Sigmund Gottfried Spaeth (1885–1965) sought to popularize classical music and improve the musical tastes of the masses by meeting the public wherever he could find them, from vaudeville halls to national radio broadcasts.

Born in a line of three generations of Lutheran clergymen, Spaeth chose a different path and became a musicologist who sought to de-mystify classical music, often demonstrating how popular melodies had origins in earlier music. He also had strong opinions about lyrics in popular music, demonstrating his distaste for “the lyric school of self-pity” in this “Onward and Upward” column. Excerpts:



Spaeth noted that not all sad songs were dripping in artificial self-pity, citing Helen Morgan’s “Why Was I Born?” as an example of a song modeled on “the legitimate blues,” marked by “a sincerity of expression in everyday language”…

* * *
Off to the Races
In his column, “Of All Things,” Howard Brubaker commented on the apparent competition and contrast between Alexander Woollcott’s book, While Rome Burns, and another with a rosier title, The Coming of the American Boom. It appears Woollcott’s book won out, at least in the long run, as I can find no trace of the Boom book, or its author.*
* One of our kind readers has identified the author: “The Coming American Boom” was written by Lawrence Lee Bazley Angas and published by Simon and Schuster in 1934. In 1939, Time noted that “Major Lawrence Lee Bazley (‘Boom’) Angas is a pink & white Britisher with a reputation for making daring predictions which have sometimes come true…. He won his nickname with a much-publicized booklet, The Coming American Boom, which heralded his arrival in the U.S. in 1934.”
Speaking of rosy outlooks, E.B. White offered some parting thoughts on Chicago’s World’s Fair, called “A Century of Progress.” Rather than focus on the grandiose exhibits, White wryly noted other signs of progress at the fair, as recounted from a letter he received from his nephew.
The Chicago World’s Fair featured all sorts of modern wonders “dedicated to the ideal of scientific advance”…
…but as with any World’s Fair, it also catered to the baser interests of the masses, with attractions such as Robert Ripley’s Believe It Or Not “Odditorium,” which was essentially a P.T. Barnum-style freak show…
…Ripley’s syndicated newspaper feature included these Odditorium attractions…
…White made light of exhibitions displaying such signs of progress as how to brush your teeth, and more examples of human freakdom…
…White’s nephew wrote of a man who could pull a wagon (containing his wife) with his eyelids, an apparently arthritic fellow who was “turning to stone,” and a man who could support heavy weights with his pierced breasts…

* * *
Letter From Paris
Paris correspondent Janet Flanner wrote that August 1934 was a “month of memories” as it marked the twentieth anniversary of the outbreak of the Great War, which we now call World War I. Flanner wrote about a new attitude that had arisen in those two decades, “a new attitude not only toward the last war but toward the next (which, ironically enough, seems increasingly inevitable to France since the death of the enemy warrior, von Hindenburg).” She continued with these observations made by French journalist and historian Emmanuel Berl (1892–1976), who wrote that as a result of the Great War, the youth in both France and Germany held few heroic illusions about war, seeing it not as a sacrifice but rather “as a means of being annihilated.”

