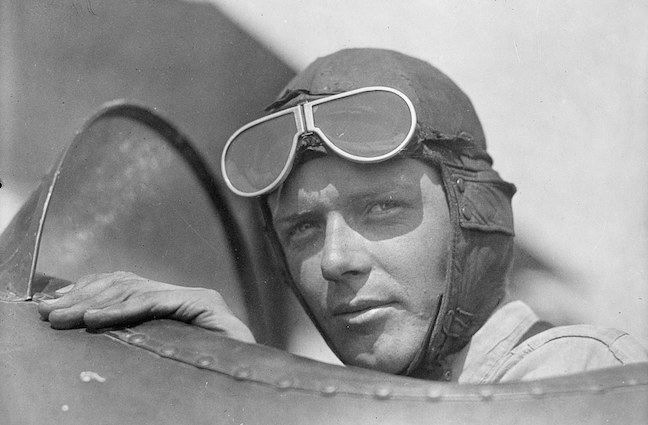
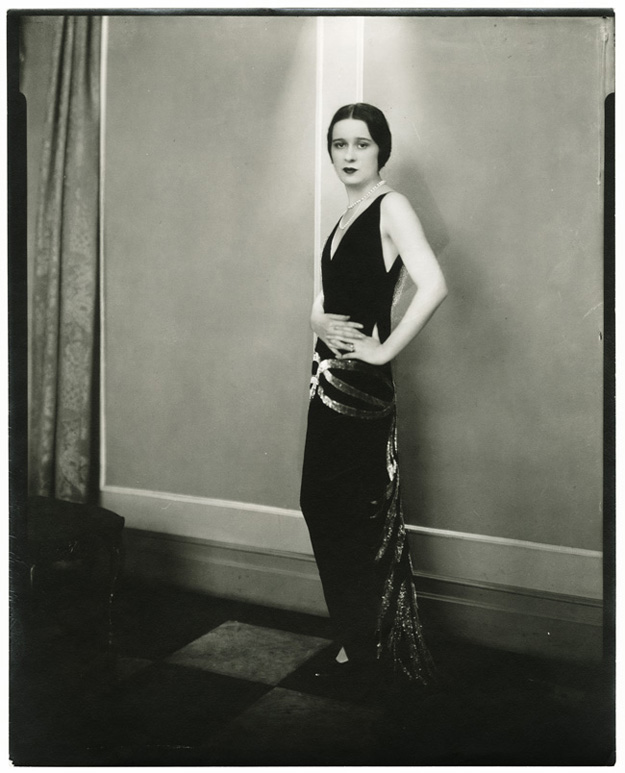
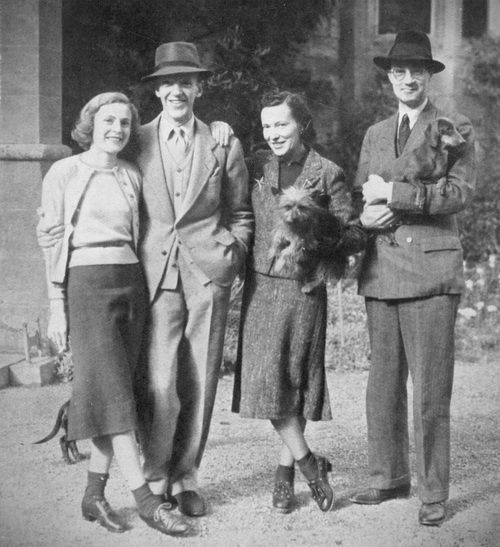
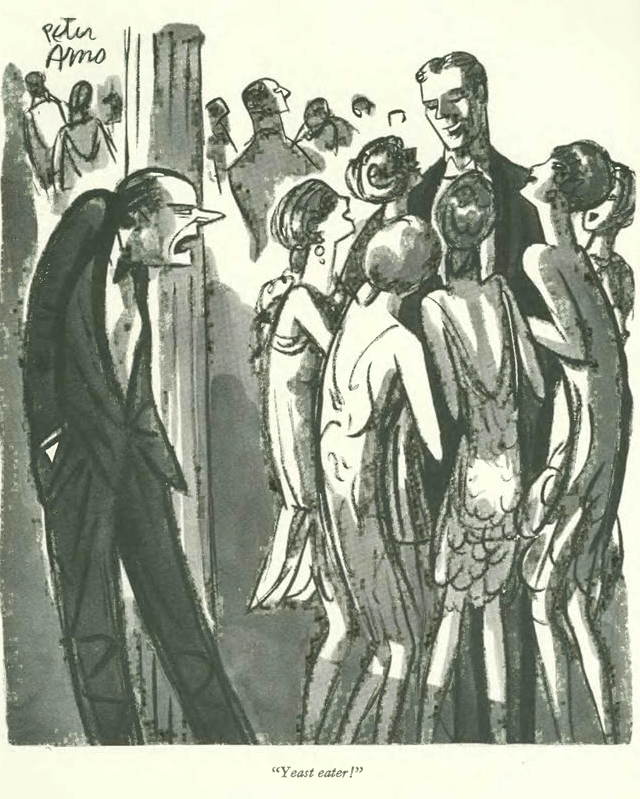Before there was Fred and Ginger, there was Fred and Adele, and during the 1920s and early 30s Fred and Adele Astaire were brother-sister dancing royalty and the toast of Broadway.

