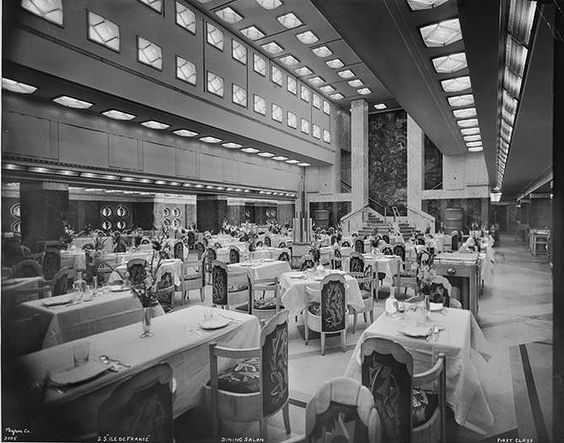
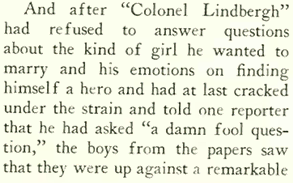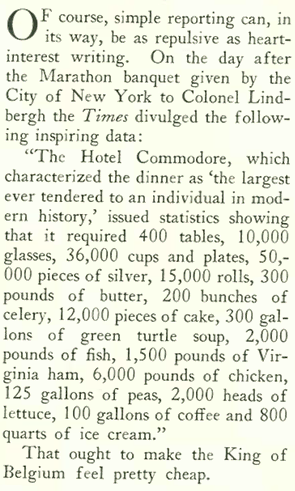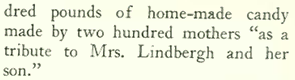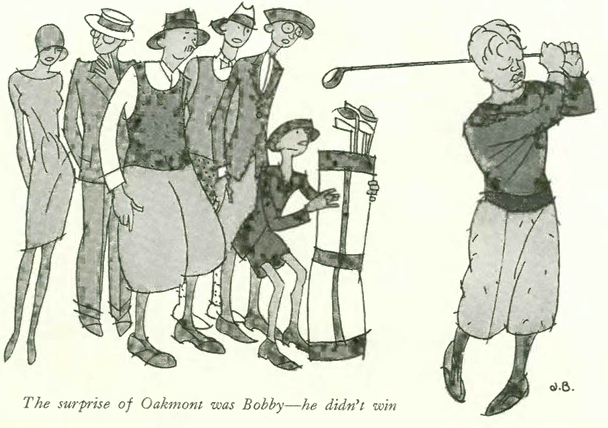Above image courtesy NASA History Office.
Charles Lindbergh was all over the July 2, 1927 issue of The New Yorker, which reported that Lindy was a better a flier than a writer, and as a celebrity the press had to be inventive with a subject who would rather be alone in a cockpit with a ham sandwich than be feted at countless banquets.

“The Talk of the Town” commented on the display at Putnam Publishing of a few manuscript pages penned by Lindbergh himself for his upcoming book, WE.
A draft of the autobiography had already been ghostwritten by New York Times reporter Carlyle MacDonald, but Lindbergh disliked MacDonald’s “false, fawning tone” and completely rewrote the manuscript himself–in longhand–using MacDonald’s manuscript as a template. Those early results were displayed in Putnam’s 45th Street window to whet the appetites of eager readers:


Nonplussed and often annoyed by all of the attention, Lindbergh was less than a colorful subject for the media. Philip Wylie (writing under the pseudonym “Horace Greeley Jr.”) in The New Yorker’s “Press in Review” column observed that reporters, seeking a more conventional image of a sentimental hero, decided to “supply him with emotions” he apparently lacked:
Other reporters resorted to treacly tributes…
…and if the subject himself wasn’t very interesting, you could always resort to listing quantities of food and drink as a measure of the spectacle…

