being uprooted to make way for a massive new apartment block:
According to Tom Miller (writing for his blog Daytonian in Manhattan), Clement Moore, the writer to whom “A Visit from St. Nicholas” (“The Night Before Christmas”) “had developed the block when he divided up his family estate, ‘Chelsea.’ On the 23rd Street block, in 1845, he commissioned Alexander Jackson Davis to design 36 elegant Greek Revival brownstone townhouses. The row was designed to appear as a single, uniform structure or ‘terrace’ (a design not lost on The New Yorker). Unusual for Manhattan, each had deep front yards planted with shrubbery and trees. He called his development ‘London Terrace.'”

By October 1929, writes Miller, “a few weeks before the collapse of the stock market and the onset of the Great Depression, (developer Henry Mandel) had acquired and demolished all the structures on the enormous block of land. All except for Tillie Hart’s house. Hart leased 429 West 23rd Street and, although her lease had legally expired, she refused to leave, firing a barrage of bricks and rocks at anyone who approached the sole-surviving house. A court battle ensued while she barricaded herself inside. Finally, just four days before Black Tuesday, sheriffs gained entry and moved all of Hart’s things onto the street. She held out one more night, sleeping on newspapers in her once-grand bedroom, then gave up. The following day her house was destroyed.”

Miller writes, “to describe the new London Terrace was to use superlatives. Consuming the entire city block, it was the largest apartment building in the world with 1,665 apartments. It boasted the largest swimming pool in the city – 75 feet by 35 feet, with mosaic walls and viewing balconies. Twenty-one stories above the street a “marine deck” was designed to mimic that of a luxury ocean liner. It had a fully-equipped gymnasium, a recreation club, a rooftop children’s play yard with professional supervisors, and a large dining room. The doormen were dressed as London bobbies.”

* * *
In other diversions, Isadore Klein looked askew at the latest headlines, namely the big fight between Gene Tunney and Tom Heeney, one of the 20th century’s many “battles of the century”…
…while Helen Hokinson, on the other hand, offered some sketches of seafaring life…
…and looked in on the challenges of buying a hat…
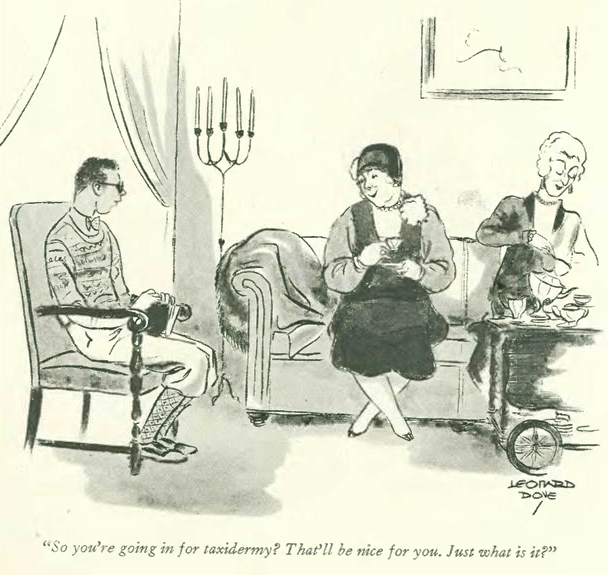
And to close, a cartoon by Leonard Dove…
…that referenced ads such as this one from the June 2, 1928 issue…
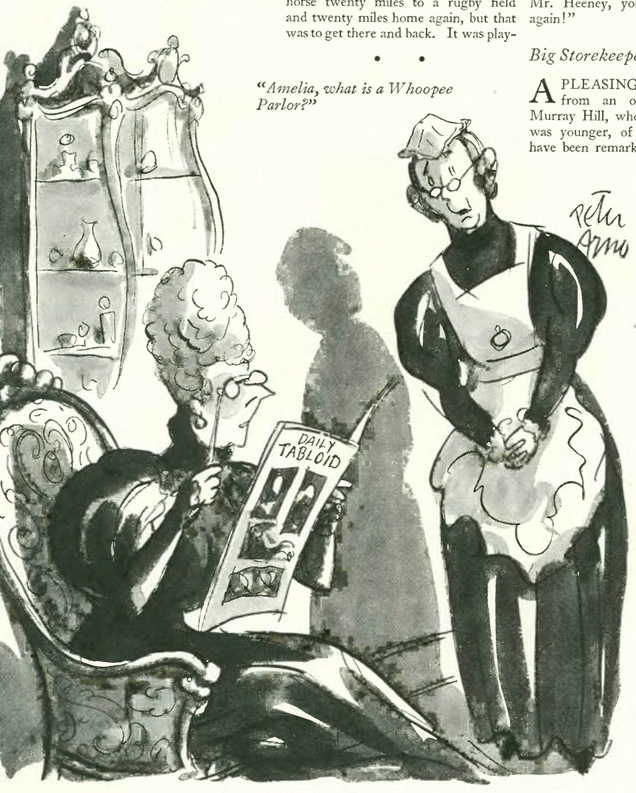
…and a comedy of manners, courtesy Peter Arno…
Next Time: Beyond 96th Street…