What do you do after an evening at the theater when the night is young and the city still thrums with excitement? In 1929 Manhattan, those willing to shell out a $5 cover charge (equivalent to nearly $120 today) and another $3 for front row seats could take in a show on the rooftop of the New Amsterdam Theatre — Florenz Ziegfeld’s Midnight Frolic.

The New Yorker’s Lois Long was on hand for opening night of the Ziegfeld Midnight Frolic, where the rich and famous gathered to enjoy after hours performances by Paul Whitman’s orchestra, singer and comedian Eddie Cantor (performing in blackface), and the boozy torch singer Helen Morgan. In her nightlife column, “Tables for Two,” Long observed:
Among the celebrities Long spotted at the Midnight Frolic’s opening night was actress and dancer Peggy Hopkins Joyce, famed for collecting men along with diamonds and furs:
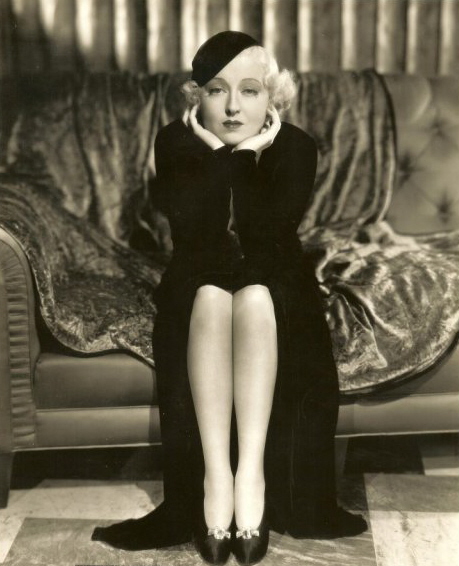


According to a Museum of the City of New York blog (posted by Nimisha Bhat), Flo Ziegfeld was tired of seeing his audiences leave after performances of his Ziegfeld Follies at the New Amsterdam Theatre on 42nd Street (and spend money elsewhere), so in 1915 he staged a new revue — the Danse de Follies! (later to be called Midnight Frolic) on the New Amsterdam’s underused 680-seat roof-top level that included tables, box seats, and a balcony. Ziegfeld added a glass walkway that would allow chorus girls to dance above the audience, affording some customers a more risqué perspective on the dancers.
Bhat writes that the club “stayed open year-round for seven years and while World War I couldn’t stop the Midnight Frolic, Prohibition was ultimately what led Ziegfeld to end the show in 1922.” In 1921 Ziegfeld told The New York Times: “The best class of people from all over the world have been in the habit of coming up on the roof … and when they are subjected to the humiliation of having policemen stand by their tables and watch what they are drinking, then I do not care to keep open any longer.” The show Lois Long attended in January 1929 was a revival of the Midnight Frolic, and although Prohibition was still the law, by 1929 it was widely flaunted if not completely ignored by many New Yorkers. Long also noted changes to the rooftop, including a new decor by famed theatrical designer Joseph Urban:




There is a filmed performance of Eddie Cantor allegedly made that night at the Ziegfeld Theatre Roof Garden, but it was actually filmed on a soundstage at the Paramount Astoria studio in Queens. You can tell it is staged because during Cantor’s performance he recognizes some of the celebrities who were at the opening (the camera shifts to them as they take bows), but when he calls out Peggy Joyce the camera stays on Cantor. Apparently she didn’t find it necessary to participate in this charade. Nevertheless, this video gives you some idea of what was presented at the Midnight Frolic. And one wonders why Cantor performed in blackface, since it’s just his standard song and gags schtick:
* * *
Mea Culpa
Also in the Jan. 12 issue was this small ad in the back pages — an apology from Texas Guinan, actress, producer, and entrepreneur well-known to New York nightlife (and to the vice squad):

* * *
Nevertheless, Prohibition Continued to Suck…
The Jan. 12 “Talk of the Town” addressed the sheer folly of Prohibition enforcement:


