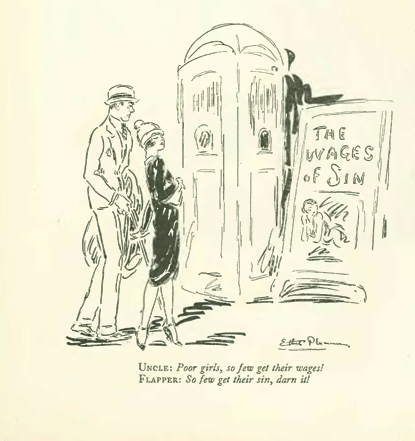ABOVE: Although Harold Ross looms large in most accounts of the early New Yorker, his wife at the time, Jane Grant, played a major role in its conception and launch.
After a year hiatus, during which I changed jobs (yes, I’m still “hewing the wood and drawing the old wet stuff,” as Bertie Wooster would put it), I am returning to A New Yorker State of Mind, just in time for the 100th anniversary of the greatest magazine in the world.

Before I continue where I left off—the tenth anniversary issue, Feb. 15, 1935—let us mark the magazine’s centennial year with a look back at the first issue, Feb. 21, 1925.
It is remarkable that after a century the magazine still retains its character, even if it is more serious these days, and more topical, and, most egregious, still fiddling with Rea Irvin’s original designs (for more on this issue, please consult Michael Maslin’s Ink Spill. In addition to being one of the magazine’s greatest cartoonists, Maslin offers a wealth of New Yorker insight and history, including his longstanding crusade to restore Irvin’s original artwork for “The Talk of the Town,” which was removed and replaced by a contemporary illustrator’s redraw in 2017).
Although founder and editor-in-chief Harold Ross set the tone for the magazine in the first issue, famously proclaiming “that it is not edited for the old lady in Dubuque,” it was Irvin that gave the magazine a signature look that set it apart from other “smart set” periodicals of the day.
It took a few issues for the editors to sort out regular features and their order of appearance. The opening section of Issue No. 1 featured the Irvin masthead—flanked by Eustace Tilley and the night owl—and Irvin’s distinctive typeface that would introduce “The Talk of Town” for many issues to come. However, in that first issue, “Of All Things” appeared under the masthead, followed by “Talk of the Town” which was (for the first and last time) under this banner:
As for Ross’s manifesto, it appeared at the end of “Of All Things,”…
…and “Talk” ended with this signature…
…In Defining New Yorker Humor, Judith Yaross Lee wrote that early readers of The New Yorker would have recognized the Van Bibber III persona “as a joke, a personification of Van Bibber cigarettes, whose ads targeted the devil-may-care, swagger young man about town all dressed up for the opening night. As an insiders view of the urban scene, Van Bibber’s accounts featured casual conversation—that is, talk.”

The magazine’s very first cartoon was by Al Frueh…
…and among the features that persisted through the years was “Profiles,” the first one featuring Giulio Gatti-Casazza (1869-1940), who served as Metropolitan Opera’s general manager for a record 27 seasons (1908-1935).
The profile featured this illustration by Miguel Covarrubias, the renowned Mexican painter, caricaturist, and illustrator, who was a frequent contributor to the early New Yorker.
“Goings On” also persists, sans the original artwork…
…the same goes for these sections…
…still others disappeared altogether…
…some would hang around for awhile…
…others for just a few issues…”The Hour Glass” featured brief vignettes of local personalities…
…such as the ever-fascinating antics of Jimmy Walker, who would soon be elected mayor…
…while “In Our Midst” detailed the comings and goings of other locals…
…including The New Yorker’s own Al Frueh.
“The Story of Manhattankind” was another short-lived feature. It offered drawings by Herb Roth and tongue-in-cheek accounts of early Manhattan life replete with cartoonish Indians and bumbling settlers. It is here where the magazine took its first of many shots at William Randolph Hearst, the perceived rival and publisher of Cosmopolitan (which was more of a literary magazine in 1925).
…other items that persisted through the early issues included “Lyrics from a Pekinese” by writer Arthur Gutterman, who was known for his silly poems…
…and this recurring column filler, “The Optimist”…a tired joke featured repeatedly in the first issues until Katharine Angell came on board and put an end to such nonsense…
…in those lean first months there was little advertising, making this back page ad seem out of place…
…since many of the early ads were small, signature ads for theatre and other diversions…
…the magazine also leaned heavily on full-page house ads to fill space…
…the one thing that has persisted to this day is the prominence of cartoonists and illustrators, although in the early issues some of the cartoons resembled those found in Punch, including this one by British graphic artist Alfred Leete, who was a regular contributor to such British magazines including Punch, the Strand Magazine and Tatler.
Also in the Punch style there were a number of “He-She” captioned cartoons, such as this Ethel Plummer cartoon of an “uncle” and a “flapper” looking at a theater bill for The Wages of Sin (most notably, Plummer was the first woman artist published in The New Yorker)…
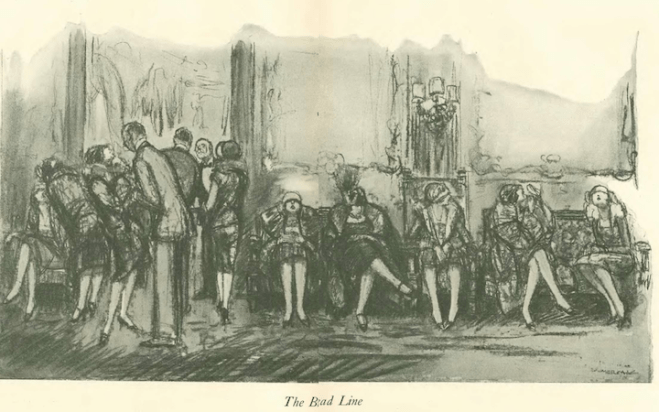
Plummer was a noted artist/illustrator in her day, as was Wallace Morgan, who contributed this two-page spread, “The Bread Line”…
…this illustration by Eldon Kelley is notable for what it lacks…namely, clothing. Early New Yorker lore has it that Ross was somewhat puritanical, and shied away from suggestions of sex or nudity, but here it is in the first issue, what Michael Maslin refers to as “The New Yorker’s First Nipples.”
…and before I go, I am wondering about The New Yorker’s first film critic, who signed his review “Will Hays Jr.” Is this the same Hays as in the “Hays Code?” I will investigate.
Next Time: A Century and a Decade…