And if the reception at the Hotel Commodore wasn’t to your liking, you could go to the new Roxy Theatre and put in a bid for 300 pounds of home-made candy:
* * *
We’ll give Lindy a break and move on to excerpts from Upton Sinclair’s “How to be Obscene,” in which he tweaks the Boston bluenoses:
And then we have this advertisement for the Orthophonic Victrola, promising to bring the clear tones of racism into your home courtesy of the Duncan Sisters:
The Duncan Sisters were a vaudeville duo who created their stage identities in the 1923 musical comedy Topsy and Eva, derived from the novel Uncle Tom’s Cabin by Harriet Beecher Stowe. The musical was a big hit.
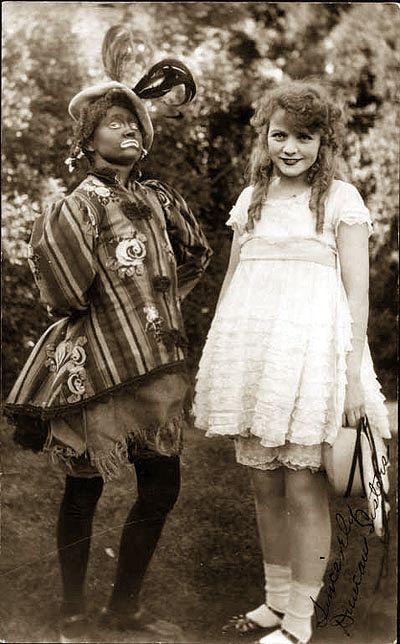


After a brief foray into movies in the early 1930s, the duo mostly entertained at night clubs and for many years continued to perform their Topsy and Eva routine even though appearing in blackface was considered impolite or offensive by later audiences. One of their final performances was on Liberace’s television show in 1956. The act ended in 1959 when Rosetta died in a car accident.

* * *
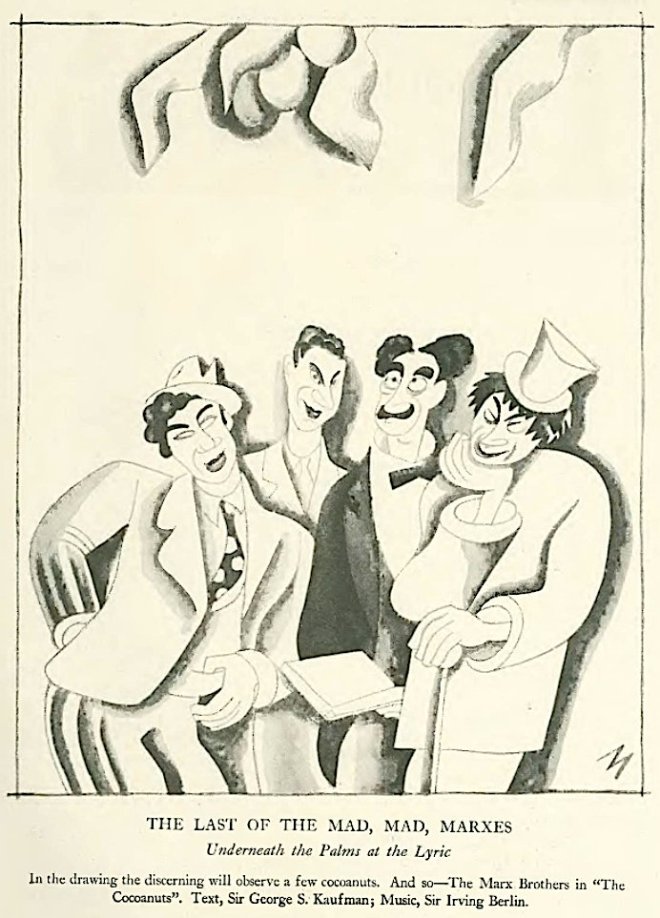
And to close, a cartoon from the July 2 issue, courtesy of Julian de Miskey:
Next Time: Summer in the City…