The “Talk” item also addressed the new police commissioner’s approach to enforcement of the unpopular law:
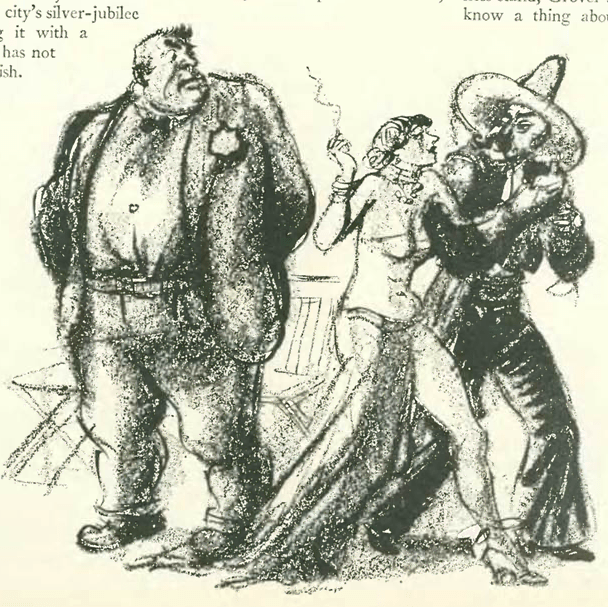
And as it happened, Grover Whalen was also the subject of the Jan. 12 “Profile,” which included this illustration by Peter Arno:
* * *
How’s the Old Ticker?
The “Talk of the Town” also marveled at the technology behind the famed news ticker in Times Square, inaugurated on election night the previous November:

The news ticker, known as the “zipper” (which inspired the news crawl at the bottom of today’s cable news channels), made Times Square the place to be when big events were announced. According to Wired magazine, the zipper, invented by Frank C. Reilly, “was the technological marvel of its day, extending 380 feet around the Times Tower and, with a band 5-feet tall, the moving letters were visible from a distance of several city blocks.” Wired cites a 2005 New York Times column to describe how it worked:
“Inside the control room, three cables poured energy into transformers. The hookup to all the bulbs totaled 88,000 soldered connections. Messages from a ticker came to a desk beside a cabinet like the case that contained type used by old-time compositors. The cabinet contained thin slabs called letter elements. An operator composed the message letter-by-letter in a frame. The frame, when filled with the letters and spaces that spelled out a news item, was inserted in a magazine at one end of a track. A chain conveyor moved the track, and each letter in the frame brushed a number of contacts. Each contact set a light flashing on Broadway.” Reilly calculated that there were 261,925,664 flashes an hour from the zipper’s 14,800 bulbs.
* * *
From Our Advertisers
A couple of clothing store ads which demonstrated a more modern look in graphic design…
…and two terrific illustrations (out of four in a two-page spread) by Reginald Marsh that decorated the “Profile” section of the magazine, featuring scenes from the Webster Hall nightclub in the East Village…
…and our cartoon, courtesy of Roch King:
Next Time: The Bootleg Spirit…















Most Times Square area “zippers” in those days used the same type of old-fashioned means to deliver their messages. Not until the 1940’s when Trans-Lux began building their “Flashcast” and “Adcast” traveling message signs, followed in that order by Naxon Telesign with their zippers, would they go to the next step in having messages transmitted to said zippers via paper perforators (about the size on some teleprinting systems) with the various alphanumeric character forms traveling through electronic systems (a more modern equivalent of the “contacts” in the system used around the Times Tower). The band may have been 5 feet, but the 12 rows seemed spaced 4.5″ apart per row, ergo the characters would have been 4′ 6″ high – and the columns 4″ apart.
When the Times Tower was stripped and recast as the Allied Chemical Tower in 1965, they installed a new zipper (Mk. II) with a reported 12,408 bulbs – which, given that this zipper was 11 rows high, made out to be 1,128 columns around the building. They went through at least three different controls [Telesign’s by Life magazine from AP dispatches; a newer, computer based system supplied by Reuters, from 1971 to 1977, which 5 x 7 type was also on Facit 4553 printers, Practical Automation printers of receipts and ticket stubs, and some scoreboards such as on a few days of the 1976 Summer Olympics in Montreal and 1980 Winter Olympics in Lake Placid; and after 1986, Daktronics’ “Venus” system as applied first by New York Newsday, then (at the point it was replaced in 1997 with an LED zipper) by Dow Jones].
LikeLike
Thanks so much for this. Amazing what they could do in the days of analog…
LikeLike