MGM spent nearly $5 million (about $70 million today) to make the silent epic Ben-Hur, filming the movie on location in Egypt, Italy and the United States. The New Yorker’s film critic Theodore Shane was not impressed.
Shane wrote that $4,999,999.95 had been spent “on massive effects and the remaining $.05 on drama.”
He noted, however, that the original story, an 1880 novel by Lew Wallace (who was a Union general in the Civil War, among other things), was pretty lacking in drama to begin with, just a “piece of bric-à-brac romance (that was) nothing more than a super Rover Boys story touched up with a Biblical background.” Here’s Shane’s entire review of the film, which was released by MGM on December 30, 1925:

This was actually the second Ben Hur film. The first was made in 1907, a 15-minute silent costing $500 (and it really was made on the cheap; the producers stole some shots of a mock chariot race at a fireworks show at Sheepshead Bay, Brooklyn, and then added some interior shots to complete the picture).
For the 1925 Ben Hur, filming on location proved difficult from the start. Italy’s new leader, Benito Mussolini, was in an anti-American mood when production began, and labor disputes often delayed filming. By all accounts, conditions were miserable. Kevin Hagopian, in an essay for the New York State Writers Institute, observed “The worst agonies were reserved for the film’s climax, the chariot race. Legendary second unit director B. Reeves Eason’s nickname “Breezy” was certainly not earned by his work on the Ben-Hur set, for his merciless pace cost the lives of over a hundred horses. As [actor Francis X.] Bushman said sadly, “If it limped, they shot it.” A stunt man was killed in a chariot crash, and [actor Ramon] Navarro himself only narrowly escaped death.”
The troubled Italian set was eventually torn down and a new one built in Culver City, California. The crowd scenes and master shots for the race were done in a single day, with forty-two cameras covering the action.

In “Profiles” Esther Carples looked at the life of Sergei Rachmaninoff, who was widely considered one of the great pianists of his day, and as a composer represented the last vestiges of Romanticism in Russian classical music. Carples painted a portrait of a brooding genius, a man with aristocratic bearing who lived in lonely exile from his native Russia.

In 1921, Rachmaninoff bought a house on 33 Riverside Drive in New York City, where he lived until 1925. There he consciously recreated the atmosphere of Ivanovka (his beloved Russian summer house) entertaining Russian guests, employing Russian servants, and observing old Russian customs.
*****

Let’s move on to the next issue, Jan. 16, 1926. “The Talk of the Town” noted another loss of a Fifth Avenue landmark with the Savoy Hotel was falling to the wrecking ball.
The Savoy, built in 1891-92, was slated to be replaced by The Savoy Plaza Hotel, which itself would be demolished in 1965-66 (amid significant public outcry and protest) to make way for the eastern headquarters building of General Motors.
It was observed that the new year would see a boon in construction of huge new buildings along the Avenue, and buildings only five years old (such as Heckscher Building) would be dwarfed by the new towers.

The New Yorker continued to have fun with actress Gloria Swanson‘s pretensions to royalty (she was married to the Marquis de La Coudraye at the time). This time it came from the pen of Jimmie the Ink (James Daugherty), part of his series of drawings that coupled famous people of the day in comic situations:
The issue also featured Helen Hokinson with a cartoon that seemed more in Barbara Shermund’s wheelhouse…
…a Julian de Miskey drawing for the theatre section…
…and a Peter Arno illustration…
To close, two ads from the Jan. 16 issue, this one appealing to Anglophilic, aristocratic aspirations of certain readers…
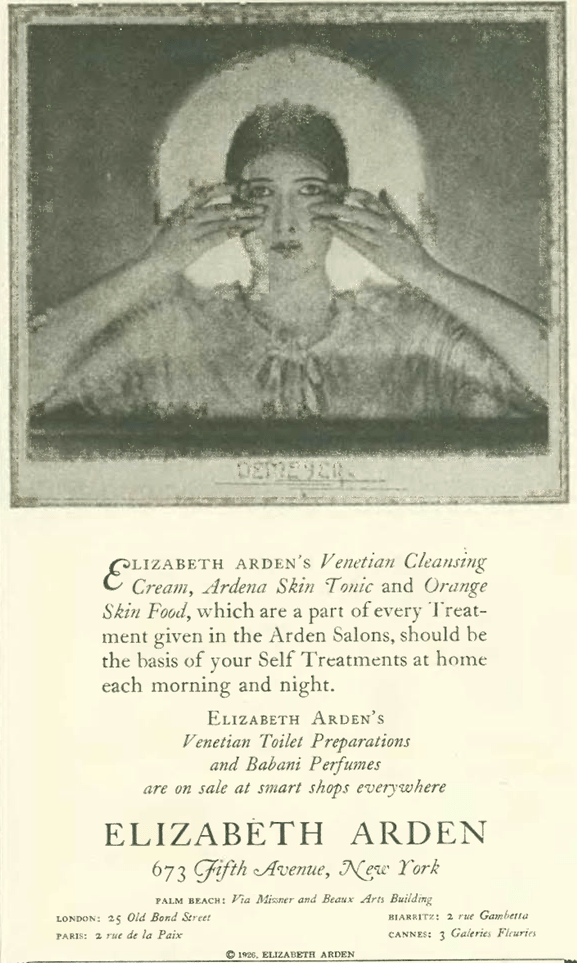
And this one from Elizabeth Arden, who will become a mainstay in the magazine with these ads featuring women with ghostly stares, usually with their heads wrapped tightly to combat sagging skin. Thanks to Hollywood, it was the age of the close-up, so wrinkles and blemishes be gone!
Next Time: Lois Long Talks Cars…