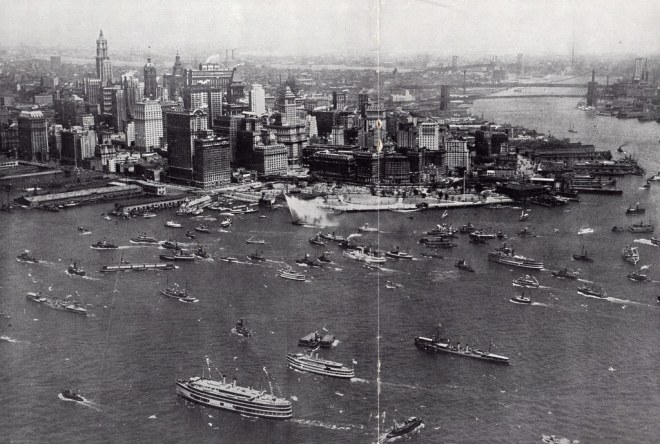
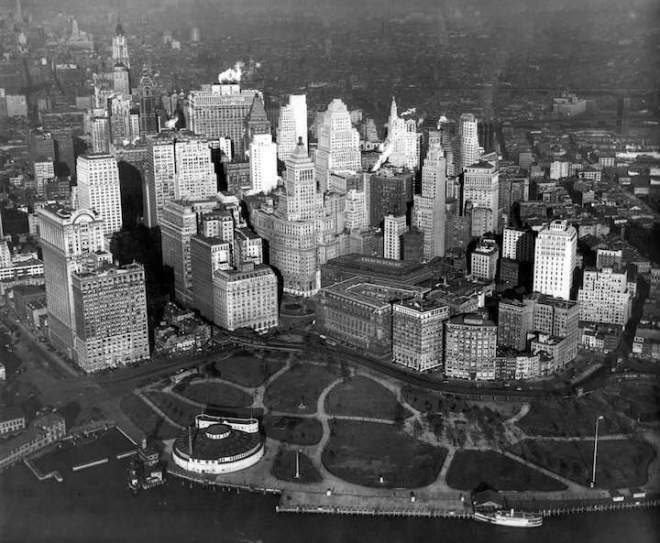
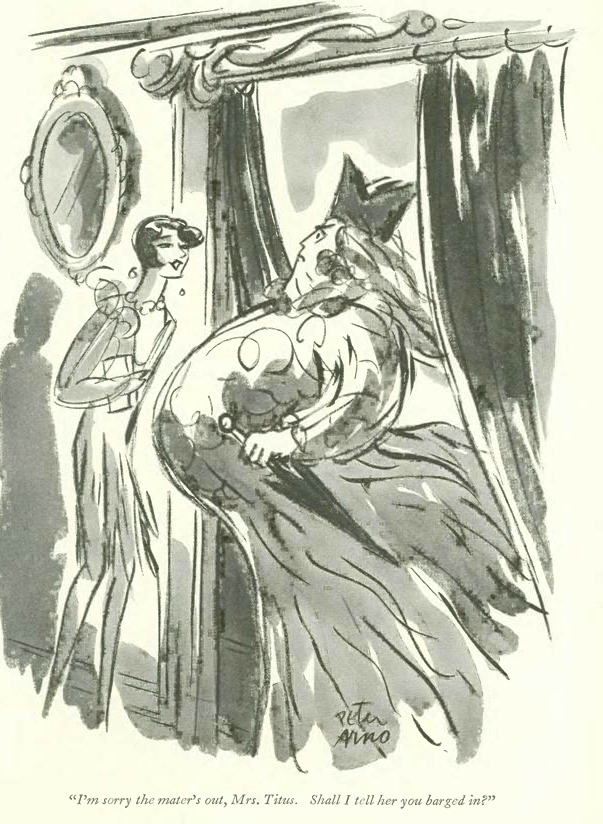Back in the days before we had a zillion different entertainment options, almost anyone with a pair of ears would tune in to hear the radio broadcast of a heavyweight title fight.

Jack Dempsey and Gene Tunney dominated the late 1920s, while Joe Louis, Max Schmeling and Jack Sharkey were marquee names in the 1930s along with Max Baer and Primo Carnera, who met on June 14, 1934 at the outdoor Madison Square Garden Bowl in Long Island City. The reigning champ Carnera (1906–1967), who stood six-and-a-half feet tall and weighed in at 260 pounds, had won more fights by knockout than any other heavyweight champion. But Baer (1909–1959) was known as a knockout puncher who beat one opponent so savagely that he died the following day.