Fred and Adele Astaire were born a year apart in Omaha (she the eldest, born in 1898). Their mother wanted the siblings to learn professional dance at an early age, so in 1903 she moved with the children to New York City, leaving their Austrian-born father in Nebraska to work at the Storz brewery. By 1905 the brother-sister act were already popular on the vaudeville circuit, making their way to the Broadway stage by 1917.

Fred became friends with composer George Gershwin, and in December 1924 the Astaires headlined George and Ira Gershwin’s first full-length New York musical, Lady, Be Good!, in which Fred and Adele played a brother-and-sister dance team down on their luck. In real life, however, their star soared above Jazz Age New York. So when rumor had it that the duo was on the verge of a break-up, “The Talk of the Town” weighed in:

Today you would be hard pressed to find anyone young or old who hasn’t heard of Fred Astaire, his legend so firmly attached to our cultural memory. But at the time it was Adele’s fun-loving ways and mischievous charm that captured the hearts of reviewers and fans alike. Brother Fred, on the other hand, was more interested in devising the duo’s clever routines.
The April 21, 1928 New Yorker was correct in noting that Adele had plans to marry and leave the country, but happily the magazine was wrong on the timing; Adele and Fred would perform together nearly four more years, capping their 27-year partnership with the successful run of The Band Wagon on Broadway.
In 1932 Adele would marry Lord Charles Cavendish and move to Ireland, not England. Home would be Lismore Castle in County Waterford. The end of the partnership with Adele was traumatic for Fred, who was indeed interested in producing and race horses, but that was not his immediate future as The New Yorker suggested. Instead, his movie career would take off like a rocket in 1933 in a string of hits with Ginger Rodgers including The Gay Divorcee (1934), Top Hat (1935) and Swing Time (1936).
Fred Astaire briefly turned his focus to horse-racing when he announced his early retirement in 1946, but he would soon return to the screen with Easter Parade in 1948 and enjoy another string of hits in the 1950s. Though separated by an ocean, the brother and sister remained close through the years.



* * *
Not So Happy Feet
Morris Markey wrote several articles under the heading, “New York Interiors” (the last post featured his look at radio broadcasting). In the April 21 issue Markey took a look at the sad world of the “taxi dancers” in the ironically named “Happiness Hall.” This was the second time The New Yorker delved into the taxi-dancing world—Maxwell Bodenheim visited a Broadway dance hall in the June 12, 1926 edition of the magazine.
In both cases, the writers described a pathetic ritual for dancers and patrons alike, and both underscored a cruel illusion we still have today that the Roaring Twenties was an age of prosperity and good times for all. Excerpts:

Later in the article, Markey described a dance with a red-haired girl who showed him the ropes…
…and described the less than elegant environment of “Happiness Hall”…
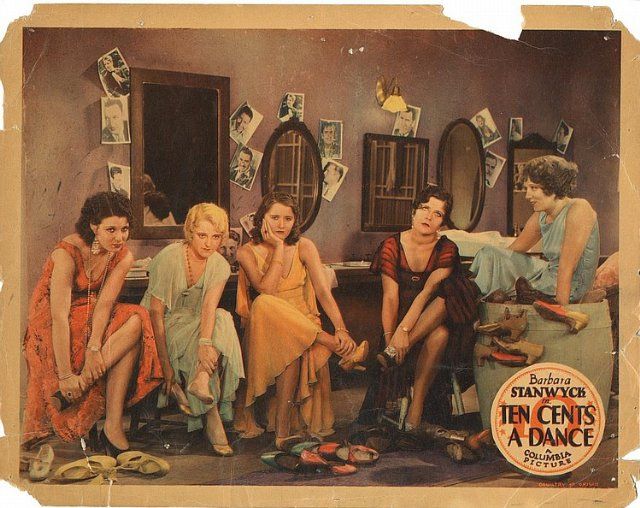
Markey concluded his visit by attempting to talk, rather than dance, with a graceful, yet hardboiled dancer:
In the 1920s Americans in general were poorer than they are today (money-wise) and lacked the safety nets that we have come to depend on in modern life. In 1929 economists considered $2,500 the income necessary to support a family. In that year, more than 60 percent of the nation’s families earned less than $2,000 a year—an income necessary for basic necessities—and more than 40 percent earned less than $1,500 annually.
For single women, such as the taxi dancers, the situation was just as bad or worse. Retail workers in U.S. faced long hours, poor working conditions and low pay, especially before the passage of the Fair Labor Standards Act in 1938. A clerk selling those beautiful clothes at Bloomingdale’s couldn’t afford those clothes herself, let alone make a living wage from the job. As Markey’s article made clear, taxi dancing was nothing but additional toil, 10 cents a pop.
From Our Advertisers…
We’ve seen cigarette advertisements featuring celebrity endorsements, but how about this one for Marlboro that suggested Christopher Columbus would have preferred their smokes…
…and then there were the ads for Fleischmann Yeast featured in nearly every issue of the early New Yorker magazine. According to Thomas Kunkel’s book, Genius in Disguise, Raoul Fleischmann was the wealthy scion of a New York yeast and baking family and a frequent guest of the Algonquin Round Table. He hated the baking business, so when founding editor Harold Ross pitched the idea of investing in his new magazine, Fleischmann obliged with $25,000. Ross and his wife, Jane Grant, together put up the other $25,000 (which included some IOU’s), but after the magazine was launched and struggled during its first months, Fleischmann was further obliged to pour in many hundreds of thousands of dollars to keep the magazine afloat (and in spite teasing from his friends that he might as well dump the money in the river).
The magazine was actually killed as early as May 8, 1925, when Fleischmann called Ross and other magazine directors together after Ross lost a large amount of money in a poker game (money he’d plan to invest in the magazine). Fortunately, the following day was fellow Round Tabler Franklin P. Adams’ wedding, and in the convivial atmosphere Ross and Fleischmann agreed to give the magazine another go. If Fleischmann was going to pour money into the magazine, he might as well get a little “free” advertising for his product. Hence the ads in The New Yorker promoting the generous consumption of fresh yeast cakes as a laxative and health tonic…
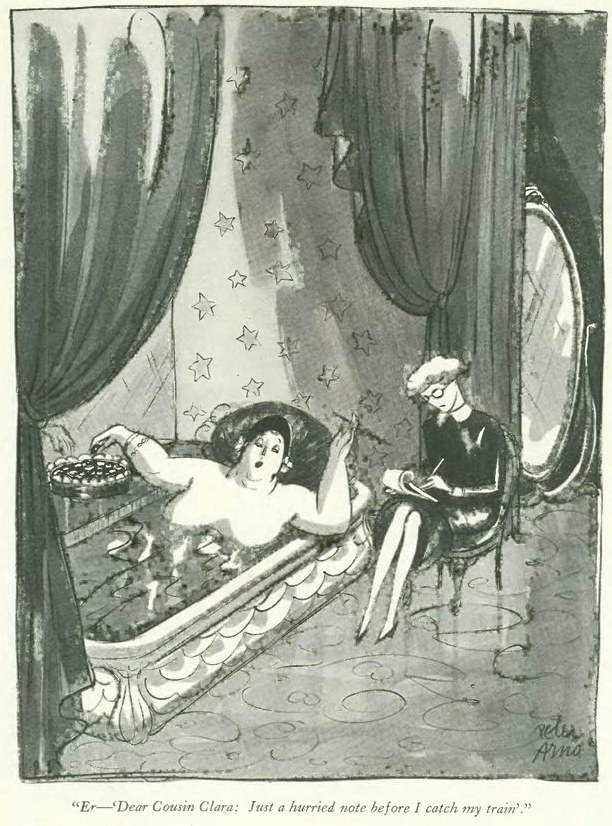
…and with that background information, this cartoon in the April 21 issue by Peter Arno makes a lot more sense
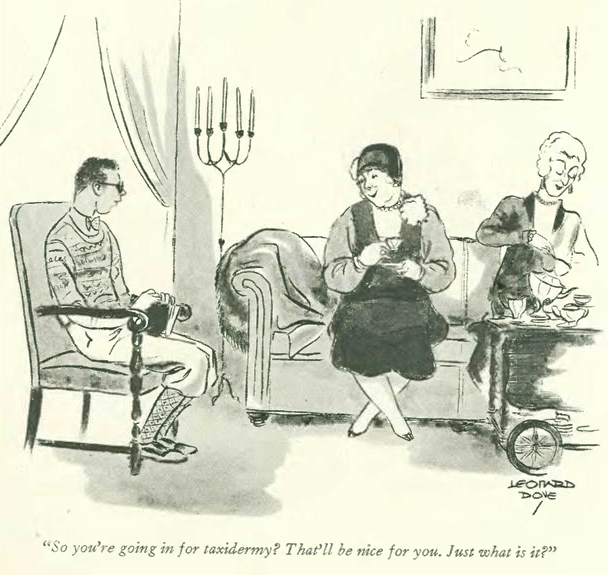
And finally, Leonard Dove takes a look at life in a growing metropolis…
Next Time: Back to Broadway…