* * *
From Our Advertisers
Clothing company Rogers Peet used the threat of humiliation to encourage young men to stock up on “authentic university fashions” before returning to campus…
…the Wanamaker department store took a different approach, offering up new styles with a heavy English accent (I say, didn’t we play tennis once at the Hon. Toppy Crew’s?)…
…the makers of Goodyear tires offered up this disturbing image to boost sales…
…this ad told us that “Mrs. Henry Field” collected fine art, loved to go to parties, and “always smoked Camel cigarettes”…I am unaware of the fate of Mrs. Henry Field, married to the grandnephew of Marshall Field, but this unseemly image suggests she was replaced by a wax figure before the photo was taken…
…on to our cartoons, we begin with spot illustrations from (clockwise, from top) Victor De Pauw, Abe Birnbaum, and an unidentified illustrator who offered this suggestion for beating the late summer heat…
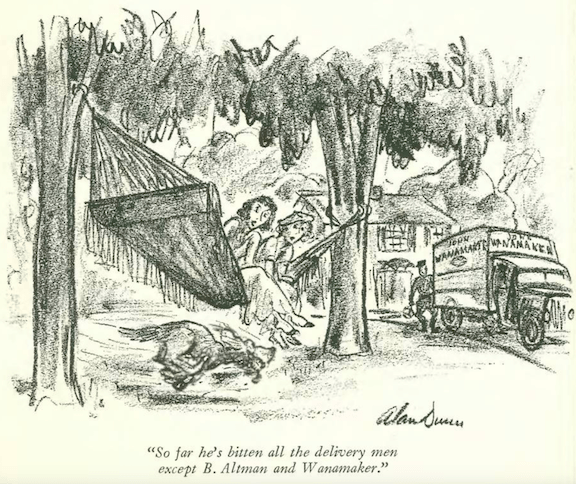
…we move along to Alan Dunn and a record-seeking pooch…
…Peter Arno with a very Arno-esque take on the stranded island trope…
…James Thurber gave us a man who was done making decisions…
…Richard Decker offered up this living history demonstration…
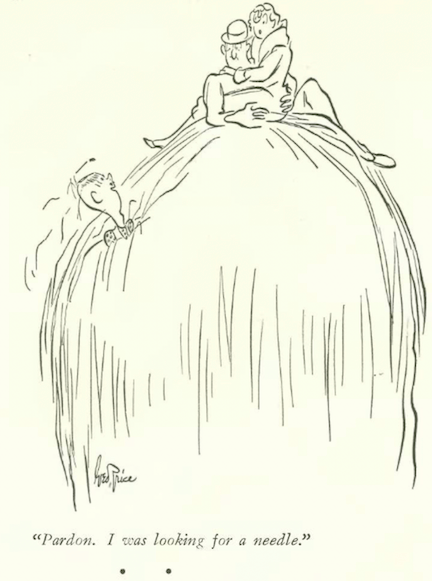
…George Price gave us two tropes for the price of one…
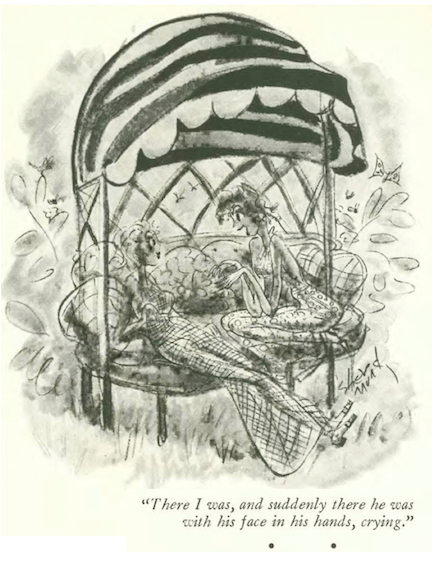
…Barbara Shermund gave us another glimpse into the lives of modern women…
…Rea Irvin continued his exploration of Manhattan’s fauna…
…our next cartoon is by Henry Steig, who used the pseudonym Henry Anton to avoid being confused with his brother, William Steig (featured on this issue’s cover)…unlike his brother, Henry was also a jazz musician, a sculptor and painter, a photographer, and a novelist…that is before he became a noted jeweler…
…Henry Steig’s jewelry shop at 590 Lexington Avenue can be glimpsed in the background of the famous subway vent scene from 1955’s The Seven Year Itch featuring Marilyn Monroe…
…and we close with Otto Soglow, and the last appearance his “Little King” in The New Yorker...William Randolph Hearst had lured Soglow away for his King Features Syndicate, debuting The Little King in his newspapers on September 9, 1934, where it would run until Soglow’s death in 1975…Soglow, however, would continue contributing cartoons of other themes to The New Yorker until 1974…
Next Time: Lunch at the Dog Wagon…