Baer was also something of a showboater, a quality Morris Markey found distasteful when he wrote about the Baer–Carnera bout in “A Reporter at Large.”


Markey further explained why Baer’s behavior in the ring was so bothersome, and how it differed from the comic antics of other famous athletes:

Complications from diabetes would take Carnera down for good at age 60. Baer would die even younger, from a heart attack, at age 50. His last words reportedly were, “Oh God, here I go.” Baer’s son, actor and director Max Baer Jr. (best known as Jethro Bodine from TV’s The Beverly Hillbillies) is still with us, at age 85.
We aren’t quite finished with the Baer–Carnera fight…E.B. White led his “Notes and Comment” with this observation regarding the fight’s mass appeal and seeming universality:
* * *
Apologies to Ms. Winslow
I seem to have given short shrift to author Thyra Samter Winslow (1886–1961) who published more than 200 stories during her career in magazines such as The Smart Set and The American Mercury. She published more than thirty in The New Yorker, from 1927 to 1942, including the serialization of her short story collection, My Own, My Native Land. The story “Poodles” was featured in the June 23 issue.
According to the Encyclopedia of Arkansas, Winslow’s early life in Fort Smith (Ark.) “provided background for her view of small towns as prejudiced, hypocritical, and suffocating places…many stories expose the hypocrisy, prejudice, and carefully maintained social structures of both small town and urban life. She was particularly adept at portraying women of every social class, often in an unfavorable light. Money, especially the pursuit of it as a means to happiness or status, is an important theme throughout her work.”

* * *
Hot Enough For Ya?
So what did New Yorkers do when the summer heat set in? The next few items offer some clues, beginning with this poem by E.B. White:
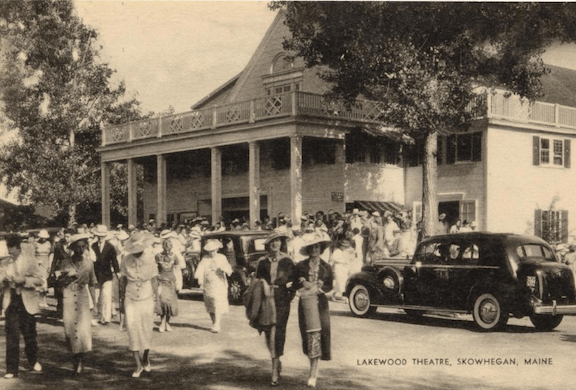
You could also take in some entertainment while enjoying the cooling breezes of the Hudson River. Robert Benchley hopped aboard the Alexander Hamilton to enjoy Bobby Sanford’s showboat revue:

“Tables for Two” took a look at summer dining options, from sidewalk cafes to hotel rooftops featuring dinner and dancing—this “Tables” was not written by Lois Long, but by Margaret Case Harriman, who knew a thing or two about nightlife (she was the daughter of the Hotel Algonquin’s owner, Frank Case)…



* * *
Get Yourself to Chi-Town
The Chicago World’s Fair (The Century of Progress) was in its second and final year, and The New Yorker found everything “terrific.” Excerpt:

* * *
From Our Advertisers
Just a couple of entries this week…You could take a plane to the Chicago World’s Fair on a United Airlines Boeing 247…
…the lower section of the ad claimed you could fly to Chicago in about five hours in planes featuring “Two pilots…stewardess…two-way radio…directive radio beam”…


…and what would our advertising section be without two fashionable people lighting up?…
…on to our cartoonists, we begin with Reginald Marsh’s illustration of a Rep Theatre production…
…Otto Soglow’s Little King found his artistic side…
…Rea Irvin continued his examination of native fauna…
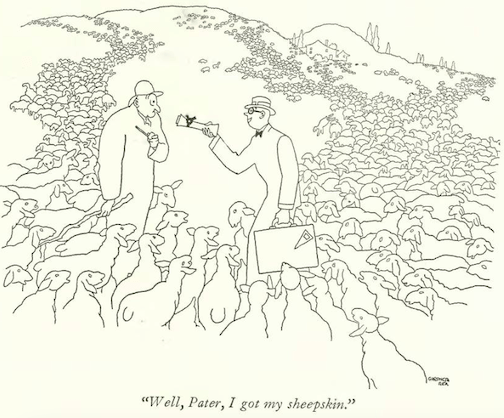
…Gardner Rea correctly predicted the global domination of Mickey Mouse…
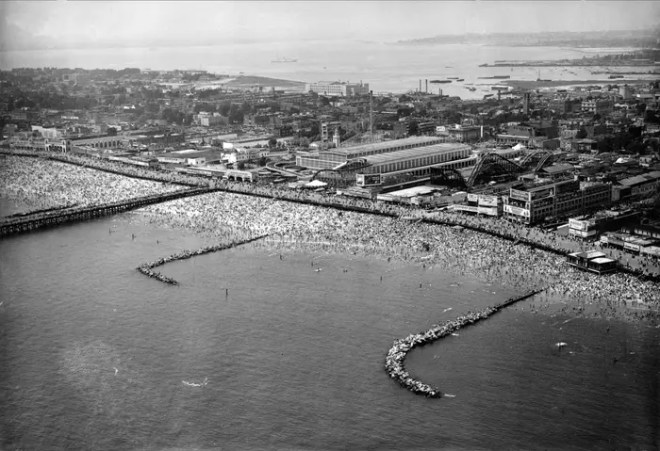
…Peter Arno showed the dizzying effects of a Coney Island ride…
…however at the altar the thrill was gone, per Garrett Price…
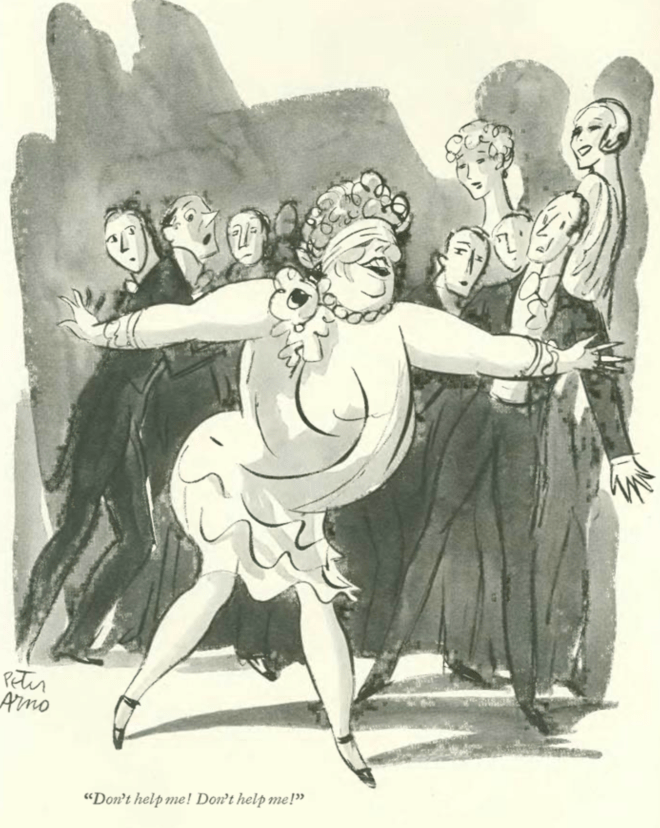
…another take on the ways of love, with Barbara Shermund...
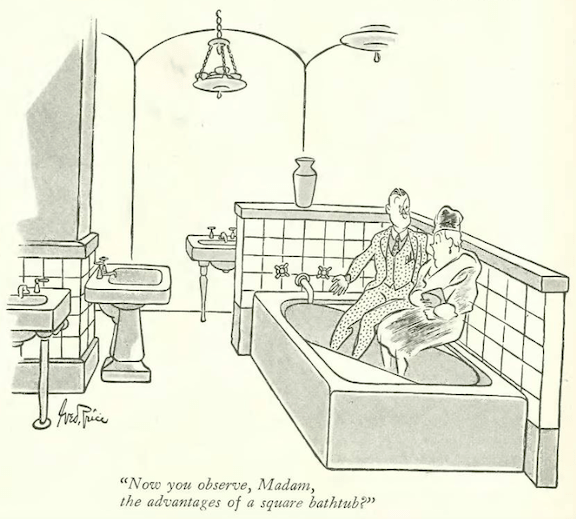
…the newfangled diagonal bathtub continued to dazzle, with George Price…
…Gardner Rea offered up some subtle irony on the farm…
…and we close with James Thurber, in a poetic moment…